16.6 Disorders of the Urinary System

Awareness Ribbon
Awareness ribbons are symbols meant to show support or to raise consciousness for a cause. Different colours are associated with different issues, often relating to health problems. The first ribbon to gain familiarity for a health issue was the red ribbon for HIV/AIDS, created in 1991. The pink ribbon for breast cancer awareness is probably the best known today. Do you know what a green ribbon like the one pictured in Figure 16.6.1 represents? Among several other health problems, a green ribbon is meant to show support or raise awareness for kidney disorders.
Disorders of the Kidneys
The kidneys play such vital roles in eliminating wastes and toxins — and in maintaining body-wide homeostasis — that disorders of the kidneys may be life threatening. Gradual loss of normal kidney function commonly occurs with a number of disorders, including diabetes mellitus and high blood pressure. Other disorders of the kidneys are caused by faulty inherited genes. Loss of kidney function may eventually progress to kidney failure.
Diabetic Nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy is a progressive kidney disease caused by damage to the capillaries in the glomeruli of the kidneys, due to long-standing diabetes mellitus (see Figure 16.6.2). It is not fully understood how diabetes leads to damage of glomerular capillaries, but it is thought that high levels of glucose in the blood are involved. In people with diabetes, diabetic nephropathy is more likely if blood glucose is poorly controlled. Having high blood pressure, a history of cigarette smoking, and a family history of kidney problems are additional risk factors. Diabetic nephropathy often has no symptoms at first. In fact, it may take up to a decade after kidney damage begins for symptoms to appear. When they do appear, they typically include severe tiredness, headaches, nausea, frequent urination, and itchy skin.
Proteins are large molecules that are usually not filtered out of blood in the glomeruli. When the glomerular capillaries are damaged, it allows proteins (such as albumin) to leak into the filtrate from the blood. As a result, albumin ends up being excreted in the urine. Finding a high level of albumin in the urine is one indicator of diabetic nephropathy and helps to diagnose the disorder. Drugs may be prescribed to reduce protein levels in the urine. Controlling high blood sugar levels and hypertension (high blood pressure) is also important to help slow kidney damage, as is a reduction of sodium intake.
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder in which multiple abnormal cysts develop and grow in the kidneys. Figure 16.6.3 shows a pair of kidneys that are riddled with cysts from PKD. In people who inherit PKD, the cysts may start to form at any point in life, from infancy through adulthood. Typically, both kidneys are affected. Symptoms of the disorder may include high blood pressure, headaches, abdominal pain, blood in the urine, and excessive urination.
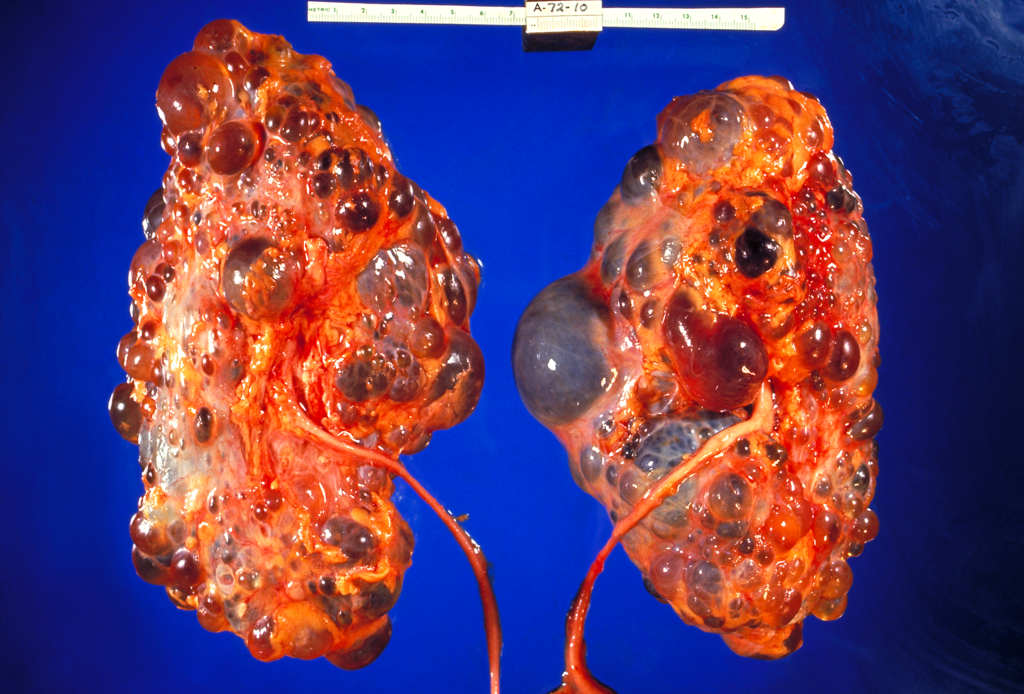
There are two types of PKD. The more common type is caused by an autosomal dominant allele, and the less common type is caused by an autosomal recessive allele. Both types together make PKD one of the most common hereditary diseases in Canada, affecting one in every 500 people. There is little or no difference in the rate of occurrence of PKD between genders or ethnic groups. Other than a kidney transplant, there is no known cure for this disease.
Kidney Failure
Both diabetic nephropathy and PKD may lead to kidney (or renal) failure(classified as end-stage kidney disease), in which the kidneys are no longer able to adequately filter metabolic wastes from the blood. Long-term, uncontrolled high blood pressure is another common cause of kidney failure. Symptoms of kidney failure may include nausea, more or less frequent urination, blood in the urine, muscle cramps, anemia, swelling of the extremities, and shortness of breath due to the accumulation of fluid in the lungs. If kidney function drops below the level needed to sustain life, then the only treatment option is kidney transplantation or some means of artificial filtration of the blood, such as by hemodialysis.
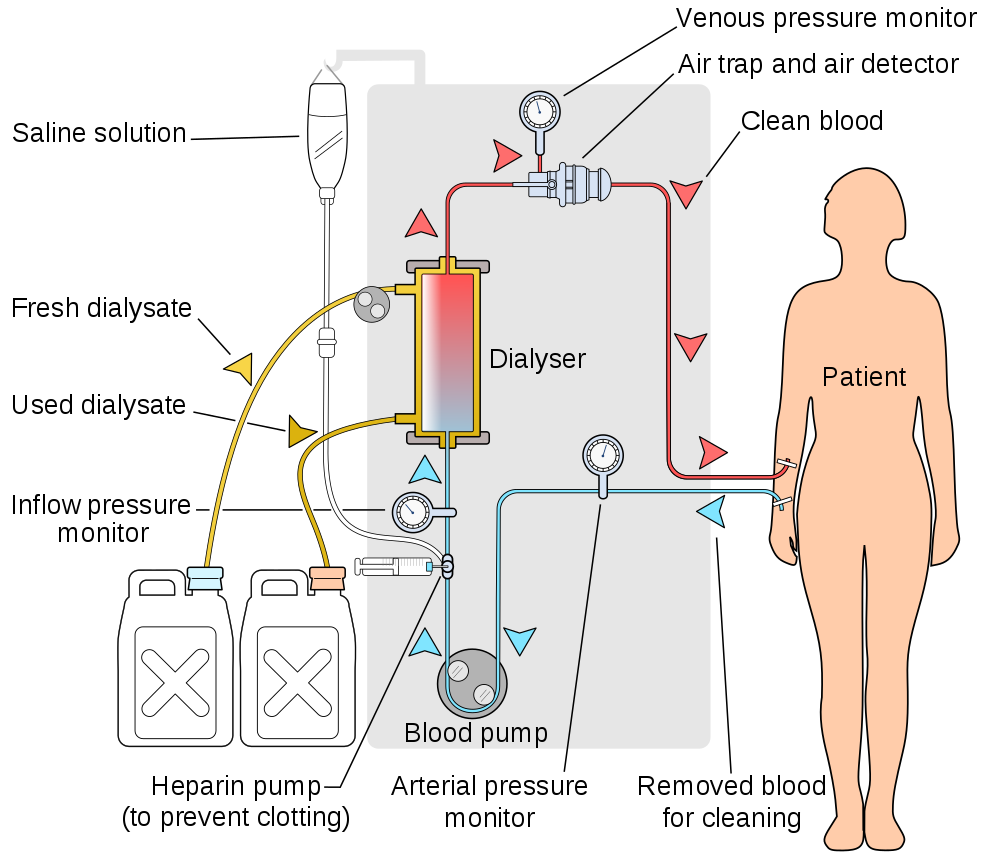
Hemodialysis is a medical procedure in which blood is filtered externally through a machine. You can see how it works in Figure 16.6.4. During dialysis, waste products (such as urea) are removed — along with excess water — from the patient’s blood before the blood is returned to the patient. Hemodialysis is typically done on an outpatient basis in a hospital or special dialysis clinic. Less frequently, it is done in the patient’s home. Depending on the patient’s size, among other factors, the blood is filtered for three to four hours roughly three times a week.
Kidney Stones

A kidney stone, (pictured in Figure 16.6.5) also known as a renal calculus, is a solid crystal that forms in a kidney from minerals in urine (see Figure 16.6.6). The majority of kidney stones consist of crystals of calcium salts. Kidney stones typically leave the body in the urine stream. A small stone may go undetected, because it can pass through the ureters and other urinary tract organs without causing symptoms. A larger stone may cause pain when it passes through the urinary tract. If a kidney stone grows large enough, it may block the ureter. Blockage of a ureter may cause a decrease in kidney function and damage to the kidney.
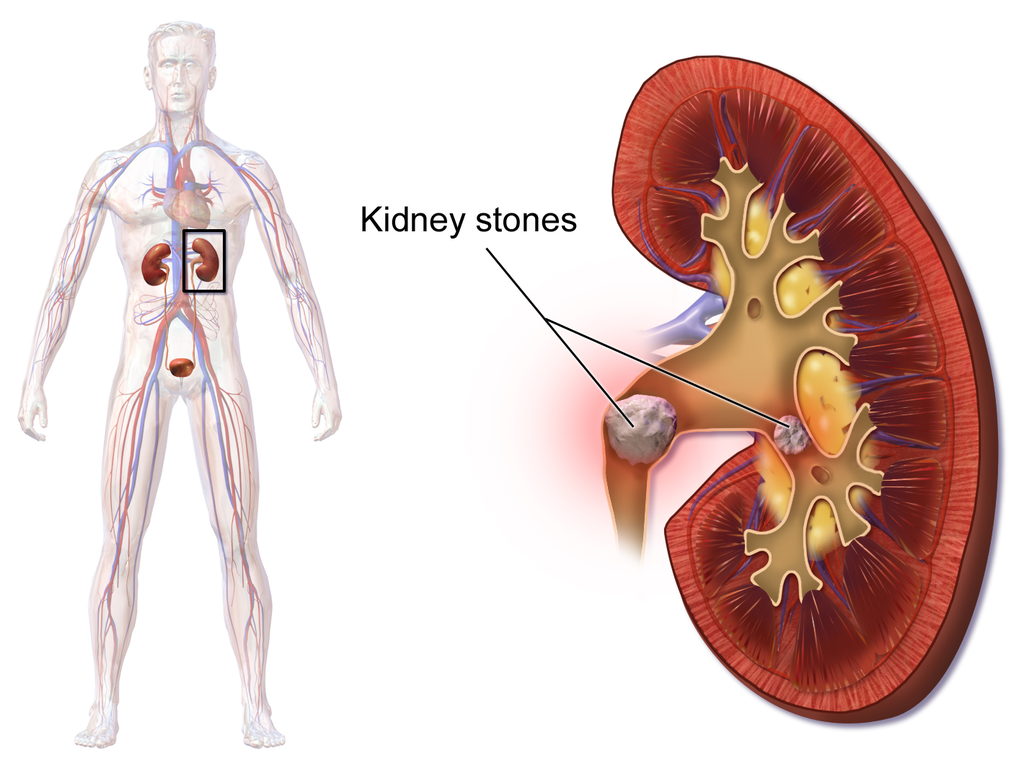
A kidney stone that causes pain is generally treated with pain medication, such as opiates, until it passes through the urinary tract. A stone that causes a blockage may be treated with lithotripsy. This is a medical procedure in which high-intensity ultrasound pulses are applied externally to cause fragmentation of the stone into pieces small enough to pass easily through the urinary tract. Although lithotripsy is noninvasive, it can cause damage to the kidneys. An alternative treatment for a stone that blocks urine flow is to insert a stent into the ureter to expand it and allow both urine and the stone to pass. In some cases, surgery may be required to physically remove a large stone from the ureter. In minor cases, sometimes drinking apple cider vinegar or lemon juice can break down small kidney stones because of the citric acid these foods contain.
A combination of lifestyle and genetic factors seem to predispose certain people to develop kidneys stones. Risk factors include high consumption of cola soft drinks, eating a diet high in animal protein, being overweight, and not drinking enough fluids. Preventive measures are obvious. They include limiting cola consumption, eating less animal protein, losing weight, and increasing fluid intake.
Other Urinary System Disorders
Although disorders of the kidneys are generally the most serious urinary system disorders, problems that affect other organs of the urinary tract are generally more common. They include bladder infections and urinary incontinence.
Bladder Infection
A bladder infection, also called cystitis, is a very common type of urinary tract infection in which the urinary bladder becomes infected by bacteria (typically E. coli), and rarely by fungi. Symptoms of bladder infections may include pain with urination, frequent urination, and feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder. In some cases, there may be blood in the urine. A much less common type of urinary tract infection is pyelonephritis, in which the kidney becomes infected. If a kidney infection occurs, it is generally because of an untreated bladder infection. Bladder infections are treated mainly with antibiotics.
Risk factors for urinary bladder infections include sexual intercourse, improper toileting technique, diabetes, obesity, and — most notably — female sex. Bladder infections are four times more common in women than in men. For women, they are the most common type of bacterial infections, and as many as one in ten women have a bladder infection in any given year. Female anatomy explains the sex difference in the incidence of bladder infections. The urethra is much shorter and closer to the anus in females than in males, so contamination of the urethra and then the bladder with GI tract bacteria is more likely in females than in males. Once the bacteria reach the bladder, they can attach to the bladder wall and form a biofilm that resists the body’s immune response.
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is a chronic problem of uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is very common, especially at older ages, and especially in women. Sometimes, urinary incontinence is a sign of another health problem, such as diabetes or obesity. Regardless of the underlying cause, the symptoms of urinary incontinence alone may have a large impact on quality of life, frequently causing inconvenience, embarrassment, and distress.
In men, urinary incontinence is most commonly caused by an enlarged prostate gland or treatment for prostate cancer. In women, there are two common types of urinary incontinence with different causes: stress incontinence and urge incontinence.
- Stress urinary incontinence is caused by loss of support of the urethra, usually due to stretching of pelvic floor muscles during childbirth. It is characterized by leakage of small amounts of urine with activities that increase abdominal pressure, such as coughing, sneezing, or lifting. Treatment of stress urinary incontinence may include Kegel exercises to strengthen the pelvic muscles. More serious cases may call for surgery to improve support for the bladder.
- Urge urinary incontinence (commonly called “overactive bladder”) is caused by uncontrolled contractions of the detrusor muscle in the wall of the bladder. This causes the bladder to empty unexpectedly. Urge incontinence is characterized by leakage of large amounts of urine in association with insufficient warning to get to the bathroom in time. Treatment of urge incontinence may include taking a medication to relax the detrusor muscle.
Feature: My Human Body
You probably have had to “donate” a urine specimen for analysis in conjunction with a medical visit. A thorough medical exam often includes clinical tests for urine. Understanding what your urine can reveal about your health may help you appreciate the need for such tests.
The most common urine test is called urinalysis. In a routine urinalysis, a urine sample may be analyzed by sight and smell, and with simple urine test strips. If a particular disorder is suspected, urinalysis may be more extensive. The urine may be analyzed with specific tests or viewed under a microscope to identify abnormal substances in the urine. If a bacterial infection is suspected, a sample of urine may be cultured in the lab to see if it grows bacteria, and which type of bacteria grow. Knowing the type of bacteria is important for deciding which class of antibiotics is likely to be most effective in treating the infection.
The colour and clarity of urine may be obvious first indicators of disorders or other abnormalities. Normal urine is yellow to amber in colour, and looks clear. If urine is nearly colourless, it could be a sign of excessive fluid intake, or it might be a sign of diabetes. Very dark urine may indicate dehydration, but it could also be caused by taking certain medications or ingesting some other substances. If urine has a reddish tinge, it is often a sign of blood in the urine, which could be due to a urinary tract infection, kidney stone, or even cancer. If urine appears cloudy instead of clear, it could be due to white blood cells in the urine, which may be another sign of a urinary tract infection.
If it is very diluted, normal urine may have virtually no odor. It will have a stronger odor if it is concentrated. Brief changes in the normal odor of urine often occur due to the ingestion of certain foods or medications. After eating asparagus, for example, urine may have a peculiar and distinctive odor for several hours. More significant is urine that has a sweet smell, because this may indicate sugar in the urine, which is a sign of diabetes.

