9.4 Pituitary Gland
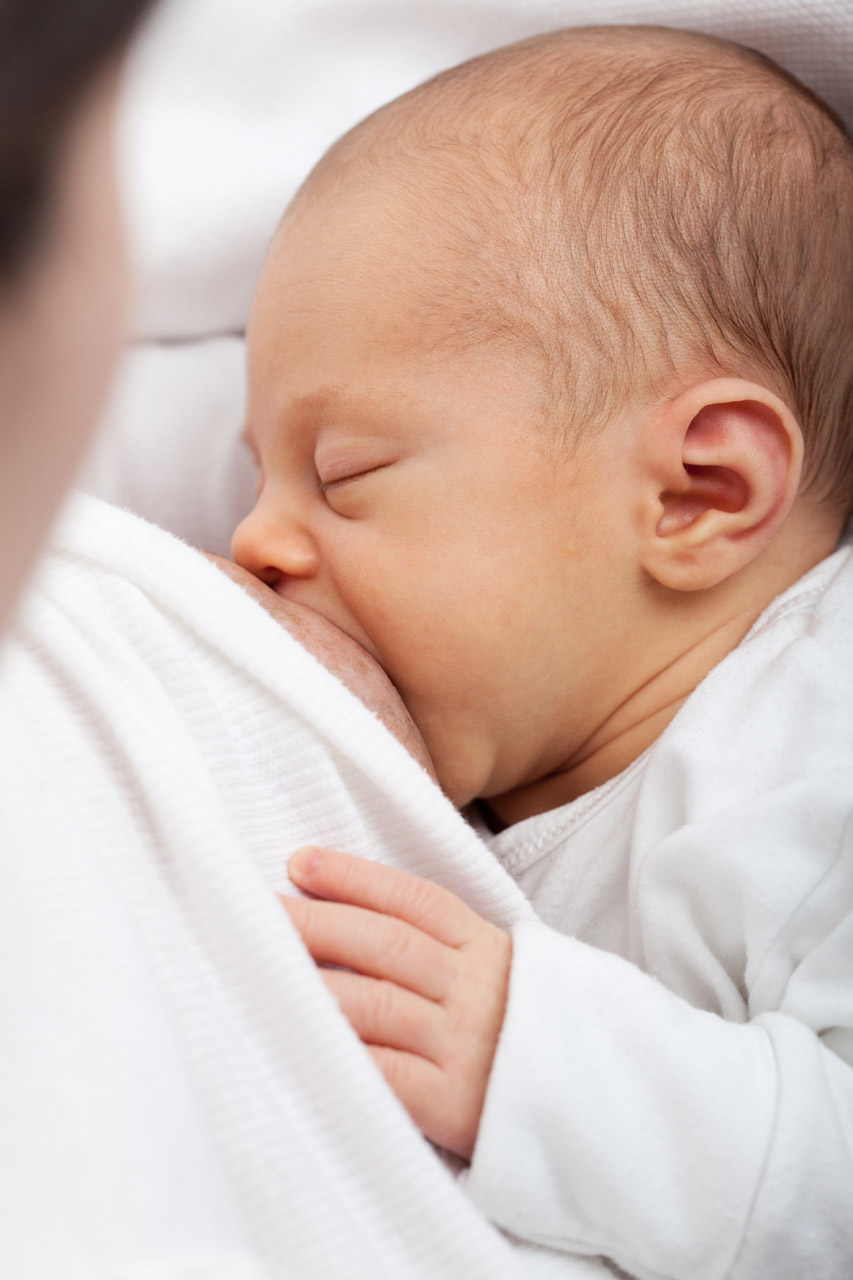

Milk on Demand
This adorable nursing infant (Figure 9.4.1) is part of a positive feedback loop. When he suckles on the nipple, it sends nerve impulses to his mother’s hypothalamus. Those nerve impulses “tell” her pituitary gland to release the hormone prolactin into her bloodstream. Prolactin travels to the mammary glands in the breasts and stimulates milk production, which motivates the infant to keep suckling.
What Is the Pituitary Gland?
The pituitary gland is the master gland of the endocrine system, which is the system of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Endocrine hormones control virtually all physiological processes. They control growth, sexual maturation, reproduction, body temperature, blood pressure, and metabolism. The pituitary gland is considered the master gland of the endocrine system, because it controls the rest of the endocrine system. Many pituitary hormones either promote or inhibit hormone secretion by other endocrine glands.
Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland is about the size of a pea. It protrudes from the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the inner brain (see Figure 9.4.2). The pituitary is connected to the hypothalamus by a thin stalk (called the infundibulum). Blood vessels and nerves in the stalk allow direct connections between the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
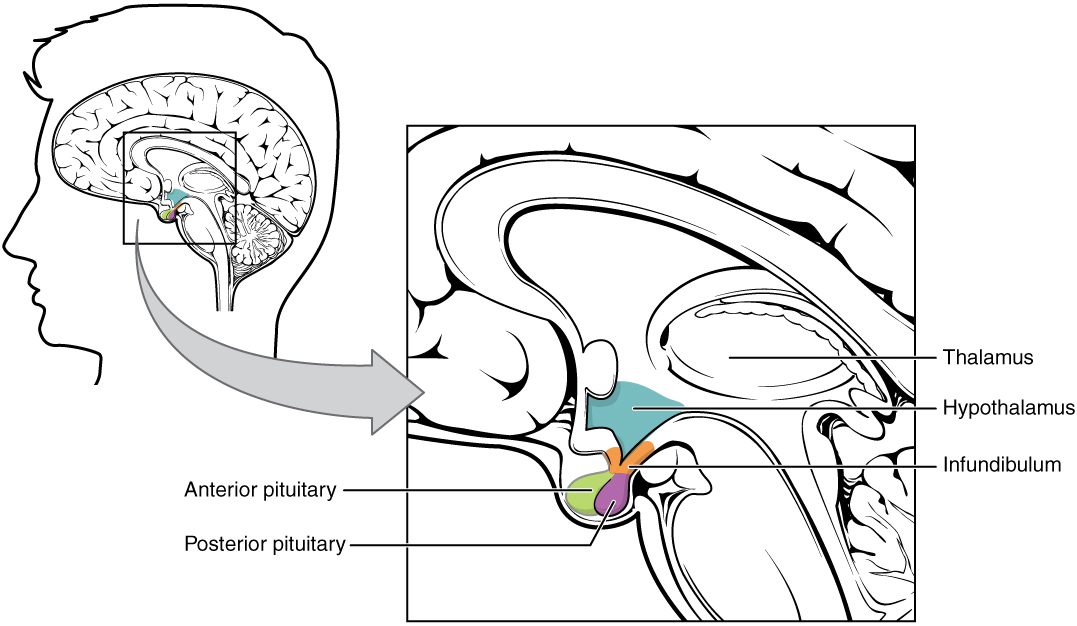
Anterior Lobe
The anterior pituitary is the lobe is at the front of the pituitary gland. It synthesizes and releases hormones into the blood. Table 9.4.1 shows some of the endocrine hormones released by the anterior pituitary, including their targets and effects.
Table 9.4.1
Endocrine Hormones Released by the Anterior Pituitary, and Their Targets and Effects.
| Anterior Pituitary Hormone | Target | Effect |
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | Adrenal glands | Stimulates the cortex of each adrenal gland to secrete its hormones. |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) | Thyroid gland | Stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete thyroid hormone. |
| Growth hormone (GH) | Body cells | Stimulates body cells to synthesize proteins and grow. |
| Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) | Ovaries, testes | Stimulates the ovaries to develop mature eggs. stimulates the testes to produce sperm. |
| Luteinizing hormone (LH) | Ovaries, testes | Stimulates the ovaries and testes to secrete sex hormones; stimulates the ovaries to release eggs. |
| Prolactin (PRL) | Mammary glands | Stimulates the mammary glands to produce milk. |
The anterior pituitary gland is regulated mainly by hormones from the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus secretes hormones (called releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones) that travel through capillaries directly to the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The hormones stimulate the anterior pituitary to either release or stop releasing particular pituitary hormones. Several of these hypothalamic hormones and their effects on the anterior pituitary are shown in the table below.
Table 9.4.2
Hypothalamic Hormones and Their Effects on the Anterior Pituitary
| Hypothalamic Hormone | Effect on Anterior Pituitary |
| Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) | Release of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) |
| Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) | Release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) |
| Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) | Release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) |
| Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) | Release of growth hormone (GH) |
| Growth hormone inhibiting hormone (GHIH) (Somatostatin) | Stopping of growth hormone release |
| Prolactin releasing hormone (PRH) | Release of prolactin |
| Prolactin inhibiting hormone (PIH) (Dopamine) | Stopping of prolactin release |
Posterior Lobe
The posterior pituitary is the lobe is at the back of the pituitary gland. This lobe does not synthesize any hormones. Instead, the posterior lobe stores hormones that come from the hypothalamus along the axons of nerves connecting the two structures (also shown in Figure 9.4.2). The posterior pituitary then secretes the hormones into the bloodstream as needed. Hypothalamic hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary include vasopressin and oxytocin.
- Vasopressin (also called antidiuretic hormone, or ADH) helps maintain homeostasis in body water. It stimulates the kidneys to conserve water by producing more concentrated urine. Specifically, vasopressin targets ducts in the kidneys and makes them more permeable to water. This allows more water to be resorbed by the body, rather than excreted in urine.
- Oxytocin (OXY) targets cells in the uterus to stimulate uterine contractions, as in childbirth. It also targets cells in the breasts of a nursing mother to stimulate the letdown of milk.
9.4 Summary
- The pituitary gland is the master gland of the endocrine system, because most of its hormones control other endocrine glands.
- The pituitary gland is at the base of the brain, where it is connected to the hypothalamus by nerves and capillaries. It has an anterior (front) lobe that synthesizes and secretes pituitary hormones and a posterior (back) lobe that stores and secretes hormones from the hypothalamus.
- Hormones synthesized and secreted by the anterior pituitary include growth hormone, which stimulates cell growth throughout the body, and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete its hormones.
- Hypothalamic hormones stored and secreted by the posterior pituitary gland include vasopressin, which helps maintain homeostasis in body water, and oxytocin, which stimulates uterine contractions during birth, as well as the letdown of milk during lactation.
9.4 Review Questions
-
-
- Explain why the pituitary gland is called the master gland of the endocrine system.
- Compare and contrast the two lobes of the pituitary gland and their general functions.
- Identify two hormones released by the anterior pituitary, their targets, and their effects.
- Explain how the hypothalamus influences the output of hormones by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
- Name and give the function of two hypothalamic hormones released by the posterior pituitary gland.
- Answer the following questions about prolactin releasing hormone (PRH) and prolactin inhibiting hormone (PIH).
- Where are these hormones produced?
- Where are their target cells located?
- What are their effects on their target cells?
- What are their ultimate effects on milk production? Explain your answer.
- When a baby nurses, which of these hormones is most likely released in the mother? Explain your answer.
- For each of the following hormones, state whether it is synthesized in the pituitary or the hypothalamus.
- gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
- growth hormone (GH)
- oxytocin
- adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
9.4 Explore More
Common Pituitary Diseases, Swedish, 2012.
Diagnosing and Treating Pituitary Tumors – California Center for Pituitary Disorders at UCSF, UCSF Neurosurgery, 2015.
Attributions
Figure 9.4.1
Breastfeeding by Petr Kratochvil on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC0 1.0 Universal
Public Domain Dedication (https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en) license.
Figure 9.4.2
The_Hypothalamus-Pituitary_Complex by OpenStax College on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
References
Betts, J. G., Young, K.A., Wise, J.A., Johnson, E., Poe, B., Kruse, D.H., Korol, O., Johnson, J.E., Womble, M., DeSaix, P. (2013, June 19). Figure 17.7 Hypothalamus–pituitary complex [digital image]. In Anatomy and Physiology (Section 17.3). OpenStax. https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/17-3-the-pituitary-gland-and-hypothalamus
Swedish. (2012, April 19). Common pituitary diseases. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jUKQFkmBuww&feature=youtu.be
UCSF Neurosurgery. (2015, May 13). Diagnosing and treating pituitary tumors – California Center for Pituitary Disorders at UCSF. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v41AJGP-XmI&feature=youtu.be
Created by CK-12 Foundation/Adapted by Christine Miller
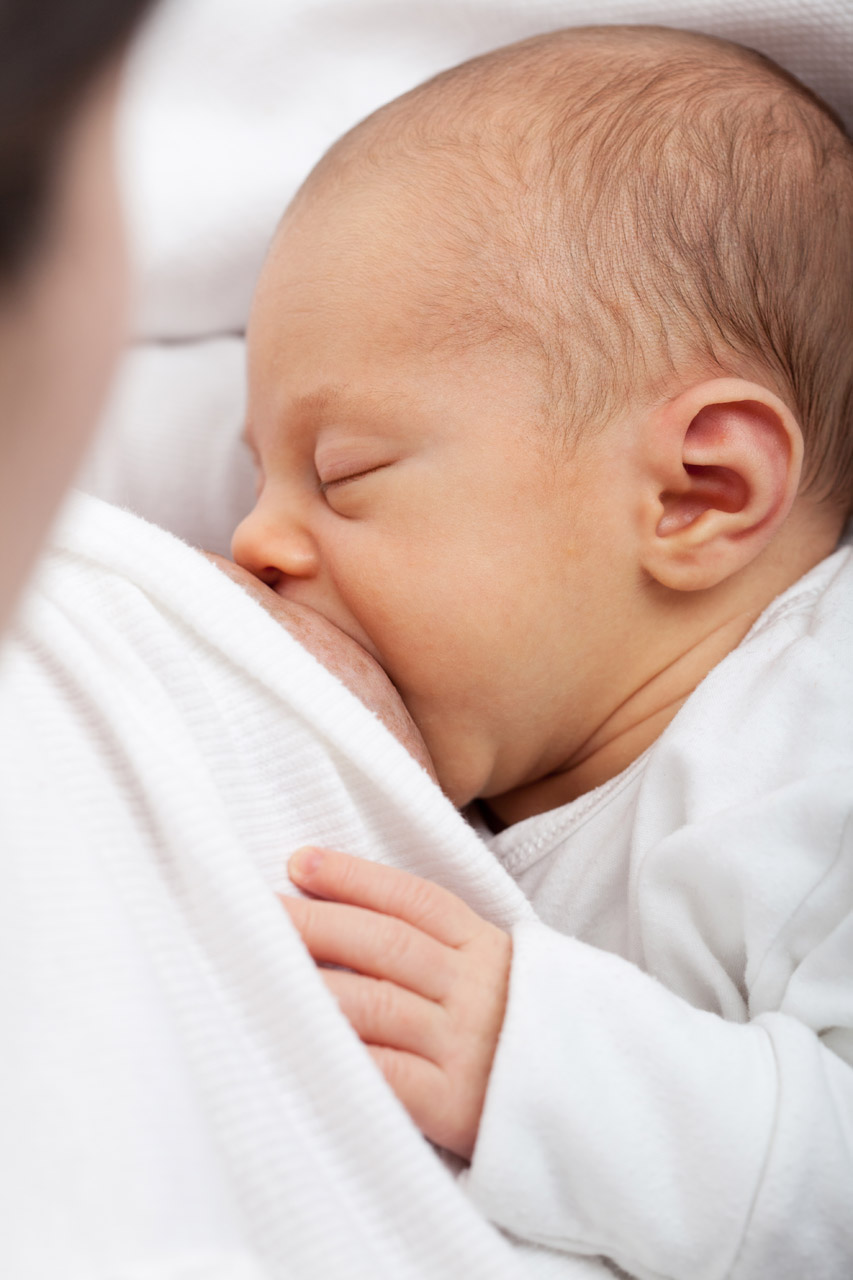

Milk on Demand
This adorable nursing infant (Figure 9.4.1) is part of a positive feedback loop. When he suckles on the nipple, it sends nerve impulses to his mother’s hypothalamus. Those nerve impulses “tell” her pituitary gland to release the hormone prolactin into her bloodstream. Prolactin travels to the mammary glands in the breasts and stimulates milk production, which motivates the infant to keep suckling.
What Is the Pituitary Gland?
The pituitary gland is the master gland of the endocrine system, which is the system of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Endocrine hormones control virtually all physiological processes. They control growth, sexual maturation, reproduction, body temperature, blood pressure, and metabolism. The pituitary gland is considered the master gland of the endocrine system, because it controls the rest of the endocrine system. Many pituitary hormones either promote or inhibit hormone secretion by other endocrine glands.
Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland is about the size of a pea. It protrudes from the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the inner brain (see Figure 9.4.2). The pituitary is connected to the hypothalamus by a thin stalk (called the infundibulum). Blood vessels and nerves in the stalk allow direct connections between the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
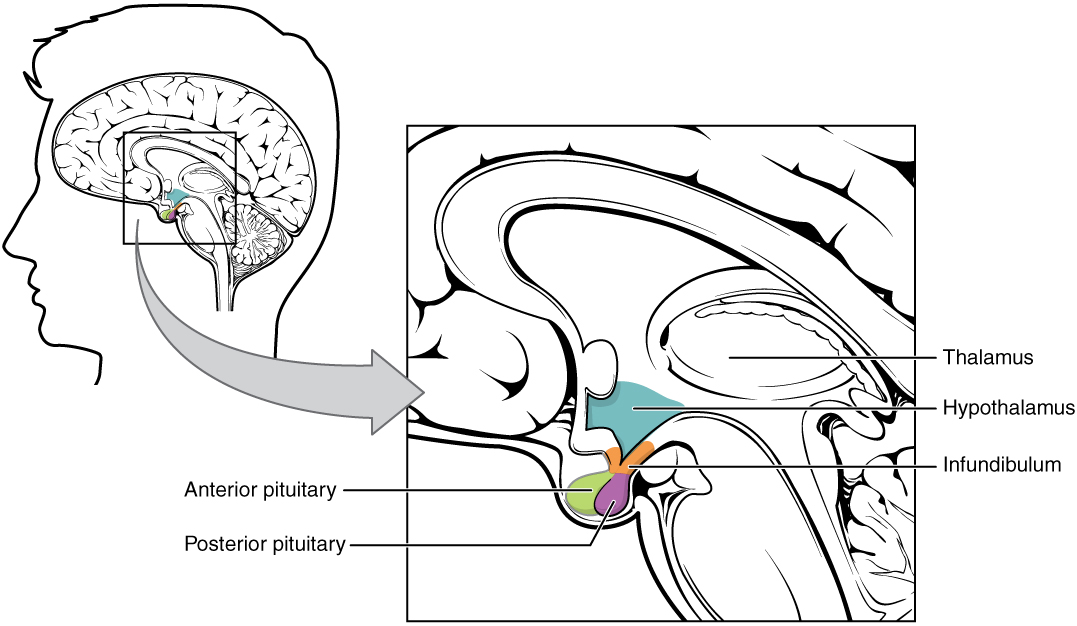
Anterior Lobe
The anterior pituitary is the lobe is at the front of the pituitary gland. It synthesizes and releases hormones into the blood. Table 9.4.1 shows some of the endocrine hormones released by the anterior pituitary, including their targets and effects.
Table 9.4.1
Endocrine Hormones Released by the Anterior Pituitary, and Their Targets and Effects.
| Anterior Pituitary Hormone | Target | Effect |
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | Adrenal glands | Stimulates the cortex of each adrenal gland to secrete its hormones. |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) | Thyroid gland | Stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete thyroid hormone. |
| Growth hormone (GH) | Body cells | Stimulates body cells to synthesize proteins and grow. |
| Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) | Ovaries, testes | Stimulates the ovaries to develop mature eggs. stimulates the testes to produce sperm. |
| Luteinizing hormone (LH) | Ovaries, testes | Stimulates the ovaries and testes to secrete sex hormones; stimulates the ovaries to release eggs. |
| Prolactin (PRL) | Mammary glands | Stimulates the mammary glands to produce milk. |
The anterior pituitary gland is regulated mainly by hormones from the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus secretes hormones (called releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones) that travel through capillaries directly to the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. The hormones stimulate the anterior pituitary to either release or stop releasing particular pituitary hormones. Several of these hypothalamic hormones and their effects on the anterior pituitary are shown in the table below.
Table 9.4.2
Hypothalamic Hormones and Their Effects on the Anterior Pituitary
| Hypothalamic Hormone | Effect on Anterior Pituitary |
| Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) | Release of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) |
| Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) | Release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) |
| Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) | Release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) |
| Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) | Release of growth hormone (GH) |
| Growth hormone inhibiting hormone (GHIH) (Somatostatin) | Stopping of growth hormone release |
| Prolactin releasing hormone (PRH) | Release of prolactin |
| Prolactin inhibiting hormone (PIH) (Dopamine) | Stopping of prolactin release |
Posterior Lobe
The posterior pituitary is the lobe is at the back of the pituitary gland. This lobe does not synthesize any hormones. Instead, the posterior lobe stores hormones that come from the hypothalamus along the axons of nerves connecting the two structures (also shown in Figure 9.4.2). The posterior pituitary then secretes the hormones into the bloodstream as needed. Hypothalamic hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary include vasopressin and oxytocin.
- Vasopressin (also called antidiuretic hormone, or ADH) helps maintain homeostasis in body water. It stimulates the kidneys to conserve water by producing more concentrated urine. Specifically, vasopressin targets ducts in the kidneys and makes them more permeable to water. This allows more water to be resorbed by the body, rather than excreted in urine.
- Oxytocin (OXY) targets cells in the uterus to stimulate uterine contractions, as in childbirth. It also targets cells in the breasts of a nursing mother to stimulate the letdown of milk.
9.4 Summary
- The pituitary gland is the master gland of the endocrine system, because most of its hormones control other endocrine glands.