Urine test strips (shown in Figure 16.6.7), much like the familiar litmus test strips used to detect acids and bases in chemistry lab, are used to identify abnormal levels of certain components in the urine. For example, urine test strips can detect and quantify the presence of nitrites in urine, which is usually a sign of infection with certain types of bacteria. Urine test strips can also be used to identify proteins such as albumin in urine, which may be a sign of a kidney infection or of kidney failure. Levels of sodium in urine can also be measured with test strips, and higher-than-normal levels may be another indication of kidney failure. In addition, test strips can identify and quantify the presence of white blood cells and blood in a urine specimen, both of which are likely to be a sign of a urinary tract infection or some other urinary system disorder.
Besides the use of urine test strips, other simple urine tests that are often performed include Benedict’s test, which is a test for the presence and quantity of glucose in urine. If the level is high, it likely indicates diabetes. The test is so simple that it may even be done by the patient at home to monitor how well sugar levels are being controlled. Testing for some other substances in urine requires the patient to collect urine over a 24-hour period. This is the case when testing for the adrenal hormone cortisol. When urine cortisol levels are higher than normal, it may indicate Cushing’s syndrome. When the levels are lower than normal, it may indicate Addison’s disease.
16.6 Summary
- Diabetic nephropathy is a progressive kidney disease caused by damage to the capillaries in the glomeruli of the kidneys due to long-standing diabetes mellitus. Years of capillary damage may occur before symptoms first appear.
- Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder (autosomal dominant or recessive) in which multiple abnormal cysts grow in the kidneys.
- Diabetic nephropathy, PKD, or chronic hypertension may lead to kidney failure, in which the kidneys are no longer able to adequately filter metabolic wastes from the blood. Kidneys may fail to such a degree that kidney transplantation or repeated, frequent hemodialysis is needed to support life. In hemodialysis, the patient’s blood is filtered artificially through a machine, and then returned to the patient’s circulation.
- A kidney stone is a solid crystal that forms in a kidney from minerals in urine. A small stone may pass undetected through the ureters and the rest of the urinary tract. A larger stone may cause pain when it passes, or be too large to pass, causing blockage of a ureter. Large kidney stones may be shattered with high-intensity ultrasound into pieces small enough to pass through the urinary tract, or they may be removed surgically.
- A bladder infection is generally caused by bacteria that reach the bladder from the GI tract and multiply. Bladder infections are much more common in females than males, because the female urethra is much shorter and closer to the anus. Treatment generally includes antibiotic drugs.
- Urinary incontinence is a chronic problem of uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is very common, especially at older ages and in women. In men, urinary incontinence is usually caused by an enlarged prostate gland. In women, it is usually caused by stretching of pelvic floor muscles during childbirth (stress incontinence) or by an “overactive bladder” that empties without warning (urge incontinence).
16.6 Review Questions
-
- Define kidney failure.
- When kidney function drops below the level needed to sustain life, what are potential treatments for kidney failure?
- Describe hemodialysis.
- How may a large kidney stone be removed from the body?
- How are bladder infections usually treated?
- Why are bladder infections much more common in females than in males?
- Compare and contrast stress incontinence and urge incontinence.
- Why is the presence of a protein(such as albumin) in the urine a cause for concern?
- Patients undergoing hemodialysis usually have to do this procedure a few times a week. Why does it need to be done so frequently?
16.6 Explore More
Urinary Tract Infections, Animation, Alila Medical Media, 2016.
What causes kidney stones? – Arash Shadman, TED-Ed, 2017.
Kegel Exercises Beginners Workout For Women, Michelle Kenway, 2013.
Attributions
Figure 16.6.1
512px-Green_ribbon.svg by MesserWoland on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/) license.
Figure 16.6.2
1024px-Blausen_0310_DiabeticNephropathy by BruceBlaus on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
Figure 16.6.3
1024px-Polycystic_kidneys,_gross_pathology_CDC_PHIL by Dr. Edwin P. Ewing, Jr. / CDC‘s Public Health Image Library (PHIL) #861. on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 16.6.4
1000px-Hemodialysis-en.svg by User:YassineMrabet on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
Figure 16.6.5
512px-Kidney_stone_1 by User:Михајло Анђелковић on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0) license.
Figure 16.6.6
Blausen_0595_KidneyStones by BruceBlaus on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
Figure 16.6.7
Amanda Cotton – Urinalysis Test Strips by Dominic Alves on Flickr is used under a CC BY 2,0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/) license.
References
Alila Medical Media. (2016, September 8). Urinary tract infections, animation. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lY2bZjggc08&feature=youtu.be
Blausen.com Staff. (2014). Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436.
Michelle Kenway. (2013, February 1). Kegel exercises beginners workout for women. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wRKhtfbJHdo&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2017, July 3). What causes kidney stones? – Arash Shadman. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W0GpIMNTPYg&feature=youtu.be
Updated Canadian expert consensus published to guide optimal management of ADPKD. (2018, December 18). PDK Foundation of Canada. https://www.endpkd.ca/canadian_expert_consensus_2018
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller

Seeing Your Breath
Why can you “see your breath” on a cold day? The air you exhale through your nose and mouth is warm like the inside of your body. Exhaled air also contains a lot of water vapor, because it passes over moist surfaces from the lungs to the nose or mouth. The water vapor in your breath cools suddenly when it reaches the much colder outside air. This causes the water vapor to condense into a fog of tiny droplets of liquid water. You release water vapor and other gases from your body through the process of respiration.
What is Respiration?
Respiration is the life-sustaining process in which gases are exchanged between the body and the outside atmosphere. Specifically, oxygen moves from the outside air into the body; and water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other waste gases move from inside the body to the outside air. Respiration is carried out mainly by the respiratory system. It is important to note that respiration by the respiratory system is not the same process as cellular respiration —which occurs inside cells — although the two processes are closely connected. Cellular respiration is the metabolic process in which cells obtain energy, usually by “burning” glucose in the presence of oxygen. When cellular respiration is aerobic, it uses oxygen and releases carbon dioxide as a waste product. Respiration by the respiratory system supplies the oxygen needed by cells for aerobic cellular respiration, and removes the carbon dioxide produced by cells during cellular respiration.
Respiration by the respiratory system actually involves two subsidiary processes. One process is ventilation, or breathing. Ventilation is the physical process of conducting air to and from the lungs. The other process is gas exchange. This is the biochemical process in which oxygen diffuses out of the air and into the blood, while carbon dioxide and other waste gases diffuse out of the blood and into the air. All of the organs of the respiratory system are involved in breathing, but only the lungs are involved in gas exchange.
Respiratory Organs
The organs of the respiratory system form a continuous system of passages, called the respiratory tract, through which air flows into and out of the body. The respiratory tract has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. The organs in each division are shown in Figure 13.2.2. In addition to these organs, certain muscles of the thorax (body cavity that fills the chest) are also involved in respiration by enabling breathing. Most important is a large muscle called the diaphragm, which lies below the lungs and separates the thorax from the abdomen. Smaller muscles between the ribs also play a role in breathing.
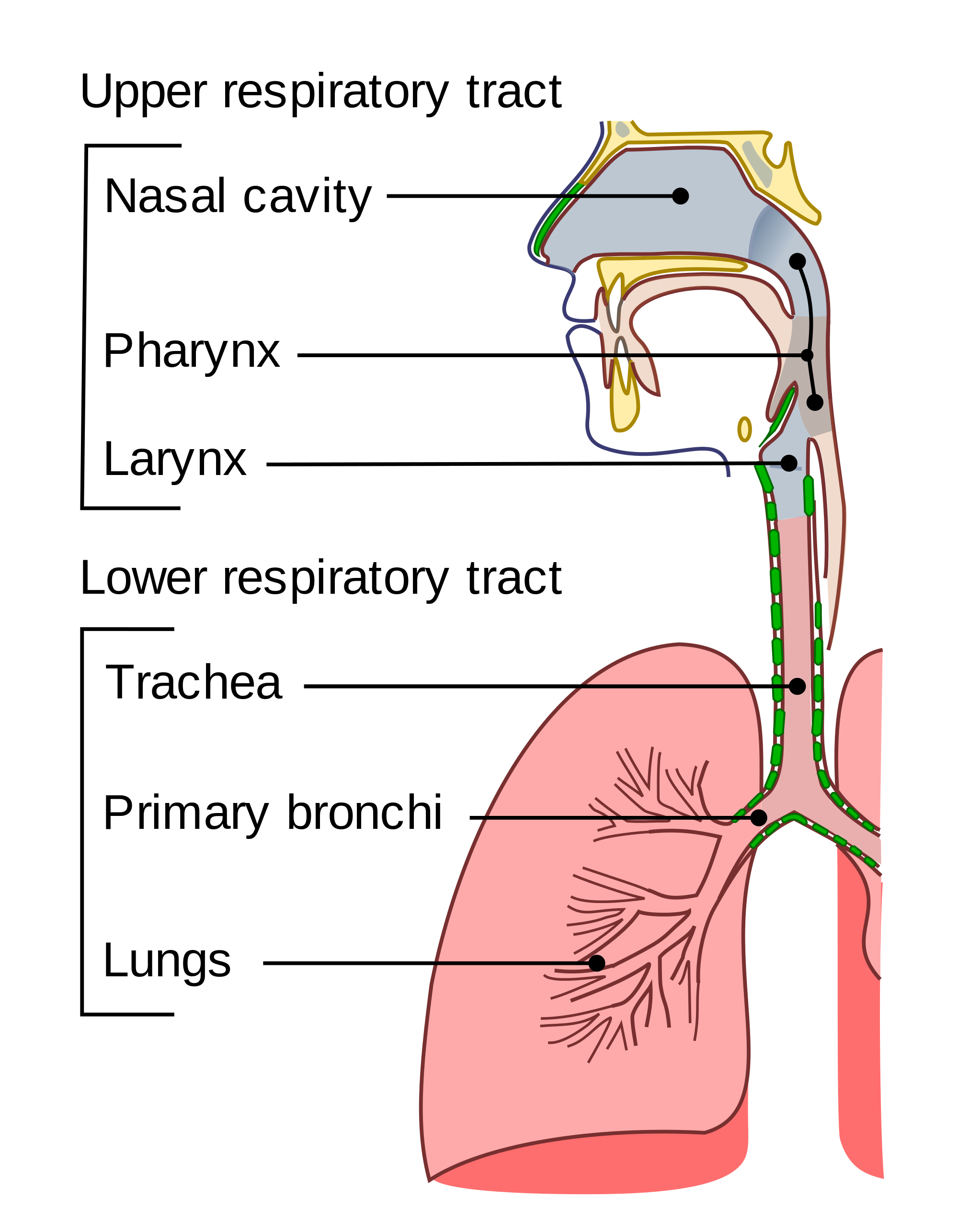
Upper Respiratory Tract
All of the organs and other structures of the upper respiratory tract are involved in conduction, or the movement of air into and out of the body. Upper respiratory tract organs provide a route for air to move between the outside atmosphere and the lungs. They also clean, humidify, and warm the incoming air. No gas exchange occurs in these organs.
Nasal Cavity
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space in the skull above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. It is a continuation of the two nostrils. As inhaled air flows through the nasal cavity, it is warmed and humidified by blood vessels very close to the surface of this epithelial tissue . Hairs in the nose and mucous produced by mucous membranes help trap larger foreign particles in the air before they go deeper into the respiratory tract. In addition to its respiratory functions, the nasal cavity also contains chemoreceptors needed for sense of smell, and contribution to the sense of taste.
Pharynx
The pharynx is a tube-like structure that connects the nasal cavity and the back of the mouth to other structures lower in the throat, including the larynx. The pharynx has dual functions — both air and food (or other swallowed substances) pass through it, so it is part of both the respiratory and the digestive systems. Air passes from the nasal cavity through the pharynx to the larynx (as well as in the opposite direction). Food passes from the mouth through the pharynx to the esophagus.
Larynx
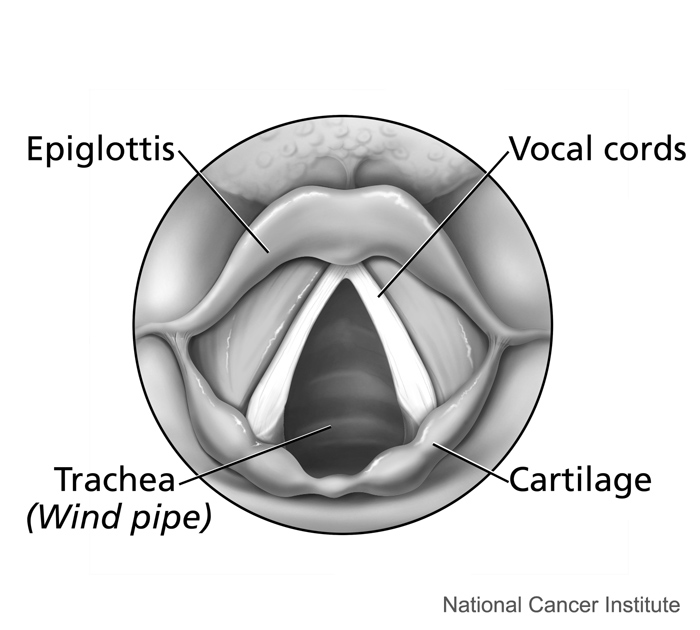
The larynx connects the pharynx and trachea, and helps to conduct air through the respiratory tract. The larynx is also called the voice box, because it contains the vocal cords, which vibrate when air flows over them, thereby producing sound. You can see the vocal cords in the larynx in Figures 13.2.3 and 13.2.4. Certain muscles in the larynx move the vocal cords apart to allow breathing. Other muscles in the larynx move the vocal cords together to allow the production of vocal sounds. The latter muscles also control the pitch of sounds and help control their volume.
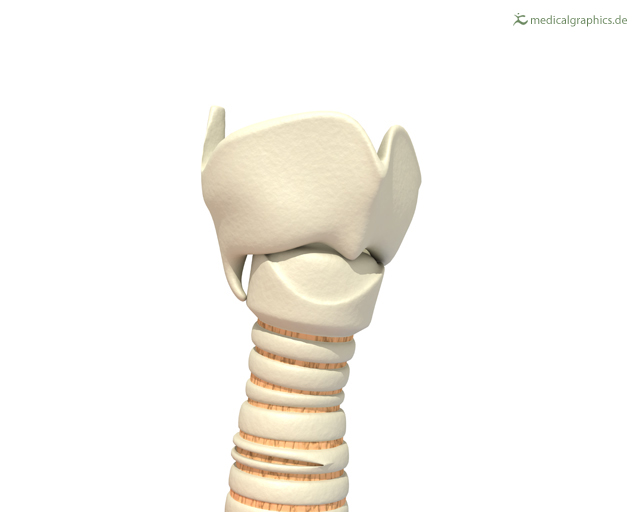 |
Figure 13.2.4 The larynx as viewed from the top. |
A very important function of the larynx is protecting the trachea from aspirated food. When swallowing occurs, the backward motion of the tongue forces a flap called the epiglottis to close over the entrance to the larynx. (You can see the epiglottis in both Figure 13.2.3 and 13.2.4.) This prevents swallowed material from entering the larynx and moving deeper into the respiratory tract. If swallowed material does start to enter the larynx, it irritates the larynx and stimulates a strong cough reflex. This generally expels the material out of the larynx, and into the throat.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BsyB88mq5rQ
Larynx Model - Respiratory System, Dr. Lotz, 2018.
Lower Respiratory Tract
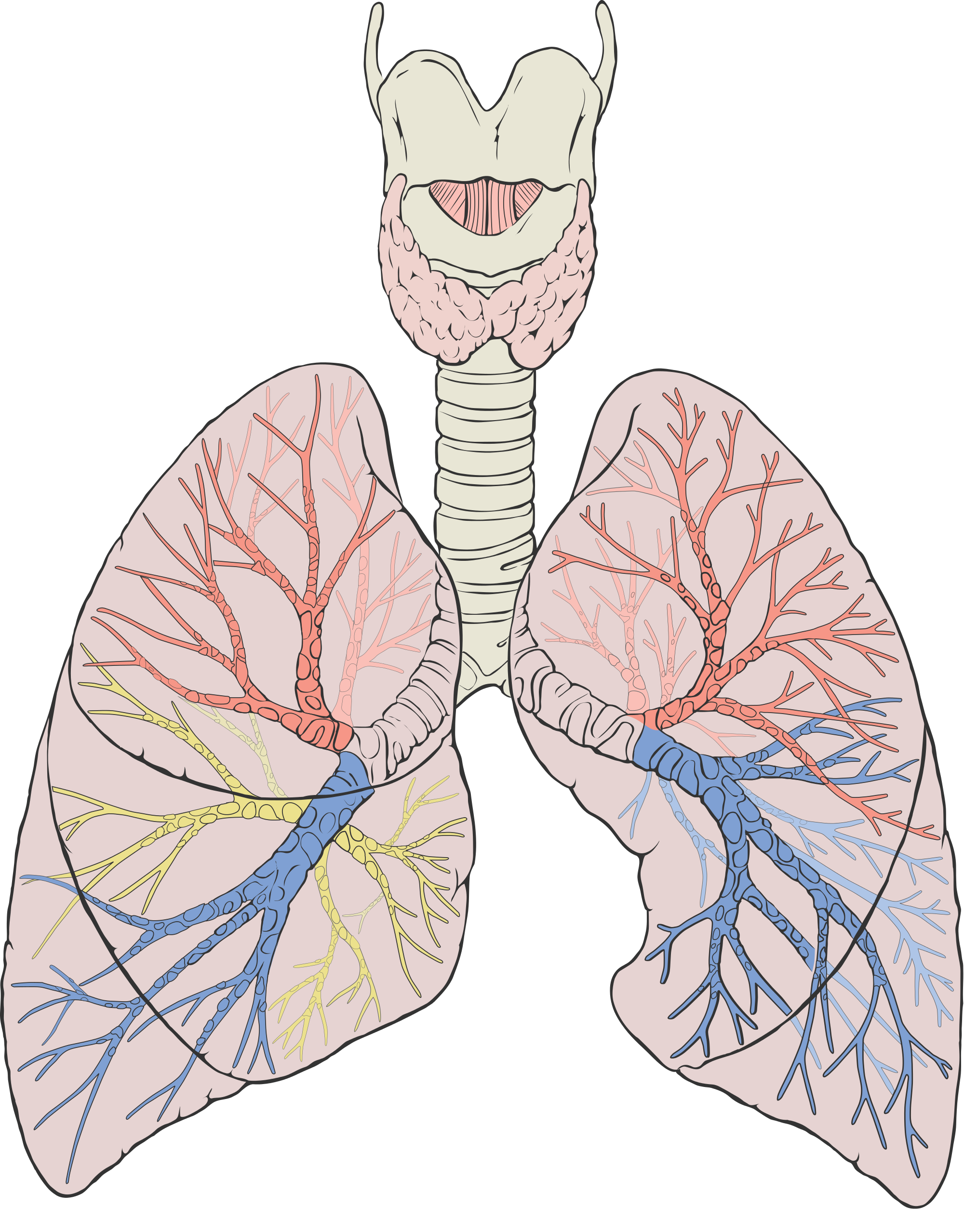
The trachea and other passages of the lower respiratory tract conduct air between the upper respiratory tract and the lungs. These passages form an inverted tree-like shape (Figure 13.2.5), with repeated branching as they move deeper into the lungs. All told, there are an astonishing 2,414 kilometres (1,500 miles) of airways conducting air through the human respiratory tract! It is only in the lungs, however, that gas exchange occurs between the air and the bloodstream.
Trachea
The trachea, or windpipe, is the widest passageway in the respiratory tract. It is about 2.5 cm wide and 10-15 cm long (approximately 1 inch wide and 4–6 inches long). It is formed by rings of cartilage, which make it relatively strong and resilient. The trachea connects the larynx to the lungs for the passage of air through the respiratory tract. The trachea branches at the bottom to form two bronchial tubes.
Bronchi and Bronchioles
There are two main bronchial tubes, or bronchi (singular, bronchus), called the right and left bronchi. The bronchi carry air between the trachea and lungs. Each bronchus branches into smaller, secondary bronchi; and secondary bronchi branch into still smaller tertiary bronchi. The smallest bronchi branch into very small tubules called bronchioles. The tiniest bronchioles end in alveolar ducts, which terminate in clusters of minuscule air sacs, called alveoli (singular, alveolus), in the lungs.
Lungs
The lungs are the largest organs of the respiratory tract. They are suspended within the pleural cavity of the thorax. The lungs are surrounded by two thin membranes called pleura, which secrete fluid that allows the lungs to move freely within the pleural cavity. This is necessary so the lungs can expand and contract during breathing. In Figure 13.2.6, you can see that each of the two lungs is divided into sections. These are called lobes, and they are separated from each other by connective tissues. The right lung is larger and contains three lobes. The left lung is smaller and contains only two lobes. The smaller left lung allows room for the heart, which is just left of the center of the chest.
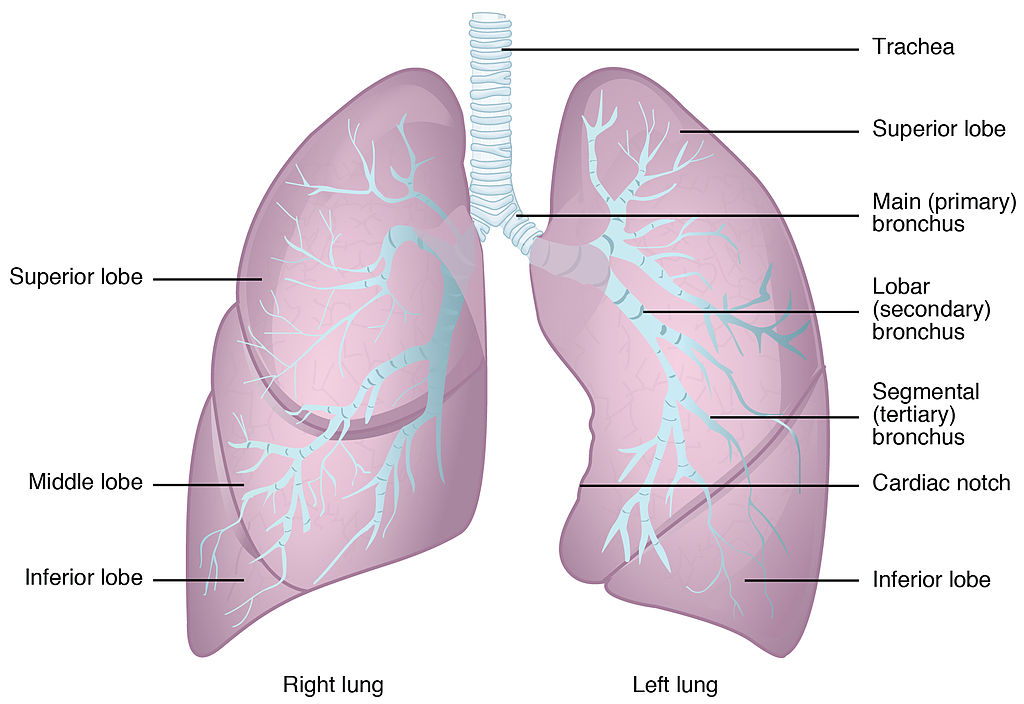
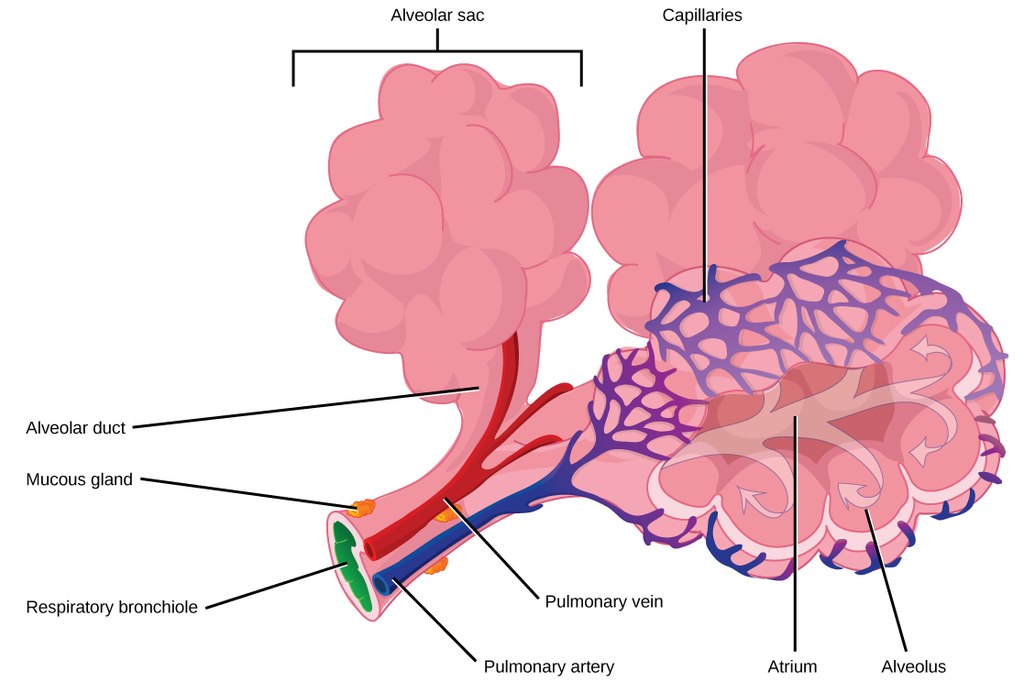
As mentioned previously, the bronchi terminate in bronchioles which feed air into alveoli, tiny sacs of simple squamous epithelial tissue which make up the bulk of the lung. The cross-section of lung tissue in the diagram below (Figure 13.2.7) shows the alveoli, in which gas exchange takes place with the capillary network that surrounds them.
 |
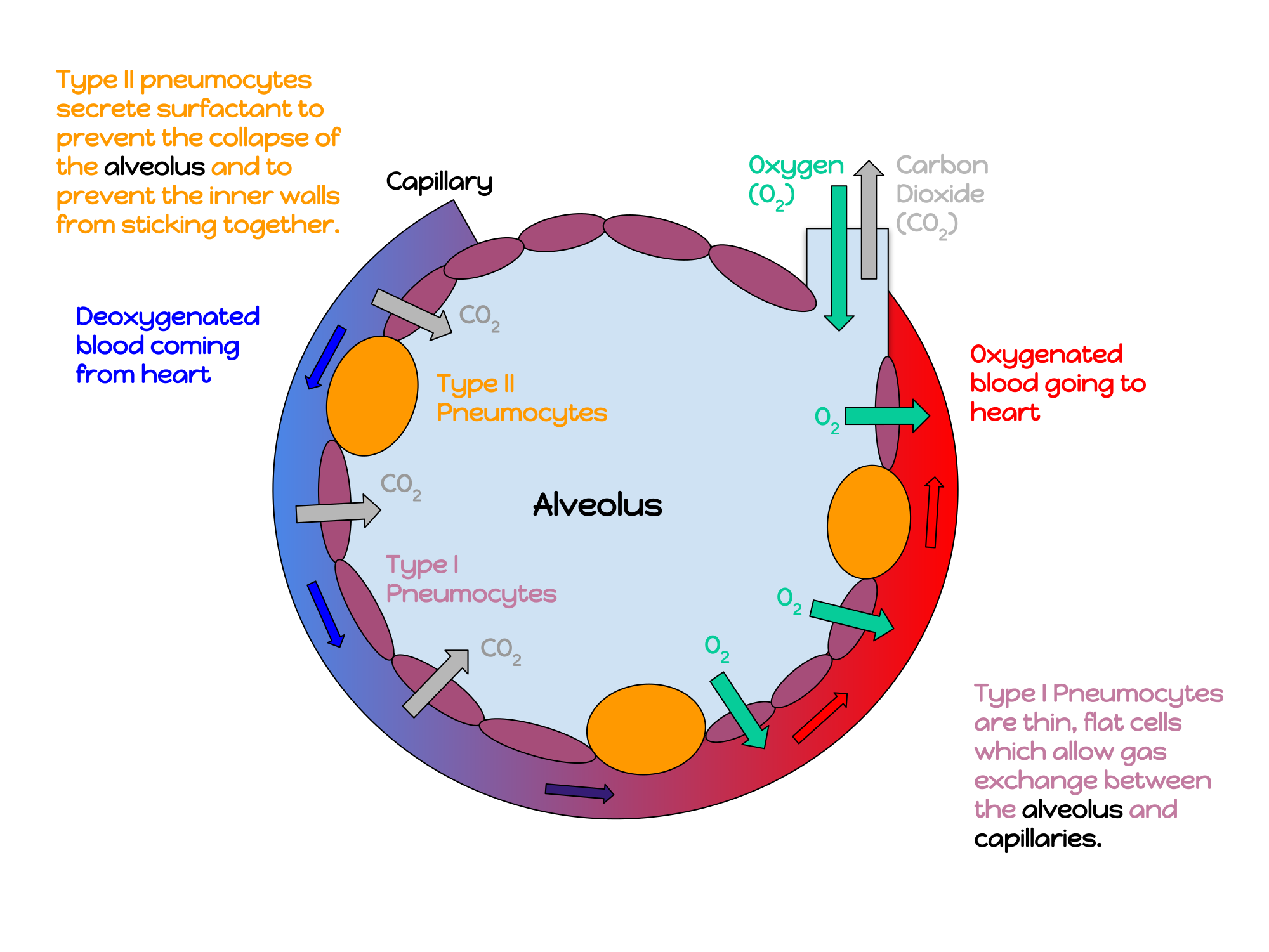 |
Lung tissue consists mainly of alveoli (see Figures 13.2.7 and 13.2.8). These tiny air sacs are the functional units of the lungs where gas exchange takes place. The two lungs may contain as many as 700 million alveoli, providing a huge total surface area for gas exchange to take place. In fact, alveoli in the two lungs provide as much surface area as half a tennis court! Each time you breathe in, the alveoli fill with air, making the lungs expand. Oxygen in the air inside the alveoli is absorbed by the blood via diffusion in the mesh-like network of tiny capillaries that surrounds each alveolus. The blood in these capillaries also releases carbon dioxide (also by diffusion) into the air inside the alveoli. Each time you breathe out, air leaves the alveoli and rushes into the outside atmosphere, carrying waste gases with it.
The lungs receive blood from two major sources. They receive deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart. This blood absorbs oxygen in the lungs and carries it back to the left side heart to be pumped to cells throughout the body. The lungs also receive oxygenated blood from the heart that provides oxygen to the cells of the lungs for cellular respiration.
Protecting the Respiratory System
You may be able to survive for weeks without food and for days without water, but you can survive without oxygen for only a matter of minutes — except under exceptional circumstances — so protecting the respiratory system is vital. Ensuring that a patient has an open airway is the first step in treating many medical emergencies. Fortunately, the respiratory system is well protected by the ribcage of the skeletal system. The extensive surface area of the respiratory system, however, is directly exposed to the outside world and all its potential dangers in inhaled air. It should come as no surprise that the respiratory system has a variety of ways to protect itself from harmful substances, such as dust and pathogens in the air.
The main way the respiratory system protects itself is called the mucociliary escalator. From the nose through the bronchi, the respiratory tract is covered in epithelium that contains mucus-secreting goblet cells. The mucus traps particles and pathogens in the incoming air. The epithelium of the respiratory tract is also covered with tiny cell projections called cilia (singular, cilium), as shown in the animation. The cilia constantly move in a sweeping motion upward toward the throat, moving the mucus and trapped particles and pathogens away from the lungs and toward the outside of the body. The upward sweeping motion of cilia lining the respiratory tract helps keep it free from dust, pathogens, and other harmful substances.
Watch "Mucociliary clearance" by I-Hsun Wu to learn more:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HMB6flEaZwI
Mucociliary clearance, I-Hsun Wu, 2015.
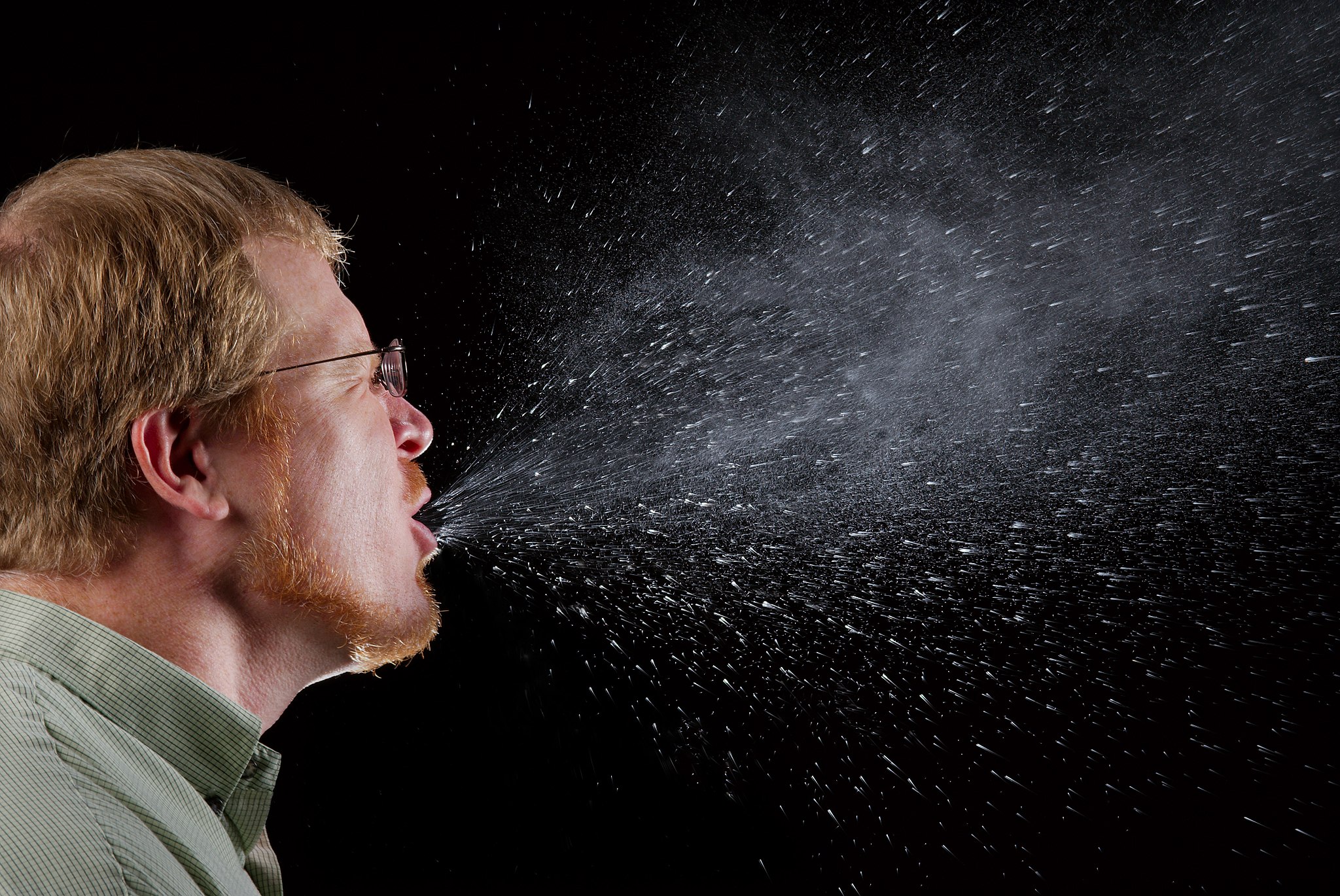