- The pituitary gland is at the base of the brain, where it is connected to the hypothalamus by nerves and capillaries. It has an anterior (front) lobe that synthesizes and secretes pituitary hormones and a posterior (back) lobe that stores and secretes hormones from the hypothalamus.
- Hormones synthesized and secreted by the anterior pituitary include growth hormone, which stimulates cell growth throughout the body, and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete its hormones.
- Hypothalamic hormones stored and secreted by the posterior pituitary gland include vasopressin, which helps maintain homeostasis in body water, and oxytocin, which stimulates uterine contractions during birth, as well as the letdown of milk during lactation.
9.4 Review Questions
-
-
- Explain why the pituitary gland is called the master gland of the endocrine system.
- Compare and contrast the two lobes of the pituitary gland and their general functions.
- Identify two hormones released by the anterior pituitary, their targets, and their effects.
- Explain how the hypothalamus influences the output of hormones by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
- Name and give the function of two hypothalamic hormones released by the posterior pituitary gland.
- Answer the following questions about prolactin releasing hormone (PRH) and prolactin inhibiting hormone (PIH).
- Where are these hormones produced?
- Where are their target cells located?
- What are their effects on their target cells?
- What are their ultimate effects on milk production? Explain your answer.
- When a baby nurses, which of these hormones is most likely released in the mother? Explain your answer.
- For each of the following hormones, state whether it is synthesized in the pituitary or the hypothalamus.
- gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
- growth hormone (GH)
- oxytocin
- adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
9.4 Explore More
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jUKQFkmBuww&feature=emb_logo
Common Pituitary Diseases, Swedish, 2012.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v41AJGP-XmI&feature=emb_logo
Diagnosing and Treating Pituitary Tumors - California Center for Pituitary Disorders at UCSF, UCSF Neurosurgery, 2015.
Attributions
Figure 9.4.1
Breastfeeding by Petr Kratochvil on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC0 1.0 Universal
Public Domain Dedication (https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en) license.
Figure 9.4.2
The_Hypothalamus-Pituitary_Complex by OpenStax College on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0) license.
References
Betts, J. G., Young, K.A., Wise, J.A., Johnson, E., Poe, B., Kruse, D.H., Korol, O., Johnson, J.E., Womble, M., DeSaix, P. (2013, June 19). Figure 17.7 Hypothalamus–pituitary complex [digital image]. In Anatomy and Physiology (Section 17.3). OpenStax. https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/17-3-the-pituitary-gland-and-hypothalamus
Swedish. (2012, April 19). Common pituitary diseases. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jUKQFkmBuww&feature=youtu.be
UCSF Neurosurgery. (2015, May 13). Diagnosing and treating pituitary tumors - California Center for Pituitary Disorders at UCSF. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v41AJGP-XmI&feature=youtu.be
The shape formed by two parallel lines that twist around each other.
Created by: CK-12/Adapted by Christine Miller

Oh, the Agony!
Wearing braces can be very uncomfortable, but it is usually worth it. Braces and other orthodontic treatments can re-align the teeth and jaws to improve bite and appearance. Braces can change the position of the teeth and the shape of the jaws because the human body is malleable. Many phenotypic traits — even those that have a strong genetic basis — can be molded by the environment. Changing the phenotype in response to the environment is just one of several ways we respond to environmental stress.
Types of Responses to Environmental Stress
There are four different types of responses that humans may make to cope with environmental stress:
- Adaptation
- Developmental adjustment
- Acclimatization
- Cultural responses
The first three types of responses are biological in nature, and the fourth type is cultural. Only adaptation involves genetic change and occurs at the level of the population or species. The other three responses do not require genetic change, and they occur at the individual level.
Adaptation
An adaptation is a genetically-based trait that has evolved because it helps living things survive and reproduce in a given environment. Adaptations generally evolve in a population over many generations in response to stresses that last for a long period of time. Adaptations come about through natural selection. Those individuals who inherit a trait that confers an advantage in coping with an environmental stress are likely to live longer and reproduce more. As a result, more of their genes pass on to the next generation. Over many generations, the genes and the trait they control become more frequent in the population.
A Classic Example: Hemoglobin S and Malaria
Probably the most frequently-cited example of a genetic adaptation to an environmental stress is sickle cell trait. As you read in the previous section, people with sickle cell trait have one abnormal allele (S) and one normal allele (A) for hemoglobin, the red blood cell protein that carries oxygen in the blood. Sickle cell trait is an adaptation to the environmental stress of malaria, because people with the trait have resistance to this parasitic disease. In areas where malaria is endemic (present year-round), the sickle cell trait and its allele have evolved to relatively high frequencies. It is a classic example of natural selection favoring heterozygotes for a gene with two alleles. This type of selection keeps both alleles at relatively high frequencies in a population.
To Taste or Not to Taste
Another example of an adaptation in humans is the ability to taste bitter compounds. Plants produce a variety of toxic compounds in order to protect themselves from being eaten, and these toxic compounds often have a bitter taste. The ability to taste bitter compounds is thought to have evolved as an adaptation, because it prevented people from eating poisonous plants. Humans have many different genes that code for bitter taste receptors, allowing us to taste a wide variety of bitter compounds.
A harmless bitter compound called phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) is not found naturally in plants, but it is similar to toxic bitter compounds that are found in plants. Humans' ability to taste this harmless substance has been tested in many different populations. In virtually every population studied, there are some people who can taste PTC (called tasters), and some people who cannot taste PTC, (called nontasters). The ratio of tasters to non-tasters varies among populations, but on average, 75 per cent of people can taste PTC and 25 per cent cannot.