Sneezing is a similar involuntary response that occurs when nerves lining the nasal passage are irritated. It results in forceful expulsion of air from the mouth, which sprays millions of tiny droplets of mucus and other debris out of the mouth and into the air, as shown in Figure 13.2.9. This explains why it is so important to sneeze into a tissue (rather than the air) if we are to prevent the transmission of respiratory pathogens.
How the Respiratory System Works with Other Organ Systems
The amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood must be maintained within a limited range for survival of the organism. Cells cannot survive for long without oxygen, and if there is too much carbon dioxide in the blood, the blood becomes dangerously acidic (pH is too low). Conversely, if there is too little carbon dioxide in the blood, the blood becomes too basic (pH is too high). The respiratory system works hand-in-hand with the nervous and cardiovascular systems to maintain homeostasis in blood gases and pH.
It is the level of carbon dioxide — rather than the level of oxygen — that is most closely monitored to maintain blood gas and pH homeostasis. The level of carbon dioxide in the blood is detected by cells in the brain, which speed up or slow down the rate of breathing through the autonomic nervous system as needed to bring the carbon dioxide level within the normal range. Faster breathing lowers the carbon dioxide level (and raises the oxygen level and pH), while slower breathing has the opposite effects. In this way, the levels of carbon dioxide, oxygen, and pH are maintained within normal limits.
The respiratory system also works closely with the cardiovascular system to maintain homeostasis. The respiratory system exchanges gases with the outside air, but it needs the cardiovascular system to carry them to and from body cells. Oxygen is absorbed by the blood in the lungs and then transported through a vast network of blood vessels to cells throughout the body, where it is needed for aerobic cellular respiration. The same system absorbs carbon dioxide from cells and carries it to the respiratory system for removal from the body.
Feature: My Human Body
Choking due to a foreign object becoming lodged in the airway results in nearly 5 thousand deaths in Canada each year. In addition, choking accounts for almost 40% of unintentional injuries in infants under the age of one. For the sake of your own human body, as well as those of loved ones, you should be aware of choking risks, signs, and treatments.
Choking is the mechanical obstruction of the flow of air from the atmosphere into the lungs. It prevents breathing, and may be partial or complete. Partial choking allows some — though inadequate — air flow into the lungs. Prolonged or complete choking results in asphyxia, or suffocation, which is potentially fatal.
Obstruction of the airway typically occurs in the pharynx or trachea. Young children are more prone to choking than are older people, in part because they often put small objects in their mouth and do not understand the risk of choking that they pose. Young children may choke on small toys or parts of toys, or on household objects, in addition to food. Foods that are round (hotdogs, carrots, grapes) or can adapt their shape to that of the pharynx (bananas, marshmallows), are especially dangerous, and may cause choking in adults, as well as children.
How can you tell if a loved one is choking? The person cannot speak or cry out, or has great difficulty doing so. Breathing, if possible, is laboured, producing gasping or wheezing. The person may desperately clutch at his or her throat or mouth. If breathing is not soon restored, the person’s face will start to turn blue from lack of oxygen. This will be followed by unconsciousness, brain damage, and possibly death if oxygen deprivation continues beyond a few minutes.
If an infant is choking, turning the baby upside down and slapping him on the back may dislodge the obstructing object. To help an older person who is choking, first encourage the person to cough. Give them a few hard back slaps to help force the lodged object out of the airway. If these steps fail, perform the Heimlich maneuver on the person. See the series of videos below, from ProCPR, which demonstrate several ways to help someone who is choking based on age and consciousness.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XOTbjDGZ7wg&t=46s
Conscious Adult Choking, ProCPR, 2016.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5kmsKNvKAvU
Unconscious Adult Choking, ProCPR, 2011.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZjmbD7aIaf0
Conscious Child Choking, ProCPR, 2009.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sba0T2XGIn4
Unconscious Child Choking, ProCPR, 2009.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=axqIju9CLKA
Conscious Infant Choking, ProCPR, 2011.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_K7Dwy6b2wQ
Unconscious Infant Choking, ProCPR, 2011.
13.2 Summary
- Respiration is the process in which oxygen moves from the outside air into the body, and in which carbon dioxide and other waste gases move from inside the body into the outside air. It involves two subsidiary processes: ventilation and gas exchange. Respiration is carried out mainly by the respiratory system.
- The organs of the respiratory system form a continuous system of passages, called the respiratory tract. It has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract.
- The upper respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx. All of these organs are involved in conduction, or the movement of air into and out of the body. Incoming air is also cleaned, humidified, and warmed as it passes through the upper respiratory tract. The larynx is called the voice box, because it contains the vocal cords, which are needed to produce vocal sounds.
- The lower respiratory tract includes the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles, and the lungs. The trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles are involved in conduction. Gas exchange takes place only in the lungs, which are the largest organs of the respiratory tract. Lung tissue consists mainly of tiny air sacs called alveoli, which is where gas exchange takes place between air in the alveoli and the blood in capillaries surrounding them.
- The respiratory system protects itself from potentially harmful substances in the air by the mucociliary escalator. This includes mucus-producing cells, which trap particles and pathogens in incoming air. It also includes tiny hair-like cilia that continually move to sweep the mucus and trapped debris away from the lungs and toward the outside of the body.
- The level of carbon dioxide in the blood is monitored by cells in the brain. If the level becomes too high, it triggers a faster rate of breathing, which lowers the level to the normal range. The opposite occurs if the level becomes too low. The respiratory system exchanges gases with the outside air, but it needs the cardiovascular system to carry the gases to and from cells throughout the body.
13.2 Review Questions
-
- What is respiration, as carried out by the respiratory system? Name the two subsidiary processes it involves.
- Describe the respiratory tract.
- Identify the organs of the upper respiratory tract. What are their functions?
- List the organs of the lower respiratory tract. Which organs are involved only in conduction?
- Where does gas exchange take place?
- How does the respiratory system protect itself from potentially harmful substances in the air?
- Explain how the rate of breathing is controlled.
- Why does the respiratory system need the cardiovascular system to help it perform its main function of gas exchange?
- Describe two ways in which the body prevents food from entering the lungs.
- What is the relationship between respiration and cellular respiration?
13.2 Explore More
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8NUxvJS-_0k
How do lungs work? - Emma Bryce, TED-Ed, 2014.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=1&v=6iFPs6JlSzY&feature=emb_logo
Why Do Men Have Deeper Voices? BrainStuff - HowStuffWorks, 2015.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rjibeBSnpJ0
Why does your voice change as you get older? - Shaylin A. Schundler, TED-Ed, 2018.
Attributions
Figure 13.2.1
Exhale by pavel-lozovikov-HYovA7yPPvI [photo] by Pavel Lozovikov on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 13.2.2
Illu_conducting_passages.svg by Lord Akryl, Jmarchn from SEER Training Modules/ National Cancer Institute on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 13.2.3
Larynx by www.medicalgraphics.de is used under a CC BY-ND 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/) license.
Figure 13.2.4
Larynx top view by Alan Hoofring (Illustrator) for National Cancer Institute is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 13.2.5
2000px-Lungs_diagram_detailed.svg by Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 2.5 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5) license. (Derivative work of Fruchtwasserembolie.png.)
Figure 13.2.6
Gross_Anatomy_of_the_Lungs by OpenStax College on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
Figure 13.2.7
Alveoli Structure by CNX OpenStax on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0) license.
Figure 13.2.8
annotated_diagram_of_an_alveolus.svg by Katherinebutler1331 on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
Figure 13.2.9
Sneeze by James Gathany at CDC Public Health Imagery Library (PHIL) #11162 on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
References
Betts, J. G., Young, K.A., Wise, J.A., Johnson, E., Poe, B., Kruse, D.H., Korol, O., Johnson, J.E., Womble, M., DeSaix, P. (2013, June 19). Figure 22.2 Major respiratory structures [digital image]. In Anatomy and Physiology (Section 22.1). OpenStax. https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/22-1-organs-and-structures-of-the-respiratory-system [CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0)].
Betts, J. G., Young, K.A., Wise, J.A., Johnson, E., Poe, B., Kruse, D.H., Korol, O., Johnson, J.E., Womble, M., DeSaix, P. (2013, June 19). Figure 22.13 Gross anatomy of the lungs [digital image]. In Anatomy and Physiology (Section 22.2). OpenStax. https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/22-2-the-lungs
BrainStuff - HowStuffWorks. (2015, December 1). Why do men have deeper voices? YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6iFPs6JlSzY&feature=youtu.be
Dr. Lotz. (2018, January 25). Larynx model - Respiratory system. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BsyB88mq5rQ&feature=youtu.be
I-Hsun Wu. (2015, March 31). Mucociliary clearance. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HMB6flEaZwI&feature=youtu.be
OpenStax. (2016, May 27). Figure 9 Terminal bronchioles are connected by respiratory bronchioles to alveolar ducts and alveolar sacs [digital image]. In OpenStax, Biology (Section 39.1). OpenStax CNX. https://cnx.org/contents/GFy_h8cu@10.53:35-R0biq@11/Systems-of-Gas-Exchange
ProCPR. (2009, November 24). Conscious child choking. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZjmbD7aIaf0&feature=youtu.be
ProCPR. (2009, November 24).Unconscious child choking. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sba0T2XGIn4&feature=youtu.be
ProCPR. (2011, February 1). Conscious infant choking. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=axqIju9CLKA&feature=youtu.be
ProCPR. (2011, February 1). Unconscious adult choking. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5kmsKNvKAvU&feature=youtu.be
ProCPR. (2011, February 1). Unconscious infant choking. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_K7Dwy6b2wQ&feature=youtu.be
ProCPR. (2016, April 8). Conscious adult choking. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XOTbjDGZ7wg&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2014, November 24). How do lungs work? - Emma Bryce. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8NUxvJS-_0k&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2018, August 2). Why does your voice change as you get older? - Shaylin A. Schundler. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rjibeBSnpJ0&feature=youtu.be
The ability of an organism to maintain constant internal conditions despite external changes.
Created by: CK-12/Adapted by Christine Miller