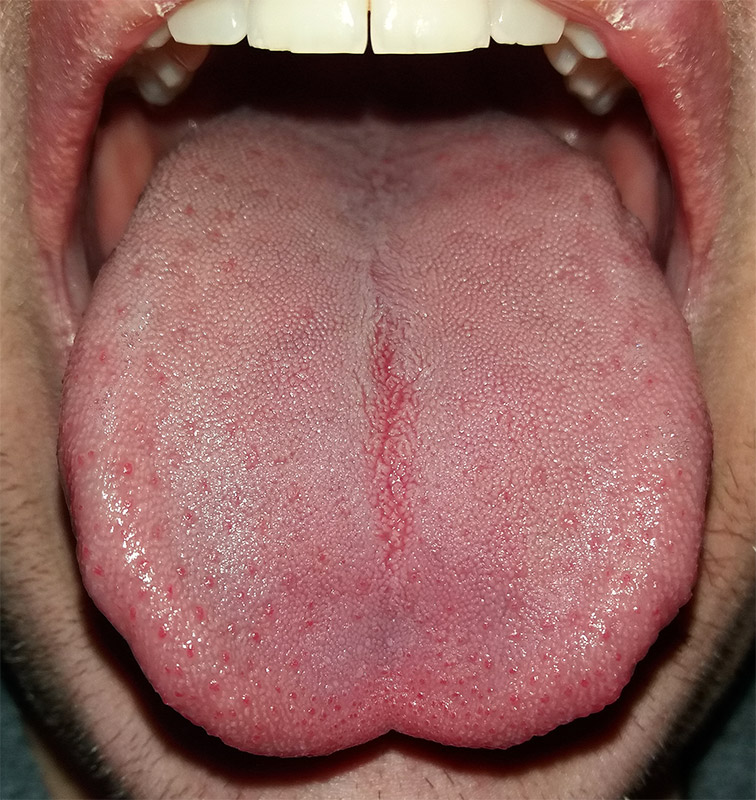
Like many scientific discoveries, human variation in PTC-taster status was discovered by chance. Around 1930, a chemist named Arthur Fox was working with powdered PTC in his lab. Some of the powder accidentally blew into the air. Another lab worker noticed that the powdered PTC tasted bitter, but Fox couldn't detect any taste at all. Fox wondered how to explain this difference in PTC-tasting ability. Geneticists soon determined that PTC-taster status is controlled by a single gene with two common alleles, usually represented by the letters T and t. The T allele encodes a chemical receptor protein (found in taste buds on the tongue, as illustrated in Figure 6.4.2) that can strongly bind to PTC. The other allele, t, encodes a version of the receptor protein that cannot bind as strongly to PTC. The particular combination of these two alleles that a person inherits determines whether the person finds PTC to taste very bitter (TT), somewhat bitter (Tt), or not bitter at all (tt).
If the ability to taste bitter compounds is advantageous, why does every human population studied contain a significant percentage of people who are nontasters? Why has the nontasting allele been preserved in human populations at all? Some scientists hypothesize that the nontaster allele actually confers the ability to taste some other, yet-to-be identified, bitter compound in plants. People who inherit both alleles would presumably be able to taste a wider range of bitter compounds, so they would have the greatest ability to avoid plant toxins. In other words, the heterozygote genotype for the taster gene would be the most fit and favored by natural selection.
Most people no longer have to worry whether the plants they eat contain toxins. The produce you grow in your garden or buy at the supermarket consists of known varieties that are safe to eat. However, natural selection may still be at work in human populations for the PTC-taster gene, because PTC tasters may be more sensitive than nontasters to bitter compounds in tobacco and vegetables in the cabbage family (that is, cruciferous vegetables, such as the broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage pictured in Figure 6.4.3).
- People who find PTC to taste very bitter are less likely to smoke tobacco, presumably because tobacco smoke has a stronger bitter taste to these individuals. In this case, selection would favor taster genotypes, because tasters would be more likely to avoid smoking and its serious health risks.
- Strong tasters find cruciferous vegetables to taste bitter. As a result, they may avoid eating these vegetables (and perhaps other foods, as well), presumably resulting in a diet that is less varied and nutritious. In this scenario, natural selection might work against taster genotypes.
Figure 6.4.3 Cruciferous vegetables.
Developmental Adjustment
It takes a relatively long time for genetic change in response to environmental stress to produce a population with adaptations. Fortunately, we can adjust to some environmental stresses more quickly by changing in nongenetic ways. One type of nongenetic response to stress is developmental adjustment. This refers to phenotypic change that occurs during development in infancy or childhood, and that may persist into adulthood. This type of change may be irreversible by adulthood.
Phenotypic Plasticity
Developmental adjustment is possible because humans have a high degree of phenotypic plasticity, which is the ability to alter the phenotype in response to changes in the environment. Phenotypic plasticity allows us to respond to changes that occur within our lifetime, and it is particularly important for species (like our own) that have a long generation time. With long generations, evolution of genetic adaptations may occur too slowly to keep up with changing environmental stresses.