Like Father, Like Son
This father-son duo share some similarities. The shape of their faces and their facial features look very similar. If you saw them together, you might well guess that they are father and son. People have long known that the characteristics of living things are similar between parents and their offspring. However, it wasn’t until the experiments of Gregor Mendel that scientists understood how those traits are inherited.
The Father of Genetics
Mendel did experiments with pea plants to show how traits such as seed shape and flower colour are inherited. Based on his research, he developed his two well known laws of inheritance: the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment. When Mendel died in 1884, his work was still virtually unknown. In 1900, three other researchers working independently came to the same conclusions that Mendel had drawn almost half a century earlier. Only then was Mendel's work rediscovered.
Mendel knew nothing about genes, because they were discovered after his death. He did think, however, that some type of "factors" controlled traits, and that those "factors" were passed from parents to offspring. We now call these "factors" genes. Mendel's laws of inheritance, now expressed in terms of genes, form the basis of genetics, the science of heredity. For this reason, Mendel is often called the father of genetics.
The Language of Genetics
Today, we know that traits of organisms are controlled by genes on chromosomes. To talk about inheritance in terms of genes and chromosomes, you need to know the language of genetics. The terms below serve as a good starting point. They are illustrated in the figure that follows.
- A gene is the part of a chromosome that contains the genetic code for a given protein. For example, in pea plants, a given gene might code for flower colour.
- The position of a given gene on a chromosome is called its locus (plural, loci). A gene might be located near the center, or at one end or the other of a chromosome.
- A given gene may have different normal versions, which are called alleles. For example, in pea plants, there is a purple-flower allele (B) and a white-flower allele (b) for the flower-colour gene. Different alleles account for much of the variation in the traits of organisms, including people.
- In sexually reproducing organisms, each individual has two copies of each type of chromosome. Paired chromosomes of the same type are called homologous chromosomes. They are about the same size and shape, and they have all the same genes at the same loci.

Genotype
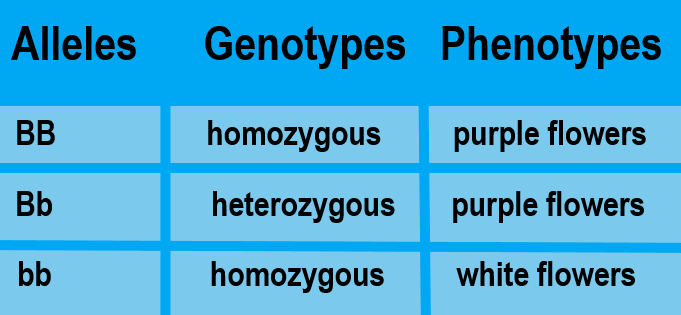
When sexual reproduction occurs, sex cells (called gametes) unite during fertilization to form a single cell called a zygote. The zygote inherits two of each type of chromosome, with one chromosome of each type coming from the father, and the other coming from the mother. Because homologous chromosomes have the same genes at the same loci, each individual also inherits two copies of each gene. The two copies may be the same allele or different alleles. The alleles an individual inherits for a given gene make up the individual’s genotype. As shown in Table 5.11.1, an organism with two of the same allele (for example, BB or bb) is called a homozygote. An organism with two different alleles (in this example, Bb) is called a heterozygote.
Table 5.11.1
Allele Combinations Associated With the Terms Homozygous and Heterozygous
Phenotype
The expression of an organism’s genotype is referred to as its phenotype, and it refers to the organism’s traits, such as purple or white flowers in pea plants. As you can see from Table 5.11.1, different genotypes may produce the same phenotype. In this example, both BB and Bb genotypes produce plants with the same phenotype, purple flowers. Why does this happen? In a Bb heterozygote, only the B allele is expressed, so the b allele doesn’t influence the phenotype. In general, when only one of two alleles is expressed in the phenotype, the expressed allele is called dominant, and the allele that isn’t expressed is called recessive.
The terms dominant and recessive may also be used to refer to phenotypic traits. For example, purple flower colour in pea plants is a dominant trait. It shows up in the phenotype whenever a plant inherits even one dominant allele for the trait. Similarly, white flower colour is a recessive trait. Like other recessive traits, it shows up in the phenotype only when a plant inherits two recessive alleles for the trait.
5.11 Summary
- Mendel's laws of inheritance, now expressed in terms of genes, form the basis of genetics, which is the science of heredity. This is why Mendel is often called the father of genetics.
- A gene is the part of a chromosome that codes for a given protein. The position of a gene on a chromosome is its locus. A given gene may have different versions, called alleles. Paired chromosomes of the same type are called homologous chromosomes. They have the same size and shape, and they have the same genes at the same loci.
- The alleles an individual inherits for a given gene make up the individual's genotype. An organism with two of the same allele is called a homozygote, and an individual with two different alleles is called a heterozygote.
- The expression of an organism's genotype is referred to as its phenotype. A dominant allele is always expressed in the phenotype, even when just one dominant allele has been inherited. A recessive allele is expressed in the phenotype only when two recessive alleles have been inherited.
5.11 Review Questions
- Define genetics.
- Why is Gregor Mendel called the father of genetics if genes were not discovered until after his death?
-
- Imagine that there are two alleles, R and r, for a given gene. R is dominant to r. Answer the following questions about this gene:
- What are the possible homozygous and heterozygous genotypes?
- Which genotype or genotypes express the dominant R phenotype? Explain your answer.
- Are R and r on different loci? Why or why not?
- Can R and r be on the same exact chromosome? Why or why not? If not, where are they located?
5.11 Explore More
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pv3Kj0UjiLE
Alleles and Genes, Amoeba Sisters, 2018.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OaovnS7BAoc
Genotypes and Phenotypes, Bozeman Science, 2011.
Attributions
Figure 5.11.1
Father holding his baby boy with matching haircut [photo] by Kelly Sikkema on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 5.11.2
Chromosome, Gene, Locus, and Allele by CK-12 Foundation is used under a CC BY-NC 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) license.
 ©CK-12 Foundation Licensed under
©CK-12 Foundation Licensed under ![]() • Terms of Use • Attribution
• Terms of Use • Attribution
Table 5.11.1
Allele Combinations Associated With the Terms Homozygous and Heterozygous by Christine Miller is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
References
Amoeba Sisters. (2018, February 1). Alleles and genes. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pv3Kj0UjiLE&feature=youtu.be
Bozeman Science. (2011, August 4). Genotypes and phenotypes. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OaovnS7BAoc&feature=youtu.be
Brainard, J/ CK-12 Foundation. (2016). Figure 2 Chromosome, gene, locus, and allele [digital image]. In CK-12 College Human Biology (Section 5.10) [online Flexbook]. CK12.org. https://www.ck12.org/book/ck-12-human-biology/section/5.9/
As per caption.
Glucose (also called dextrose) is a simple sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight.
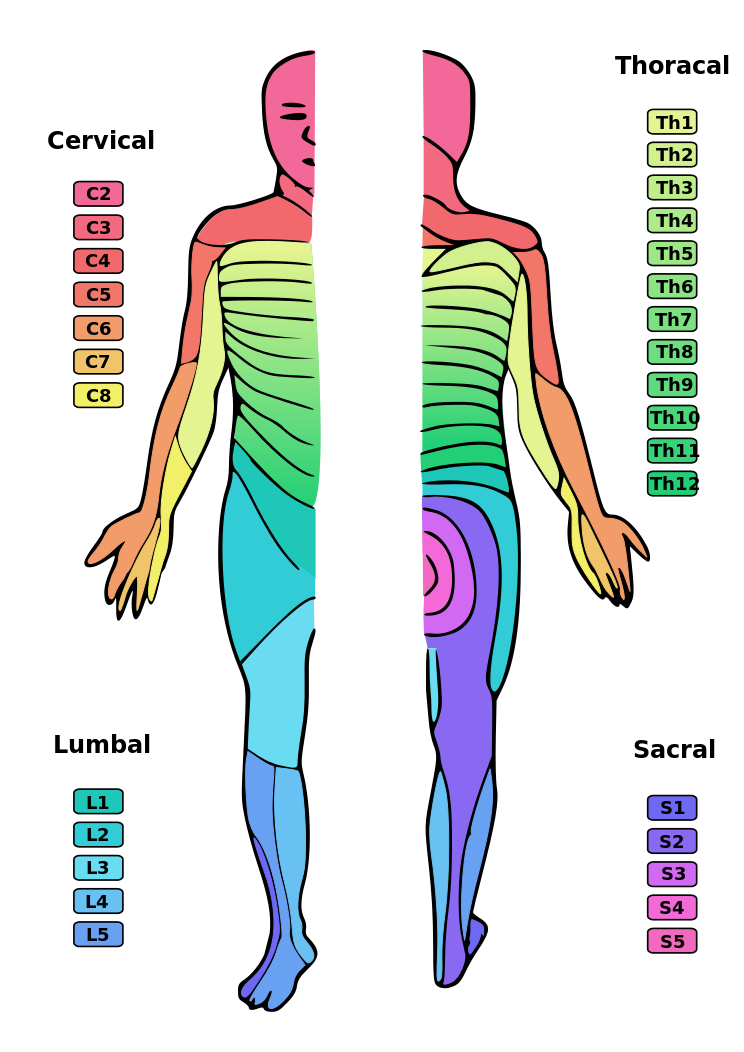
A diagram showing human dermatomes, i.e., skin regions with respect to the routing of their afferent nerves through the spinal cord.
A testable proposed explanation for a phenomenon.
Refers to the relationship between two versions of a gene. Individuals receive two versions of each gene, known as alleles, from each parent. If the alleles of a gene are different, one allele will be expressed; it is the dominant gene. The effect of the other allele, called recessive, is masked.
A variant form of a given gene, meaning it is one of two or more versions of a known mutation at the same place on a chromosome. It can also refer to different sequence variations for a several-hundred base-pair or more region of the genome that codes for a protein.
Body cavity that fills the lower half of the trunk and holds the kidneys and the digestive and reproductive organs.
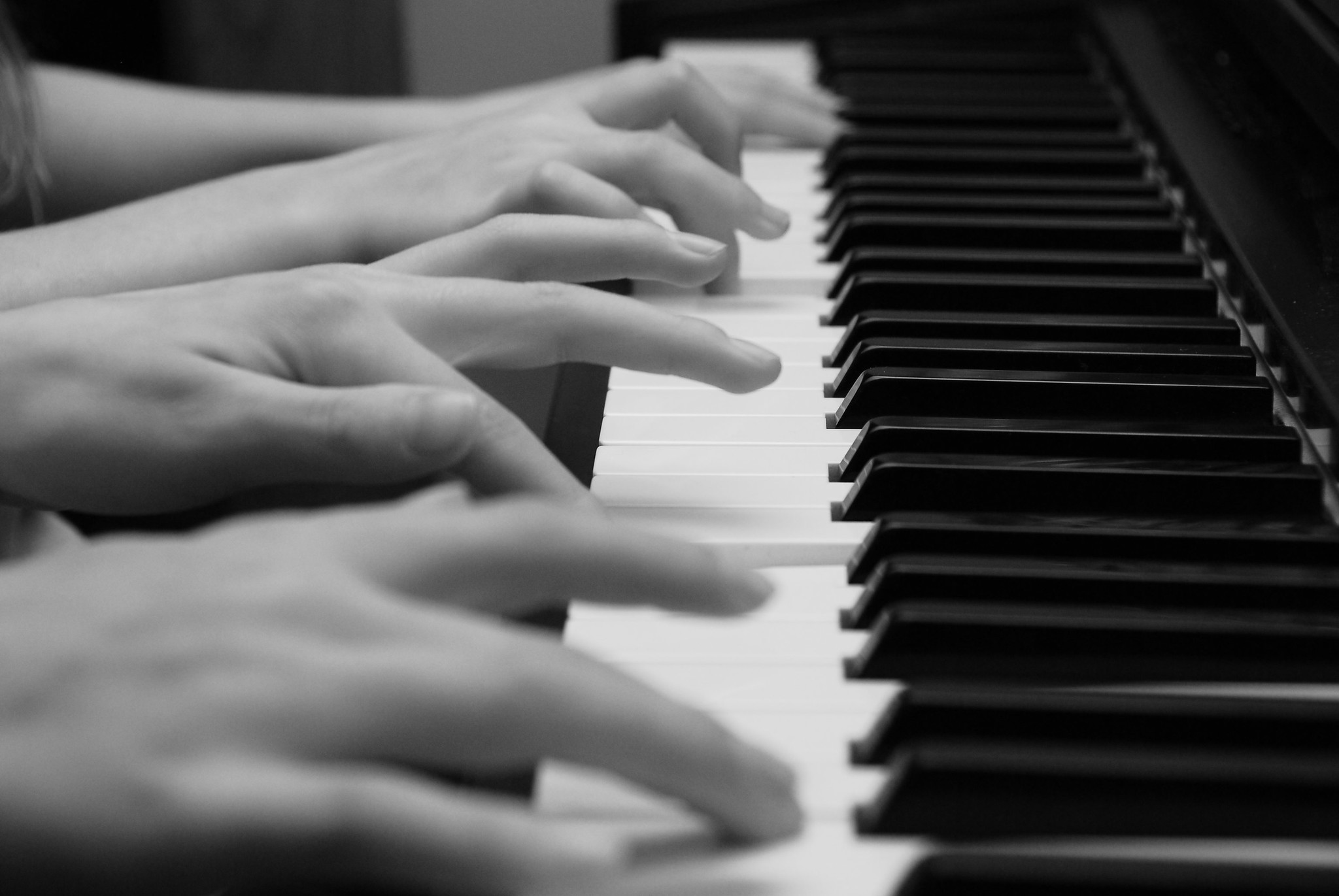