Developmental Adjustment and Cultural Practices
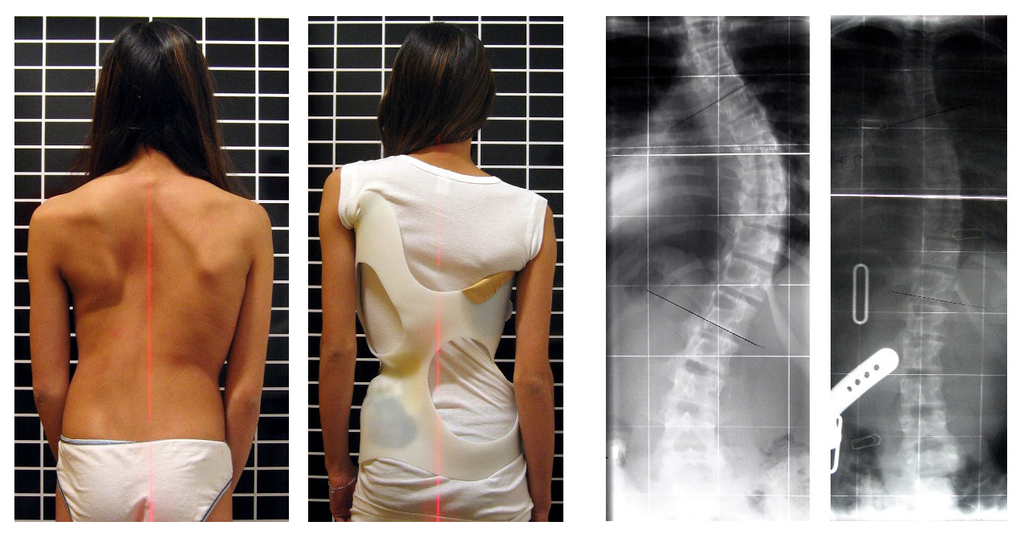
Developmental adjustment may be the result of naturally occurring environmental stresses or cultural practices, including medical or dental treatments. Like our example at the beginning of this section, using braces to change the shape of the jaw and the position of the teeth is an example of a dental practice that brings about a developmental adjustment. Another example of developmental adjustment is the use of a back brace to treat scoliosis (see images in Figure 6.4.4). Scoliosis is an abnormal curvature from side to side in the spine. If the problem is not too severe, a brace, if worn correctly, should prevent the curvature from worsening as a child grows, although it cannot straighten a curve that is already present. Surgery may be required to do that.
Developmental Adjustment and Nutritional Stress
An important example of developmental adjustment that results from a naturally occurring environmental stress is the cessation of physical growth that occurs in children who are under nutritional stress. Children who lack adequate food to fuel both growth and basic metabolic processes are likely to slow down in their growth rate — or even to stop growing entirely. Shunting all available calories and nutrients into essential life functions may keep the child alive at the expense of increasing body size.
Table 6.4.1 shows the effects of inadequate diet on children's' growth in several countries worldwide. For each country, the table gives the prevalence of stunting in children under the age of five. Children are considered stunted if their height is at least two standard deviations below the median height for their age in an international reference population.
Table 6.4.1
Percentage of Stunting in Young Children in Selected Countries (2011-2015)
| Percentage of Stunting in Young Children in Selected Countries (2011-2015) | |
| Country | Per cent of Children Under Age 5 with Stunting |
| United States | 2.1 |
| Turkey | 9.5 |
| Mexico | 13.6 |
| Thailand | 16.3 |
| Iraq | 22.6 |
| Philippines | 33.6 |
| Pakistan | 45.0 |
| Papua New Guinea | 49.5 |
After a growth slow-down occurs and if adequate food becomes available, a child may be able to make up the loss of growth. If food is plentiful, the child may grow more rapidly than normal until the original, genetically-determined growth trajectory is reached. If the inadequate diet persists, however, the failure of growth may become chronic, and the child may never reach his or her full potential adult size.
Phenotypic plasticity of body size in response to dietary change has been observed in successive generations within populations. For example, children in Japan were taller, on average, in each successive generation after the end of World War II. Boys aged 14-15 years old in 1986 were an average of about 18 cm (7 in.) taller than boys of the same age in 1959, a generation earlier. This is a highly significant difference, and it occurred too quickly to be accounted for by genetic change. Instead, the increase in height is a developmental adjustment, thought to be largely attributable to changes in the Japanese diet since World War II. During this period, there was an increase in the amount of animal protein and fat, as well as in the total calories consumed.
Acclimatization
Other responses to environmental stress are reversible and not permanent, whether they occur in childhood or adulthood. The development of reversible changes to environmental stress is called acclimatization. Acclimatization generally develops over a relatively short period of time. It may take just a few days or weeks to attain a maximum response to a stress. When the stress is no longer present, the acclimatized state declines, and the body returns to its normal baseline state. Generally, the shorter the time for acclimatization to occur, the more quickly the condition is reversed when the environmental stress is removed.
Acclimatization to UV Light
A common example of acclimatization is tanning of the skin (see Figure 6.4.5). This occurs in many people in response to exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Special pigment cells in the skin, called melanocytes, produce more of the brown pigment melanin when exposed to sunlight. The melanin collects near the surface of the skin where it absorbs UV radiation so it cannot penetrate and potentially damage deeper skin structures. Tanning is a reversible change in the phenotype that helps the body deal temporarily with the environmental stress of high levels of UV radiation. When the skin is no longer exposed to the sun’s rays, the tan fades, generally over a period of a few weeks or months.
Figure 6.4.5 Tanning of the skin occurs in many people in response to exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
Acclimatization to Heat
Another common example of acclimatization occurs in response to heat. Changes that occur with heat acclimatization include increased sweat output and earlier onset of sweat production, which helps the body stay cool because evaporation of sweat takes heat from the body’s surface in a process called evaporative cooling. It generally takes a couple of weeks for maximum heat acclimatization to come about by gradually working out harder and longer at high air temperatures. The changes that occur with acclimatization just as quickly subside when the body is no longer exposed to excessive heat.