One Piano, Four Hands
Did you ever see two people play the same piano? How do they coordinate all the movements of their own fingers — let alone synchronize them with those of their partner? The peripheral nervous system plays an important part in this challenge.
What Is the Peripheral Nervous System?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of all the nervous tissue that lies outside of the central nervous system (CNS). The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the rest of the organism. It serves as a communication relay, going back and forth between the CNS and muscles, organs, and glands throughout the body.
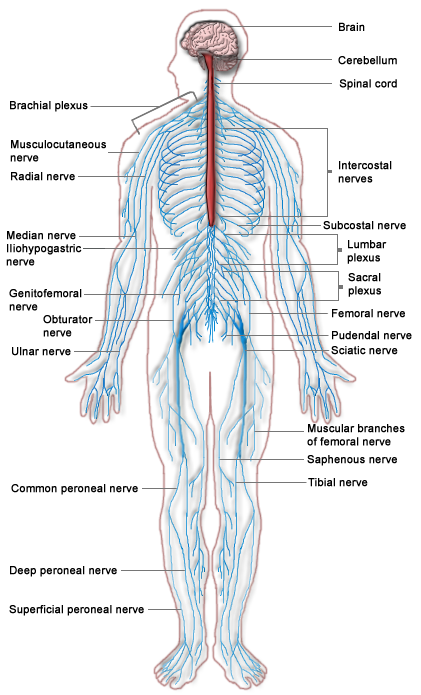
Tissues of the Peripheral Nervous System
The PNS is mostly made up of cable-like bundles of axons called nerves, as well as clusters of neuronal cell bodies called ganglia (singular, ganglion). Nerves are generally classified as sensory, motor, or mixed nerves based on the direction in which they carry nerve impulses.
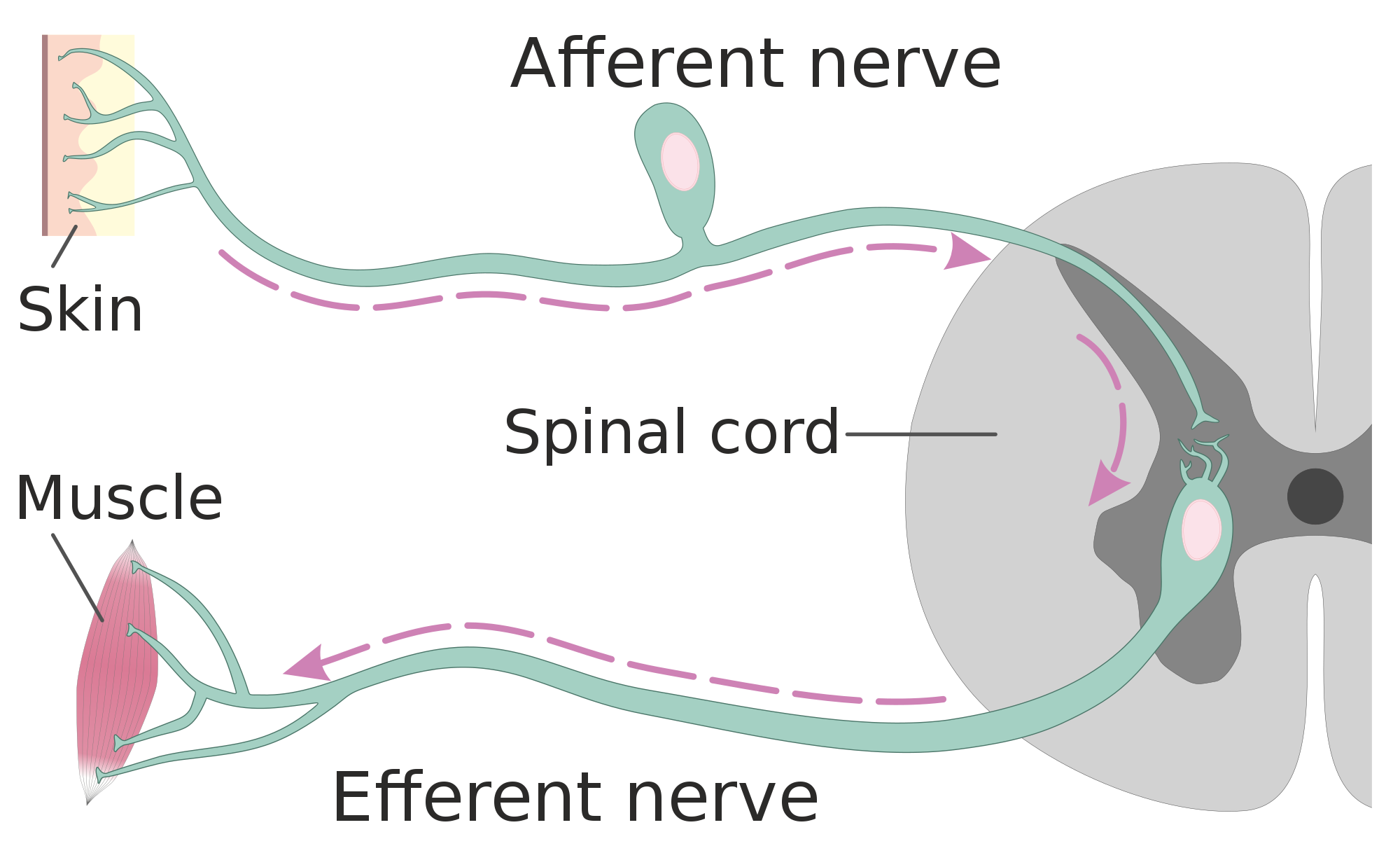
- Sensory nerves transmit information from sensory receptors in the body to the CNS. Sensory nerves are also called afferent nerves. You can see an example in the figure below.
- Motor nerves transmit information from the CNS to muscles, organs, and glands. Motor nerves are also called efferent nerves. You can see one in the figure below.
- Mixed nerves contain both sensory and motor neurons, so they can transmit information in both directions. They have both afferent and efferent functions.
Divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System
The PNS is divided into two major systems, called the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. In the diagram below, the autonomic system is shown on the left, and the somatic system on the right. Both systems of the PNS interact with the CNS and include sensory and motor neurons, but they use different circuits of nerves and ganglia.
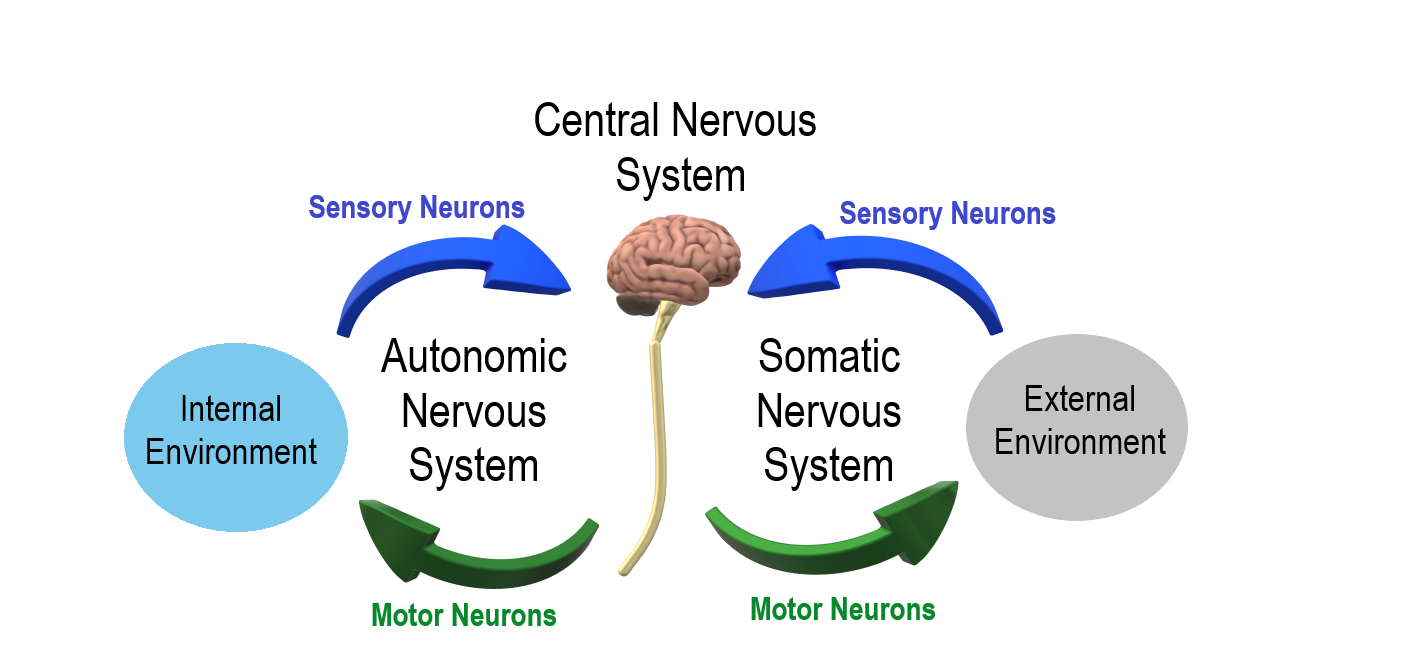
Somatic Nervous System
The somatic nervous system primarily senses the external environment and controls voluntary activities about which decisions and commands come from the cerebral cortex of the brain. When you feel too warm, for example, you decide to turn on the air conditioner. As you walk across the room to the thermostat, you are using your somatic nervous system. In general, the somatic nervous system is responsible for all of your conscious perceptions of the outside world, as well as all of the voluntary motor activities you perform in response. Whether it’s playing a piano, driving a car, or playing basketball, you can thank your somatic nervous system for making it possible.
Somatic sensory and motor information is transmitted through 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Cranial nerves are in the head and neck and connect directly to the brain. Sensory components of cranial nerves transmit information about smells, tastes, light, sounds, and body position. Motor components of cranial nerves control skeletal muscles of the face, tongue, eyeballs, throat, head, and shoulders. Motor components of cranial nerves also control the salivary glands and swallowing. Four of the 12 cranial nerves participate in both sensory and motor functions as mixed nerves, having both sensory and motor neurons.
Spinal nerves emanate from the spinal column between vertebrae. All of the spinal nerves are mixed nerves, containing both sensory and motor neurons. The areas of skin innervated by the 31 pairs of spinal nerves are shown in the figure below. These include sensory nerves in the skin that sense pressure, temperature, vibrations, and pain. Other sensory nerves are in the muscles, and they sense stretching and tension. Spinal nerves also include motor nerves that stimulate skeletal muscles to contract, allowing for voluntary body movements.
Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system primarily senses the internal environment and controls involuntary activities. It is responsible for monitoring conditions in the internal environment and bringing about appropriate changes in them. In general, the autonomic nervous system is responsible for all the activities that go on inside your body without your conscious awareness or voluntary participation.
Structurally, the autonomic nervous system consists of sensory and motor nerves that run between the CNS (especially the hypothalamus in the brain), internal organs (such as the heart, lungs, and digestive organs), and glands (such as the pancreas and sweat glands). Sensory neurons in the autonomic system detect internal body conditions and send messages to the brain. Motor nerves in the autonomic system affect appropriate responses by controlling contractions of smooth or cardiac muscle, or glandular tissue. For example, when sensory nerves of the autonomic system detect a rise in body temperature, motor nerves signal smooth muscles in blood vessels near the body surface to undergo vasodilation, and the sweat glands in the skin to secrete more sweat to cool the body.
The autonomic nervous system, in turn, has three subdivisions: the sympathetic division, parasympathetic division, and enteric division. The first two subdivisions of the autonomic system are summarized in the figure below. Both affect the same organs and glands, but they generally do so in opposite ways.
- The sympathetic division controls the fight-or-flight response. Changes occur in organs and glands throughout the body that prepare the body to fight or flee in response to a perceived danger. For example, the heart rate speeds up, air passages in the lungs become wider, more blood flows to the skeletal muscles, and the digestive system temporarily shuts down.
- The parasympathetic division returns the body to normal after the fight-or-flight response has occurred. For example, it slows down the heart rate, narrows air passages in the lungs, reduces blood flow to the skeletal muscles, and stimulates the digestive system to start working again. The parasympathetic division also maintains internal homeostasis of the body at other times.
- The enteric division is made up of nerve fibres that supply the organs of the digestive system. This division allows for the local control of many digestive functions.
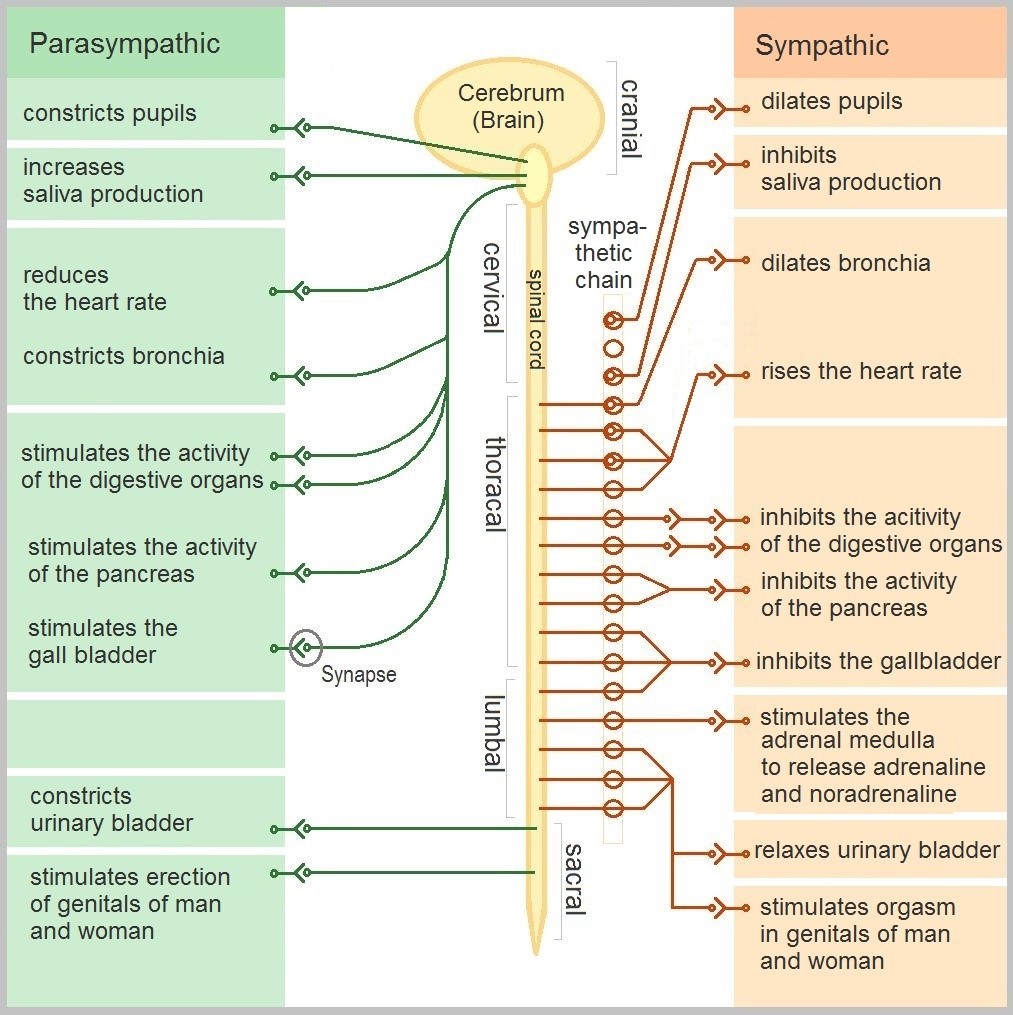
Disorders of the Peripheral Nervous System
Unlike the CNS — which is protected by bones, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid — the PNS has no such protections. The PNS also has no blood-brain barrier to protect it from toxins and pathogens in the blood. Therefore, the PNS is more subject to injury and disease than is the CNS. Causes of nerve injury include diabetes, infectious diseases (such as shingles), and poisoning by toxins (such as heavy metals). PNS disorders often have symptoms like loss of feeling, tingling, burning sensations, or muscle weakness. If a traumatic injury results in a nerve being transected (cut all the way through), it may regenerate, but this is a very slow process and may take many months.
Two other diseases of the PNS are Guillain-Barre syndrome and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
- Guillain-Barre syndrome is a rare disease in which the immune system attacks nerves of the PNS, leading to muscle weakness and even paralysis. The exact cause of Guillain-Barre syndrome is unknown, but it often occurs after a viral or bacterial infection. There is no known cure for the syndrome, but most people eventually make a full recovery. Recovery can be slow, however, lasting anywhere from several weeks to several years.
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a hereditary disorder of the nerves, and one of the most common inherited neurological disorders. It affects predominantly the nerves in the feet and legs, and often in the hands and arms, as well. The disease is characterized by loss of muscle tissue and sense of touch. It is presently incurable.
Feature: My Human Body
The autonomic nervous system is considered to be involuntary because it doesn't require conscious input. However, it is possible to exert some voluntary control over it. People who practice yoga or other so-called mind-body techniques, for example, can reduce their heart rate and certain other autonomic functions. Slowing down these otherwise involuntary responses is a good way to relieve stress and reduce the wear-and-tear that stress can place on the body. Such techniques may also be useful for controlling post-traumatic stress disorder and chronic pain. Three types of integrative practices for these purposes are breathing exercises, body-based tension modulation exercises, and mindfulness techniques.
Breathing exercises can help control the rapid, shallow breathing that often occurs when you are anxious or under stress. These exercises can be learned quickly, and they provide immediate feelings of relief. Specific breathing exercises include paced breath, diaphragmatic breathing, and Breathe2Relax or Chill Zone on MindShift™ CBT, which are downloadable breathing practice mobile applications, or "Apps". Try syncing your breathing with Eric Klassen's "Triangle breathing, 1 minute" video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u9Q8D6n-3qw
Triangle breathing, 1 minute, Erin Klassen, 2015.
Body-based tension modulation exercises include yoga postures (also known as “asanas”) and tension manipulation exercises. The latter include the Trauma/Tension Release Exercise (TRE) and the Trauma Resiliency Model (TRM). Watch this video for a brief — but informative — introduction to the TRE program:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=67R974D8swM&feature=youtu.be
TRE® : Tension and Trauma Releasing Exercises, an Introduction with Jessica Schaffer, Jessica Schaffer Nervous System RESET, 2015.
Mindfulness techniques have been shown to reduce symptoms of depression, as well as those of anxiety and stress. They have also been shown to be useful for pain management and performance enhancement. Specific mindfulness programs include Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) and Mindfulness Mind-Fitness Training (MMFT). You can learn more about MBSR by watching the video below.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0TA7P-iCCcY&feature=youtu.be
Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (UMass Medical School, Center for Mindfulness), Palouse Mindfulness, 2017.
8.6 Summary
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of all the nervous tissue that lies outside the central nervous system (CNS). Its main function is to connect the CNS to the rest of the organism.
- The PNS is made up of nerves and ganglia. Nerves are bundles of axons, and ganglia are groups of cell bodies. Nerves are classified as sensory, motor, or a mix of the two.
- The PNS is divided into the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. The somatic system controls voluntary activities, whereas the autonomic system controls involuntary activities.
- The autonomic nervous system is further divided into sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric divisions. The sympathetic division controls fight-or-flight responses during emergencies, the parasympathetic system controls routine body functions the rest of the time, and the enteric division provides local control over the digestive system.
- The PNS is not as well protected physically or chemically as the CNS, so it is more prone to injury and disease. PNS problems include injury from diabetes, shingles, and heavy metal poisoning. Two disorders of the PNS are Guillain-Barre syndrome and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
8.6 Review Questions
- Describe the general structure of the peripheral nervous system. State its primary function.
- What are ganglia?
- Identify three types of nerves based on the direction in which they carry nerve impulses.
- Outline all of the divisions of the peripheral nervous system.
- Compare and contrast the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
- When and how does the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system affect the body?
- What is the function of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system? Specifically, how does it affect the body?
- Name and describe two peripheral nervous system disorders.
- Give one example of how the CNS interacts with the PNS to control a function in the body.
- For each of the following types of information, identify whether the neuron carrying it is sensory or motor, and whether it is most likely in the somatic or autonomic nervous system:
- Visual information
- Blood pressure information
- Information that causes muscle contraction in digestive organs after eating
- Information that causes muscle contraction in skeletal muscles based on the person’s decision to make a movement
-
8.6 Explore More
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ySIDMU2cy0Y&feature=emb_logo
Phantom Limbs Explained, Plethrons, 2015.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=1&v=73yo5nJne6c&feature=emb_logo
Why Do Hot Peppers Cause Pain? Reactions, 2015.
Attributions
Figure 8.6.1
Kid’s piant duet by PJMixer on Flickr is used under a CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/2.0/) license.
Figure 8.6.2
Nervous_system_diagram by ¤~Persian Poet Gal on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 8.6.3
Afferent_and_efferent_neurons_en.svg by Helixitta on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
Figure 8.6.4
Autonomic and Somatic Nervous System by Christinelmiller on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
Figure 8.6.5
Dermatoms.svg by Ralf Stephan (mailto:ralf@ark.in-berlin.de) on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 8.6.6
The_Autonomic_Nervous_System by Geo-Science-International on Wikimedia Commons is used and adapted by Christine Miller under a CC0 1.0 Universal
Public Domain Dedication license (https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/).
References
Erin Klassen. (2015, December 15). Triangle breathing, 1 minute. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u9Q8D6n-3qw&feature=youtu.be
Jessica Schaffer Nervous System RESET. (2015, January 15). TRE® : Tension and trauma releasing exercises, an Introduction with Jessica Schaffer. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=67R974D8swM&feature=youtu.be
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/charcot-marie-tooth-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350517
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Diabetes [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20371444
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Guillain-Barre syndrome [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/guillain-barre-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20362793
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Shingles [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/shingles/symptoms-causes/syc-20353054
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Stroke [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20350113
Palouse Mindfulness. (2017, March 25). Mindfulness-based stress reduction (UMass Medical School, Center for Mindfulness), YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0TA7P-iCCcY&feature=youtu.be
Plethrons, (2015, March 23). Phantom limbs explained. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ySIDMU2cy0Y&feature=youtu.be
Reactions. (2015, December 1). Why do hot peppers cause pain? YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=73yo5nJne6c&feature=youtu.be
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller

One Piano, Four Hands
Did you ever see two people play the same piano? How do they coordinate all the movements of their own fingers — let alone synchronize them with those of their partner? The peripheral nervous system plays an important part in this challenge.
What Is the Peripheral Nervous System?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of all the nervous tissue that lies outside of the central nervous system (CNS). The main function of the PNS is to connect the CNS to the rest of the organism. It serves as a communication relay, going back and forth between the CNS and muscles, organs, and glands throughout the body.

Tissues of the Peripheral Nervous System
The PNS is mostly made up of cable-like bundles of axons called nerves, as well as clusters of neuronal cell bodies called ganglia (singular, ganglion). Nerves are generally classified as sensory, motor, or mixed nerves based on the direction in which they carry nerve impulses.
- Sensory nerves transmit information from sensory receptors in the body to the CNS. Sensory nerves are also called afferent nerves. You can see an example in the figure below.
- Motor nerves transmit information from the CNS to muscles, organs, and glands. Motor nerves are also called efferent nerves. You can see one in the figure below.
- Mixed nerves contain both sensory and motor neurons, so they can transmit information in both directions. They have both afferent and efferent functions.

Divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System
The PNS is divided into two major systems, called the autonomic nervous system and the somatic nervous system. In the diagram below, the autonomic system is shown on the left, and the somatic system on the right. Both systems of the PNS interact with the CNS and include sensory and motor neurons, but they use different circuits of nerves and ganglia.

Somatic Nervous System
The somatic nervous system primarily senses the external environment and controls voluntary activities about which decisions and commands come from the cerebral cortex of the brain. When you feel too warm, for example, you decide to turn on the air conditioner. As you walk across the room to the thermostat, you are using your somatic nervous system. In general, the somatic nervous system is responsible for all of your conscious perceptions of the outside world, as well as all of the voluntary motor activities you perform in response. Whether it’s playing a piano, driving a car, or playing basketball, you can thank your somatic nervous system for making it possible.
Somatic sensory and motor information is transmitted through 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Cranial nerves are in the head and neck and connect directly to the brain. Sensory components of cranial nerves transmit information about smells, tastes, light, sounds, and body position. Motor components of cranial nerves control skeletal muscles of the face, tongue, eyeballs, throat, head, and shoulders. Motor components of cranial nerves also control the salivary glands and swallowing. Four of the 12 cranial nerves participate in both sensory and motor functions as mixed nerves, having both sensory and motor neurons.
Spinal nerves emanate from the spinal column between vertebrae. All of the spinal nerves are mixed nerves, containing both sensory and motor neurons. The areas of skin innervated by the 31 pairs of spinal nerves are shown in the figure below. These include sensory nerves in the skin that sense pressure, temperature, vibrations, and pain. Other sensory nerves are in the muscles, and they sense stretching and tension. Spinal nerves also include motor nerves that stimulate skeletal muscles to contract, allowing for voluntary body movements.

Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system primarily senses the internal environment and controls involuntary activities. It is responsible for monitoring conditions in the internal environment and bringing about appropriate changes in them. In general, the autonomic nervous system is responsible for all the activities that go on inside your body without your conscious awareness or voluntary participation.
Structurally, the autonomic nervous system consists of sensory and motor nerves that run between the CNS (especially the hypothalamus in the brain), internal organs (such as the heart, lungs, and digestive organs), and glands (such as the pancreas and sweat glands). Sensory neurons in the autonomic system detect internal body conditions and send messages to the brain. Motor nerves in the autonomic system affect appropriate responses by controlling contractions of smooth or cardiac muscle, or glandular tissue. For example, when sensory nerves of the autonomic system detect a rise in body temperature, motor nerves signal smooth muscles in blood vessels near the body surface to undergo vasodilation, and the sweat glands in the skin to secrete more sweat to cool the body.
The autonomic nervous system, in turn, has three subdivisions: the sympathetic division, parasympathetic division, and enteric division. The first two subdivisions of the autonomic system are summarized in the figure below. Both affect the same organs and glands, but they generally do so in opposite ways.
- The sympathetic division controls the fight-or-flight response. Changes occur in organs and glands throughout the body that prepare the body to fight or flee in response to a perceived danger. For example, the heart rate speeds up, air passages in the lungs become wider, more blood flows to the skeletal muscles, and the digestive system temporarily shuts down.
- The parasympathetic division returns the body to normal after the fight-or-flight response has occurred. For example, it slows down the heart rate, narrows air passages in the lungs, reduces blood flow to the skeletal muscles, and stimulates the digestive system to start working again. The parasympathetic division also maintains internal homeostasis of the body at other times.
- The enteric division is made up of nerve fibres that supply the organs of the digestive system. This division allows for the local control of many digestive functions.

Disorders of the Peripheral Nervous System
Unlike the CNS — which is protected by bones, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid — the PNS has no such protections. The PNS also has no blood-brain barrier to protect it from toxins and pathogens in the blood. Therefore, the PNS is more subject to injury and disease than is the CNS. Causes of nerve injury include diabetes, infectious diseases (such as shingles), and poisoning by toxins (such as heavy metals). PNS disorders often have symptoms like loss of feeling, tingling, burning sensations, or muscle weakness. If a traumatic injury results in a nerve being transected (cut all the way through), it may regenerate, but this is a very slow process and may take many months.
Two other diseases of the PNS are Guillain-Barre syndrome and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
- Guillain-Barre syndrome is a rare disease in which the immune system attacks nerves of the PNS, leading to muscle weakness and even paralysis. The exact cause of Guillain-Barre syndrome is unknown, but it often occurs after a viral or bacterial infection. There is no known cure for the syndrome, but most people eventually make a full recovery. Recovery can be slow, however, lasting anywhere from several weeks to several years.
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a hereditary disorder of the nerves, and one of the most common inherited neurological disorders. It affects predominantly the nerves in the feet and legs, and often in the hands and arms, as well. The disease is characterized by loss of muscle tissue and sense of touch. It is presently incurable.
Feature: My Human Body
The autonomic nervous system is considered to be involuntary because it doesn't require conscious input. However, it is possible to exert some voluntary control over it. People who practice yoga or other so-called mind-body techniques, for example, can reduce their heart rate and certain other autonomic functions. Slowing down these otherwise involuntary responses is a good way to relieve stress and reduce the wear-and-tear that stress can place on the body. Such techniques may also be useful for controlling post-traumatic stress disorder and chronic pain. Three types of integrative practices for these purposes are breathing exercises, body-based tension modulation exercises, and mindfulness techniques.
Breathing exercises can help control the rapid, shallow breathing that often occurs when you are anxious or under stress. These exercises can be learned quickly, and they provide immediate feelings of relief. Specific breathing exercises include paced breath, diaphragmatic breathing, and Breathe2Relax or Chill Zone on MindShift™ CBT, which are downloadable breathing practice mobile applications, or "Apps". Try syncing your breathing with Eric Klassen's "Triangle breathing, 1 minute" video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u9Q8D6n-3qw
Triangle breathing, 1 minute, Erin Klassen, 2015.
Body-based tension modulation exercises include yoga postures (also known as “asanas”) and tension manipulation exercises. The latter include the Trauma/Tension Release Exercise (TRE) and the Trauma Resiliency Model (TRM). Watch this video for a brief — but informative — introduction to the TRE program:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=67R974D8swM&feature=youtu.be
TRE® : Tension and Trauma Releasing Exercises, an Introduction with Jessica Schaffer, Jessica Schaffer Nervous System RESET, 2015.
Mindfulness techniques have been shown to reduce symptoms of depression, as well as those of anxiety and stress. They have also been shown to be useful for pain management and performance enhancement. Specific mindfulness programs include Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) and Mindfulness Mind-Fitness Training (MMFT). You can learn more about MBSR by watching the video below.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0TA7P-iCCcY&feature=youtu.be
Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (UMass Medical School, Center for Mindfulness), Palouse Mindfulness, 2017.
8.6 Summary
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of all the nervous tissue that lies outside the central nervous system (CNS). Its main function is to connect the CNS to the rest of the organism.
- The PNS is made up of nerves and ganglia. Nerves are bundles of axons, and ganglia are groups of cell bodies. Nerves are classified as sensory, motor, or a mix of the two.
- The PNS is divided into the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. The somatic system controls voluntary activities, whereas the autonomic system controls involuntary activities.
- The autonomic nervous system is further divided into sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric divisions. The sympathetic division controls fight-or-flight responses during emergencies, the parasympathetic system controls routine body functions the rest of the time, and the enteric division provides local control over the digestive system.
- The PNS is not as well protected physically or chemically as the CNS, so it is more prone to injury and disease. PNS problems include injury from diabetes, shingles, and heavy metal poisoning. Two disorders of the PNS are Guillain-Barre syndrome and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
8.6 Review Questions
- Describe the general structure of the peripheral nervous system. State its primary function.
- What are ganglia?
- Identify three types of nerves based on the direction in which they carry nerve impulses.
- Outline all of the divisions of the peripheral nervous system.
- Compare and contrast the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
- When and how does the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system affect the body?
- What is the function of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system? Specifically, how does it affect the body?
- Name and describe two peripheral nervous system disorders.
- Give one example of how the CNS interacts with the PNS to control a function in the body.
- For each of the following types of information, identify whether the neuron carrying it is sensory or motor, and whether it is most likely in the somatic or autonomic nervous system:
- Visual information
- Blood pressure information
- Information that causes muscle contraction in digestive organs after eating
- Information that causes muscle contraction in skeletal muscles based on the person’s decision to make a movement
-
8.6 Explore More
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ySIDMU2cy0Y&feature=emb_logo
Phantom Limbs Explained, Plethrons, 2015.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=1&v=73yo5nJne6c&feature=emb_logo
Why Do Hot Peppers Cause Pain? Reactions, 2015.
Attributions
Figure 8.6.1
Kid’s piant duet by PJMixer on Flickr is used under a CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/2.0/) license.
Figure 8.6.2
Nervous_system_diagram by ¤~Persian Poet Gal on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 8.6.3
Afferent_and_efferent_neurons_en.svg by Helixitta on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
Figure 8.6.4
Autonomic and Somatic Nervous System by Christinelmiller on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0) license.
Figure 8.6.5
Dermatoms.svg by Ralf Stephan (mailto:ralf@ark.in-berlin.de) on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 8.6.6
The_Autonomic_Nervous_System by Geo-Science-International on Wikimedia Commons is used and adapted by Christine Miller under a CC0 1.0 Universal
Public Domain Dedication license (https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/).
References
Erin Klassen. (2015, December 15). Triangle breathing, 1 minute. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u9Q8D6n-3qw&feature=youtu.be
Jessica Schaffer Nervous System RESET. (2015, January 15). TRE® : Tension and trauma releasing exercises, an Introduction with Jessica Schaffer. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=67R974D8swM&feature=youtu.be
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/charcot-marie-tooth-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350517
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Diabetes [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20371444
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Guillain-Barre syndrome [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/guillain-barre-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20362793
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Shingles [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/shingles/symptoms-causes/syc-20353054
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Stroke [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stroke/symptoms-causes/syc-20350113
Palouse Mindfulness. (2017, March 25). Mindfulness-based stress reduction (UMass Medical School, Center for Mindfulness), YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0TA7P-iCCcY&feature=youtu.be
Plethrons, (2015, March 23). Phantom limbs explained. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ySIDMU2cy0Y&feature=youtu.be
Reactions. (2015, December 1). Why do hot peppers cause pain? YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=73yo5nJne6c&feature=youtu.be
Image show a diagram of light entering the eye in a patient exhibiting Myopia. The light entering the eye is focused by the lens, but instead of the point of focus coming to the retina, it is in front of the retina, focused somewhere in the interior of the eye.
Image shows a diagram of the eye of a patient suffering from hyperopia. Light enters the eye and is focused by the lens. Instead of the light coming to a point of focus at the retina, it comes to a point at a location somewhere behind the retina.
Image shows a diagram of a human ear with all structures labelled. The outer ear consists of the pinna, ear canal and ear drum. The middle ear consists of three tiny bones: the malleus, incus and stapes. The inner ear includes the semicircular canals which contribute to our sense of balance and the cochlea, which detects sound waves.
Image shows a diagram of a taste bud. A taste pore is a small opening in the epithelial tissue lining the oral cavity. Embedded in the epithelium is a taste receptor cell, which is located directly under the taste pore, so as to have access to the contents of the mount. The taste receptor cell is connected to afferent nerve fibers and is anchored in connective tissue.
Image shows a diagram of the olfactory cells which are pervasive in the nasal cavities/sinuses. These all connect back to the olfactory nerve which brings sensory information related to smell to the brain.
Seeing Is Believing
At first glance, Figure 8.7.1 appears to be just random dots of colour, but hidden within it is the three-dimensional shape of a bee. Can you see it among the dots? This figure is an example of a stereogram, which is a two-dimensional picture that, when viewed correctly, reveals a three-dimensional object. If you can’t see the hidden image, it doesn’t mean that there is anything wrong with your eyes. It’s all in how your brain interprets what your eyes are sensing. The eyes are special sensory organs, and vision is one of our special senses.
Special and General Senses
The human body has two basic types of senses, called special senses and general senses. Special senses have specialized sense organs that gather sensory information and change it into nerve impulses. Special senses include vision (for which the eyes are the specialized sense organs), hearing (ears), balance (ears), taste (tongue), and smell (nasal passages). General senses, in contrast, are all associated with the sense of touch. They lack special sense organs. Instead, sensory information about touch is gathered by the skin and other body tissues, all of which have important functions besides gathering sense information. Whether the senses are special or general, however, they all depend on cells called sensory receptors.
Sensory Receptors
A sensory receptor is a specialized nerve cell that responds to a stimulus in the internal or external environment by generating a nerve impulse. The nerve impulse then travels along the sensory (afferent) nerve to the central nervous system for processing and to form a response.
There are several different types of sensory receptors that respond to different kinds of stimuli:
- Mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical forces, such as pressure, roughness, vibration, and stretching. Most mechanoreceptors are found in the skin and are needed for the sense of touch. Mechanoreceptors are also found in the inner ear, where they are needed for the senses of hearing and balance.
- Thermoreceptors respond to variations in temperature. They are found mostly in the skin and detect temperatures that are above or below body temperature.
- Nociceptors respond to potentially damaging stimuli, which are generally perceived as pain. They are found in internal organs, as well as on the surface of the body. Different nociceptors are activated depending on the particular stimulus. Some detect damaging heat or cold, others detect excessive pressure, and still others detect painful chemicals (such as very hot spices in food).
- Photoreceptors detect and respond to light. Most photoreceptors are found in the eyes and are needed for the sense of vision.
- Chemoreceptors respond to certain chemicals. They are found mainly in taste buds on the tongue — where they are needed for the sense of taste — and in nasal passages, where they are needed for the sense of smell.
Touch
Touch is the ability to sense pressure, vibration, temperature, pain, and other tactile stimuli. These types of stimuli are detected by mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, and nociceptors all over the body, most noticeably in the skin. These receptors are especially concentrated on the tongue, lips, face, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. Various types of tactile receptors in the skin are shown in Figure 8.7.2.

Vision
Vision (or sight) is the ability to sense light and see. The eye is the special sensory organ that collects and focuses light and forms images. The eye, however, is not sufficient for us to see. The brain also plays a necessary role in vision. Vision is our primary sense and more than 50 per cent of the cerebral cortex is devoted to processing visual information. A person with normal colour vision can differentiate between hundreds of thousands of different colours, hues, and shades.
How the Eye Works
Figure 8.7.4 (below) shows the anatomy of the human eye in cross-section. The eye gathers and focuses light to form an image, and then changes the image to nerve impulses that travel to the brain. The eye's functions are summarized in the following steps.
- Light passes first through the cornea, which is a clear outer layer that protects the eye and helps to focus the light by refracting (or bending) it.
- Next, light enters the interior of the eye through an opening called the pupil. The size of this opening is controlled by the coloured part of the eye (called the iris), which adjusts the size based on the brightness of the light. The iris causes the pupil to narrow in bright light and widen in dim light. Filling the space between the cornea and the iris is a semi-gelatinous fluid called aqueous humor and functions to maintain the shape of the eye.
- The light then passes through the lens, which refracts the light even more and focuses it on the retina at the back of the eye, as an inverted image. Sitting behind the lens is a gelatinous fluid called vitreous humor, which functions to maintain the shape of the eye.
- The retina contains two types of photoreceptors: rod and cone cells . Rod cells, which are found mainly in all areas of the retina other than the very center, are particularly sensitive to low levels of light. Cone cells, which are found mainly in the center of the retina, are sensitive to light of different colours, and allow colour vision. The rods and cones convert the light that strikes them to nerve impulses.
- The nerve impulses from the rods and cones travel to the optic nerve via the optic disc (also known as the optic nerve), which is a circular area at the back of the eye where the optic nerve connects to the retina.
Colour Vision
Humans have colour vision because we have three types of cone cells: blue, green and red. Each of these types of cone cell detects a specific wavelength of light, for which they are named. The combined stimulus is then perceived as a specific colour, based on the ratio of the amount stimulus coming from each of the three types of cone cells. Do you know what else uses these same three pieces of information to communicate colour? Your computer monitor! When working in a creative program, such as Paint, these three reference points of red (R), green (G), and blue (B), can be used to create any of the million colours the human eye can perceive, as illustrated in Figure 8.7.5. Take a look at each of the numerical values for red, green, and blue and what colour their combined values create:
Figure 8.7.5 RGB colours.
Role of the Brain in Vision
The optic nerves from both eyes meet and cross just below the bottom of the hypothalamus in the brain. The information from both eyes is sent to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe of the cerebrum, which is part of the cerebral cortex. The visual cortex is the largest system in the human brain, and is responsible for processing visual images. It interprets messages from both eyes and “tells” us what we are seeing.
Vision Problems

Vision problems are very common. Two of the most common are myopia and hyperopia, and they often start in childhood or adolescence. Another common problem, called presbyopia, occurs in most people, beginning in middle adulthood. In all three conditions, the eyes fail to focus images correctly on the retina, resulting in blurred vision.
Myopia
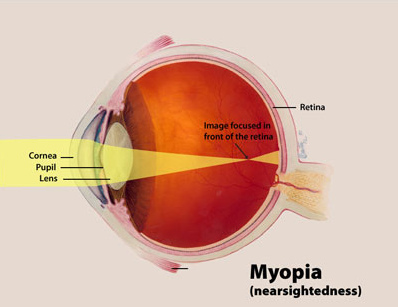
Myopia (or nearsightedness) occurs when the light that comes into the eye does not directly focus on the retina, but in front of it, as shown in Figure 8.7.7. As a result, distant objects may appear out of focus, but the focus of close objects is not affected. Myopia may occur because the eyeball is elongated from front to back, or because the cornea is too curved. Myopia can be corrected with the use of corrective lenses, either eyeglasses or contact lenses. Myopia can also be corrected by refractive surgery performed with a laser.
Hyperopia
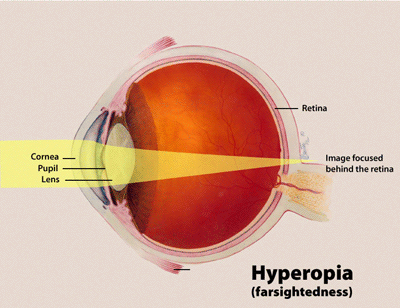
Hyperopia (or farsightedness) happens when the light coming into the eye does not directly focus on the retina but behind it, as shown in Figure 8.7.8. This causes close objects to appear out of focus, but does not affect the focus of distant objects. Hyperopia may occur because the eyeball is too short from front to back, or because the lens is not curved enough. Hyperopia can be corrected through the use of corrective lenses or laser surgery.
Presbyopia
Presbyopia is a vision problem associated with aging, in which the eye gradually loses its ability to focus on close objects. The precise origin of presbyopia is not known for certain, but evidence suggests that the lens may become less elastic with age, causing the muscles that control the lens to lose power as people grow older. The first signs of presbyopia — eyestrain, difficulty seeing in dim light, problems focusing on small objects and fine print — are usually first noticed between the ages of 40 and 50. Most older people with this problem use corrective lenses to focus on close objects, because surgical procedures to correct presbyopia have not been as successful as those for myopia and hyperopia.
Hearing
Hearing is the ability to sense sound waves, and the ear is the organ that senses sound. Sound waves enter the ear through the ear canal and travel to the eardrum (see the diagram of the ear Figure 8.7.9). The sound waves strike the eardrum, and make it vibrate. The vibrations then travel through the three tiny bones (incus, malleus and stapes) of the middle ear, which amplify the vibrations. From the middle ear, the vibrations pass to the cochlea in the inner ear. The cochlea is a coiled tube filled with liquid. The liquid moves in response to the vibrations, causing tiny hair cells(which are mechanoreceptors) lining the cochlea to bend. In response, the hair cells send nerve impulses to the auditory nerve, which carries the impulses to the brain. The brain interprets the impulses and “tells” us what we are hearing.
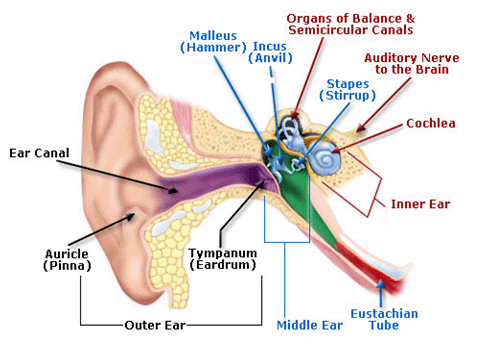
Balance
The ears are also responsible for the sense of balance. Balance is the ability to sense and maintain an appropriate body position. The semicircular canals inside the ear (see the figure above) contain fluid that moves when the head changes position. Tiny hairs lining the semicircular canals sense movement of the fluid. In response, they send nerve impulses to the vestibular nerve, which carries the impulses to the brain. The brain interprets the impulses and sends messages to the peripheral nervous system, which triggers contractions of skeletal muscles as needed to maintain balance.
Taste and Smell
Taste and smell are both abilities to sense chemicals, so both taste and olfactory (odor) receptors are chemoreceptors. Both types of chemoreceptors send nerve impulses to the brain along sensory nerves, and the brain “tells” us what we are tasting or smelling.
Taste receptors are found in tiny bumps on the tongue called taste buds.You can see a diagram of a taste receptor cell and related structures in Figure 8.7.10. Taste receptor cells make contact with chemicals in food through tiny openings called taste pores. When certain chemicals bind with taste receptor cells, it generates nerve impulses that travel through afferent nerves to the CNS. There are separate taste receptors for sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and meaty tastes. The meaty — or savory — taste is called umami.
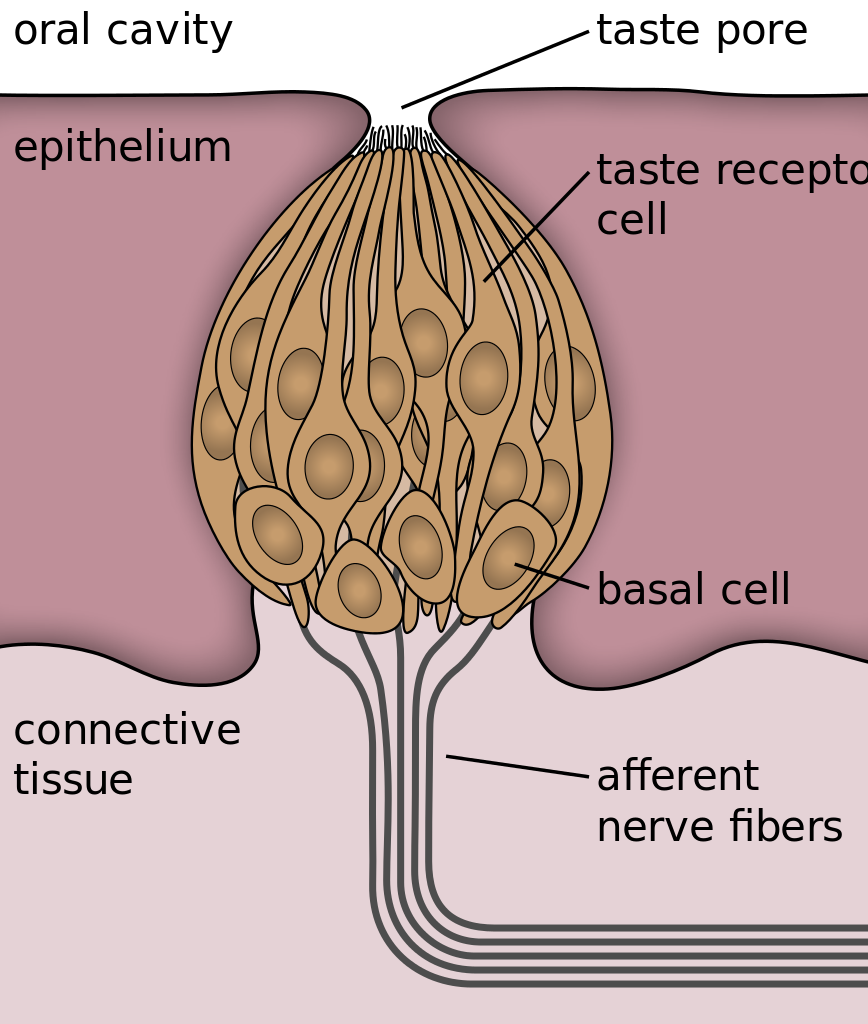
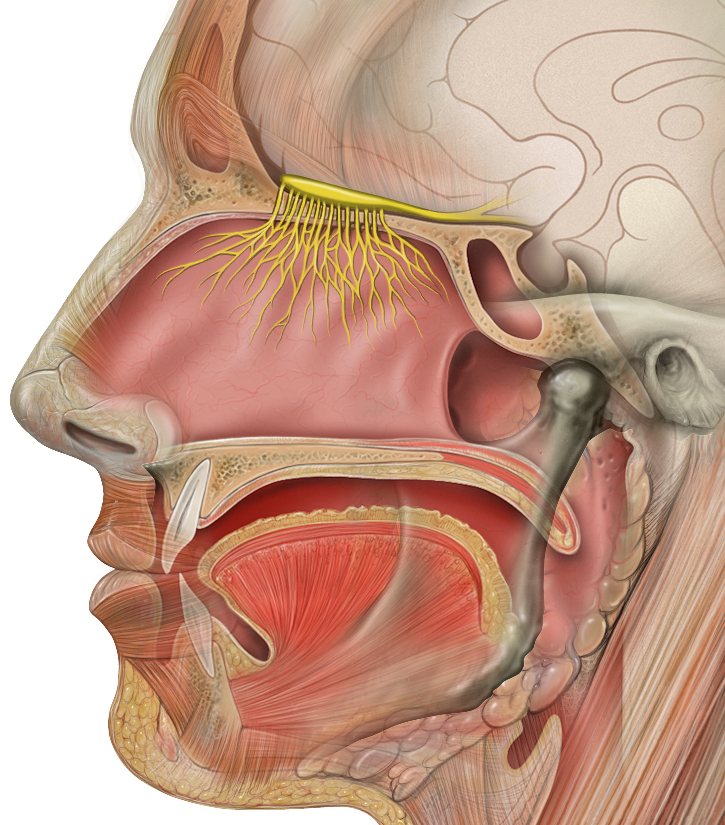
Feature: Human Biology in the News
The most common cause of blindness in the Western hemisphere is age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Approximately 1.4 million people in Canada have this type of blindness, and 196 million people are affected worldwide and is expected to increase to 288 millions people by the year 2040. At present, there is no cure for AMD. The disease occurs with the death of a layer of cells called retinal pigment epithelium, which normally provides nutrients and other support to the macula of the eye. The macula is an oval-shaped pigmented area near the center of the retina that is specialized for high visual acuity and has the retina’s greatest concentration of cones. When the epithelial cells die and the macula is no longer supported or nourished, the macula also starts to die. Patients experience a black spot in the center of their vision, and as the disease progresses, the black spot grows outward. Patients eventually lose the ability to read and even to recognize familiar faces before developing total blindness.
In 2016, a landmark surgery was performed as a trial on a patient with severe AMD. In the first ever operation of its kind, Dr. Pete Coffey of the University of London implanted a tiny patch of cells behind the retina in each of the patient’s eyes. The cells were retinal pigmented epithelial cells that had been grown in a lab from stem cells, which are undifferentiated cells that can develop into other cell types. Within six months of the operation, the new cells were still surviving, and the doctor was hopeful that the patient’s vision loss would stop and even be reversed. At that point, several other operations had already been planned to test the new procedure. If these cases are a success, Dr. Coffey predicts that the surgery will become as routine as cataract surgery, and that it will prevent millions of patients from losing their vision.
8.7 Summary
- The human body has two major types of senses: special senses and general senses. Special senses have specialized sense organs and include vision (eyes), hearing (ears), balance (ears), taste (tongue), and smell (nasal passages). General senses are all associated with touch and lack special sense organs. Touch receptors are found throughout the body, but particularly in the skin.
- All senses depend on sensory receptor cells to detect sensory stimuli and transform them into nerve impulses. Types of sensory receptors include mechanoreceptors (mechanical forces), thermoreceptors (temperature), nociceptors (pain), photoreceptors (light), and chemoreceptors (chemicals).
- Touch is the ability to sense pressure, vibration, temperature, pain, and other tactile stimuli. The skin includes several different types of touch receptor cells.
- Vision is the ability to sense light and see. The eye is the special sensory organ that collects and focuses light, forms images, and changes them to nerve impulses. Optic nerves send information from the eyes to the brain, which processes the visual information and “tells” us what we are seeing.
- Common vision problems include myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and presbyopia (age-related decline in close vision). Vision problems can be corrected with lenses (eyeglasses or contacts) or — in many cases — with laser surgery.
- Hearing is the ability to sense sound waves, and the ear is the organ that senses sound. It changes sound waves to vibrations that trigger nerve impulses, which travel to the brain through the auditory nerve. The brain processes the information and “tells” us what we are hearing.
- The ear is also the organ responsible for the sense of balance, which is the ability to sense and maintain an appropriate body position. The ears send impulses about head position to the brain, which sends messages to skeletal muscles via the peripheral nervous system. The muscles respond by contracting to maintain balance.
- Taste and smell are both abilities to sense chemicals. Taste receptors in taste buds on the tongue sense chemicals in food, while olfactory receptors in the nasal passages sense chemicals in the air. Sense of smell contributes significantly to sense of taste.
8.7 Review Questions
-
- Compare and contrast special senses and general senses.
- What are sensory receptors?
-
- Describe the range of tactile stimuli detected in the sense of touch.
- Explain how the eye collects and focuses light to form an image, and how it converts it to nerve impulses.
- Identify two common vision problems,along with their causes and their effects on vision.
-
- Explain how structures of the ear collect and amplify sound waves and transform them to nerve impulses.
- What role does the ear play in balance? Which structures of the ear are involved in balance?
- Describe two ways that the body senses chemicals. What are the special sense organs involved in these senses?
- Explain why your skin can detect different types of stimuli, such as pressure and temperature.
- Is sensory information sent to the central nervous system via efferent or afferent nerves?
- Identify a mechanoreceptor used in two different human senses. Describe the type of mechanical stimuli that each detects.
- If a person is blind, but their retina is functioning properly, where do you think the damage might be? Explain your answer.
- When you see colours, what receptor cells are activated? Where are these receptors located? What lobe of the brain is primarily used to process visual information?
- The auditory nerve carries _______________.
-
-
- smell information
- taste information
- balance information
- sound information
-
8.7 Explore More
https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=4&v=rkRbebvoYqI&feature=emb_logo
What color is Tuesday? Exploring synesthesia - Richard E. Cytowic, TED-Ed, 2013.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL8YSLhqa5U&feature=emb_logo
What Is Vertigo & Why Do We Get It?, Seeker, 2016.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t3CjTU7TaNA
How do animals see in the dark? - Anna Stöckl, TED-Ed, 2016.
https://youtu.be/Y6e_m9iq-4Q
What are those floaty things in your eye? - Michael Mauser, TED-Ed, 2014.
Attributions
Figure 8.7.1
Bee Stereogram by Be Mosaic on Flickr is used under a CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/) license.
Figure 8.7.2
Skin_TactileReceptors by BruceBlaus on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
Figure 8.7.3
Macro shot photograph of someone's right eye [photo] by Jordan Whitfield on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 8.7.4
EyeAnatomy_01 by BruceBlaus on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
Figure 8.7.5
RGB colours [screenshots] from Microsoft Paint.
Figure 8.7.6
Through the reading glasses [photo] by Dmitry Ratushny on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 8.7.7
Myopia_Diagram by National Eye Institute/ National Institutes of Health on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0) license.
Figure 8.7.8
Hyperopia by National Institute of Health/NIH on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 8.7.9
AnatomyHumanEar by unknown author from Occupational Safety & Health Administration on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 8.7.10
Taste_bud_2_eng.svg by Jonas Töle on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication license (https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en).
Figure 8.7.11
Head_olfactory_nerve by Patrick.lynch, medical illustrator on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 2.5 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5/deed.en) license.
References
Age-Related Macular Degeneration. (n.d.). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/eye-health/macular-degeneration/age-related-macular-degeneration-overview#3 (Reviewed by Alan Kozarsky, MD on October 26, 2019)
Blausen.com Staff. (2014). Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436.
da Cruz, L., Fynes, K., Georgiadis, O. et al. (2018, March 19). Phase 1 clinical study of an embryonic stem cell–derived retinal pigment epithelium patch in age-related macular degeneration. Natural Biotechnology, 36, 328–337. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4114
File:Eye Diagram without text.gif. (2018, February 9). Wikimedia Commons. https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:Eye_Diagram_without_text.gif&oldid=286008241 (original image from National Eye Institute - modified by User:Nordelch) [public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain)]
Occupational Health and Safety Administration. (n.d.). Figure 7. Anatomy of the human ear [diagram]. In OSHA Technical Manual (Section III, Chapter 5 - Noise). United States Department of Labour [online]. https://www.osha.gov/dts/osta/otm/new_noise/
Seeker. (2016, March 18). What is vertigo & why do we get it? YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL8YSLhqa5U&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2013, June 10). What color is Tuesday? Exploring synesthesia - Richard E. Cytowic. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rkRbebvoYqI&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2014, December 1). What are those floaty things in your eye? - Michael Mauser. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y6e_m9iq-4Q&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2016, August 25). How do animals see in the dark? - Anna Stöckl. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t3CjTU7TaNA&feature=youtu.be
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller

Fashion Statement
This colourful hairstyle makes quite a fashion statement. Many people spend a lot of time and money on their hair, even if they don’t have an exceptional hairstyle like this one. Besides its display value, hair actually has important physiological functions.
What is Hair?
Hair is a filament that grows from a hair follicle in the dermis of the skin. It consists mainly of tightly packed, keratin-filled cells called keratinocytes. The human body is covered with hair follicles, with the exception of a few areas, including the mucous membranes, lips, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet.
Structure of Hair
The part of the hair located within the follicle is called the hair root. The root is the only living part of the hair. The part of the hair that is visible above the surface of the skin is the hair shaft. The shaft of the hair has no biochemical activity and is considered dead.
Follicle and Root
Hair growth begins inside a follicle (see Figure 10.5.2 below). Each hair follicle contains stem cells that can keep dividing, which allows hair to grow. The stem cells can also regrow a new hair after one falls out. Another structure associated with a hair follicle is a sebaceous gland that produces oily sebum. The sebum lubricates and helps to waterproof the hair. A tiny arrector pili muscle is also attached to the follicle. When it contracts, the follicle moves, and the hair in the follicle stands up.
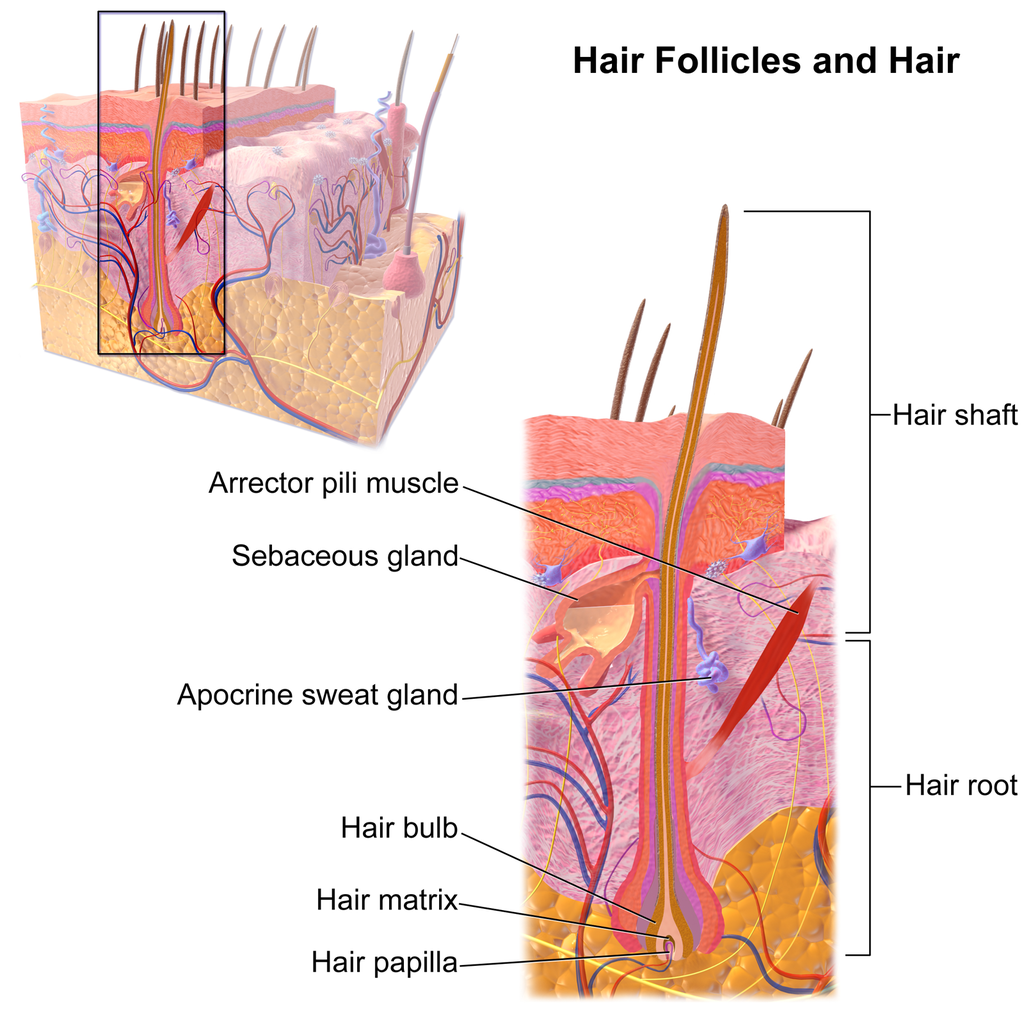
Shaft
The hair shaft is a hard filament that may grow very long. Hair normally grows in length by about half an inch a month. In cross-section, a hair shaft can be divided into three zones, called the cuticle, cortex, and medulla.
- The cuticle (or outer coat) is the outermost zone of the hair shaft. It consists of several layers of flat, thin keratinocytes that overlap one another like shingles on a roof. This arrangement helps the cuticle repel water. The cuticle is also covered with a layer of lipids, just one molecule thick, which increases its ability to repel water. This is the zone of the hair shaft that is visible to the eye.
- The cortex is the middle zone of the hair shaft, and it is also the widest part. The cortex is highly structured and organized, consisting of keratin bundles in rod-like structures. These structures give hair its mechanical strength. The cortex also contains melanin, which gives hair its colour.
- The medulla is the innermost zone of the hair shaft. This is a small, disorganized, and more open area at the center of the hair shaft. The medulla is not always present. When it is present, it contains highly pigmented cells full of keratin.
Characteristics of Hair
Two visible characteristics of hair are its colour and texture. In adult males, the extent of balding is another visible characteristic. All three characteristics are genetically controlled.
Hair Colour
All natural hair colours are the result of melanin, which is produced in hair follicles and packed into granules in the hair. Two forms of melanin are found in human hair: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Eumelanin is the dominant pigment in brown hair and black hair, and pheomelanin is the dominant pigment in red hair. Blond hair results when you have only a small amount of melanin in the hair. Gray and white hair occur when melanin production slows down, and eventually stops.
Figure 10.5.3 Variation in hair colouration. Which types of melanin are present for each hair colour shown?
Hair Texture
Hair exists in a variety of textures. The main aspects of hair texture are the curl pattern, thickness, and consistency.
- The shape of the hair follicle determines the shape of the hair shaft. The shape of the hair shaft, in turn, determines the curl pattern of the hair. Round hair shafts produce straight hair. Hair shafts that are oval or have other shapes produce wavy or curly hair .
- The size of the hair follicle determines the thickness of hair. Thicker hair has greater volume than thinner hair.
- The consistency of hair is determined by the hair follicle volume and the condition of the hair shaft. The consistency of hair is generally classified as fine, medium, or coarse. Fine hair has the smallest circumference, and coarse hair has the largest circumference. Medium hair falls in between these two extremes. Coarse hair also has a more open cuticle than thin or medium hair does, which causes it to be more porous.

Figure 10.5.4 Curly hair has a differently shaped shaft than straight hair.
Functions of Hair
In humans, one function of head hair is to provide insulation and help the head retain heat. Head hair also protects the skin on the head from damage by UV light.
The function of hair in other locations on the body is debated. One idea is that body hair helps keep us warm in cold weather. When the body is too cold, arrector pili muscles contract and cause hairs to stand up (shown in Figure 10.5.5), trapping a layer of warm air above the epidermis. However, this is more effective in mammals that have thick hair or fur than it is in relatively hairless human beings.
Human hair has an important sensory function, as well. Sensory receptors in the hair follicles can sense when the hair moves, whether it moves because of a breeze, or because of the touch of a physical object. The receptors may also provide sensory awareness of the presence of parasites on the skin.

Some hairs, such as the eyelashes, are especially sensitive to the presence of potentially harmful matter. The eyelashes grow at the edge of the eyelid and can sense when dirt, dust, or another potentially harmful object is too close to the eye. The eye reflexively closes as a result of this sensation. The eyebrows also provide some protection to the eyes. They protect the eyes from dirt, sweat, and rain. In addition, the eyebrows play a key role in nonverbal communication (see Figure 10.5.6). They help express emotions such as sadness, anger, surprise, and excitement.
Hair in Human Evolution
Among mammals, humans are nearly unique in having undergone significant loss of body hair during their evolution. Humans are also unlike most other mammals in having curly hair as one variation in hair texture. Even non-human primates (see Figure 10.5.7) all have straight hair. This suggests that curly hair evolved at some point during human evolution.

Loss of Body Hair
One hypothesis for the loss of body hair in the human lineage is that it would have facilitated cooling of the body by the evaporation of sweat. Humans also evolved far more sweat glands than other mammals, which is consistent with this hypothesis, because sweat evaporates more quickly from less hairy skin. Another hypothesis for human hair loss is that it would have led to fewer parasites on the skin. This might have been especially important when humans started living together in larger, more crowded social groups.
These hypotheses may explain why we lost body hair, but they can’t explain why we didn’t also lose head hair and hair in the pubic region and armpits. It is possible that head hair was retained because it protected the scalp from UV light. As our bipedal ancestors walked on the open savannas of equatorial Africa, the skin on the head would have been an area exposed to the most direct rays of sunlight in an upright hominid. Pubic and armpit hair may have been retained because they served as signs of sexual maturity, which would have been important for successful mating and reproduction.
Evolution of Curly Hair
Greater protection from UV light has also been posited as a possible selective agent favoring the evolution of curly hair. Researchers have found that straight hair allows more light to pass into the body through the hair shaft via the follicle than does curly hair. In this way, human hair is like a fibre optic cable. It allows light to pass through easily when it is straight, but it impedes the passage of light when it is kinked or coiled. This is indirect evidence that UV light may have been a selective agent leading to the evolution of curly hair.
Social and Cultural Significance of Hair
Hair has great social significance for human beings. Body hair is an indicator of biological sex, because hair distribution is sexually dimorphic. Adult males are generally hairier than adult females, and facial hair in particular is a notable secondary male sex characteristic. Hair may also be an indicator of age. White hair is a sign of older age in both males and females, and male pattern baldness is a sign of older age in males. In addition, hair colour and texture can be a sign of ethnic ancestry.
Hair also has great cultural significance. Hairstyle and colour may be an indicator of social group membership and for better or worse can be associated with specific stereotypes. Head shaving has been used in many times and places as a punishment, especially for women. On the other hand, in some cultures, cutting off one’s hair symbolizes liberation from one’s past. In other cultures, it is a sign of mourning. There are also many religious-based practices involving hair. For example, the majority of Muslim women hide their hair with a headscarf. Sikh men grow their hair long and cover it with a turban. Amish men (like the one pictured in Figure 10.5.8) grow facial hair only after they marry — but just a beard, and not a mustache.

Unfortunately, sometimes hairstyle, colour and characteristics are used to apply stereotypes, particularly with respect to women. "Blonde jokes" are a good example of how negative stereotypes are maintained despite having no actual truth behind them. Many stereotypes related to hair are hidden, even from persons perpetrating the stereotype. Often a hairstyle is judged by another as having ties to gender, sexuality, worldview and/or socioeconomic status; even when these inferences are woefully inaccurate. It is important to be aware of our own biases and determine if these biases are appropriate - take a look at the collage in Figure 10.5.9. What are your initial reactions? Are these reactions founded in fact? Do you harbor an unfair bias?
Figure 10.5.9 What are your biases? Are they fair?
10.5 Summary
- Hair is a filament that grows from a hair follicle in the dermis of the skin. It consists mainly of tightly packed, keratin-filled cells called keratinocytes. The human body is almost completely covered with hair follicles.
- The part of a hair that is within the follicle is the hair root. This is the only living part of a hair. The part of a hair that is visible above the skin surface is the hair shaft. It consists of dead cells.
- Hair growth begins inside a follicle when stem cells within the follicle divide to produce new keratinocytes. An individual hair may grow to be very long.
- A hair shaft has three zones: the outermost zone called the cuticle; the middle zone called the cortex; and the innermost zone called the medulla.
- Genetically controlled, visible characteristics of hair include hair colour, hair texture, and the extent of balding in adult males. Melanin (eumelanin and/or pheomelanin) is the pigment that gives hair its colour. Aspects of hair texture include curl pattern, thickness, and consistency.
- Functions of head hair include providing insulation and protecting skin on the head from UV light. Hair everywhere on the body has an important sensory function. Hair in eyelashes and eyebrows protects the eyes from dust, dirt, sweat, and other potentially harmful substances. The eyebrows also play a role in nonverbal communication.
- Among mammals, humans are nearly unique in having undergone significant loss of body hair during their evolution, probably because sweat evaporates more quickly from less hairy skin. Curly hair also is thought to have evolved at some point during human evolution, perhaps because it provided better protection from UV light.
- Hair has social significance for human beings, because it is an indicator of biological sex, age, and ethnic ancestry. Human hair also has cultural significance. Hairstyle may be an indicator of social group membership, for example.
10.5 Review Questions
-
- Compare and contrast the hair root and hair shaft.
- Describe hair follicles.
-
-
- Explain variation in human hair colour.
- What factors determine the texture of hair?
- Describe two functions of human hair.
- What hypotheses have been proposed for the loss of body hair during human evolution?
- Discuss the social and cultural significance of human hair.
- Describe one way in which hair can be used as a method of communication in humans.
- Explain why waxing or tweezing body hair, which typically removes hair down to the root, generally keeps the skin hair-free for a longer period of time than shaving, which cuts hair off at the surface of the skin.
10.5 Explore More
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8diYLhl8bWU
Why do some people go bald? - Sarthak Sinha, TED-Ed, 2015.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kNw8V_Fkw28
Hair Love | Oscar®-Winning Short Film (Full) | Sony Pictures Animation, 2019.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hDW5e3NR1Cw
Why do we care about hair | Naomi Abigail | TEDxBaDinh, TEDx Talks, 2015.
Attributions
Figure 10.5.1
Hair by jessica-dabrowski-TETR8YLSqt4 [photo] by Jessica Dabrowski on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 10.5.2
Blausen_0438_HairFollicleAnatomy_02 by BruceBlaus on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
Figure 10.5.3
- Standing tall by Ilaya Raja on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
- Blond-haired woman smiling by Carlos Lindner on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
- Smith Mountain Lake redhead by Chris Ross Harris on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
- Through the look of experience by Laura Margarita Cedeño Peralta on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 10.5.4
Curly hair by chris-benson-clvEami9RN4 [photo] by Chris Benson on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 10.5.5
1024px-PilioerectionAnimation by AnthonyCaccese on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en) license.
Figure 10.5.6
Pout by alexander-dummer-Em8I8Z_DwA4 [photo] by Alexander Dummer on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 10.5.7
Cotton_top_tamarin_monkey._(12046035746) by Bernard Spragg. NZ, from Christchurch, New Zealand on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC0 1.0 Universal
Public Domain Dedication license (https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en).
Figure 10.5.8
Amish hairstyle by CK-12 Foundation is used under a CC BY-NC 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) license.
 ©CK-12 Foundation Licensed under
©CK-12 Foundation Licensed under ![]() • Terms of Use • Attribution
• Terms of Use • Attribution
Figure 10.5.9
- Rainbow Hair Bubble Man by Behrouz Jafarnezhad on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
- Pink hair in Atlanta, United States by Tammie Allen on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
- Magdalena 2 by Valerie Elash on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
- Perfect Style by Daria Volkova on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license)
- Stay Classy by Fayiz Musthafa on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license)
- Take your time by Jan Tinneberg on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license)
References
Blausen.com staff. (2014). Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436.
Brainard, J/ CK-12 Foundation. (2016). Figure 7 This style of facial hair is adopted by most Amish men after they marry [digital image]. In CK-12 College Human Biology (Section 12.5) [online Flexbook]. CK12.org. https://www.ck12.org/book/ck-12-college-human-biology/section/12.5/
Sony Pictures Animation. (2019, December 5). Hair love | Oscar®-winning short film (Full) | Sony Pictures Animation. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kNw8V_Fkw28
TED-Ed. (2015, August 25). Why do some people go bald? – Sarthak Sinha. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8diYLhl8bWU
TEDx Talks. (2015, February 4). Why do we care about hair | Naomi Abigail | TEDxBaDinh. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hDW5e3NR1Cw
Facts and statistics collected together for reference or analysis.
An explanation of an aspect of the natural world that can be repeatedly tested and verified in accordance with the scientific method.