Acclimatization to High Altitude
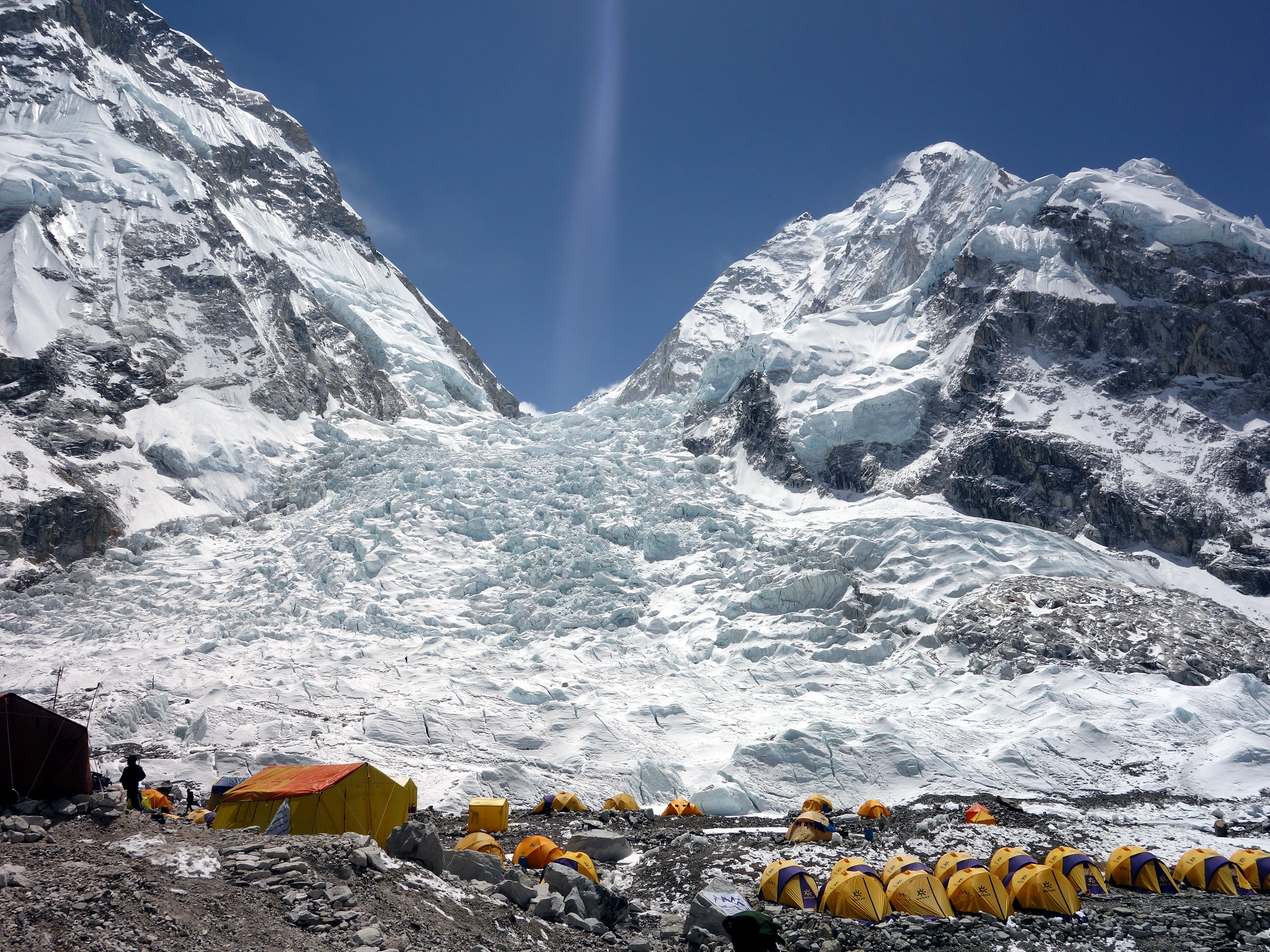

Short term acclimatization to high altitude occurs as a response to low levels of oxygen in the blood. This reduced level of oxygen is detected by carotid bodies, which will trigger in increase in breathing and heart rate. Over a period of weeks the body will compensate by increasing red blood cell production, thereby improving the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. This is why mountaineers wishing to climb to the peak of Mount Everest must complete the full climb in portions; it is recommended that climbers spend 2-3 days acclimatizing for every 600 metres of elevation increase. In addition, the higher to altitude, the longer it make take to acclimatize; climbers are advised to spend 4-5 days acclimatizing at base camp (whether the base camp in Nepal or China) before completing the final leg of the climb to the peak. The concentration of red blood cells gradually decreases to normal levels once a climber returns to their normal elevation.
Cultural Responses
More than any other species, humans respond to environmental stresses with learned behaviors and technology. These cultural responses allow us to change our environments to control stresses, rather than changing our bodies genetically or physiologically to cope with the stresses. Even archaic humans responded to some environmental stresses in this way. For example, Neanderthals used shelters, fires, and animal hides as clothing to stay warm in the cold climate in Europe during the last ice age. Today, we use more sophisticated technologies to stay warm in cold climates while retaining our essentially tropical-animal anatomy and physiology. We also use technology (such as furnaces and air conditioners) to avoid temperature stress and stay comfortable in hot or cold climates.
6.4 Summary
- Humans may respond to environmental stress in four different ways: adaptation, developmental adjustment, acclimatization, and cultural responses.
- An adaptation is a genetically based trait that has evolved because it helps living things survive and reproduce in a given environment. Adaptations evolve by natural selection in populations over a relatively long period to time. Examples of adaptations include sickle cell trait as an adaptation to the stress of endemic malaria and the ability to taste bitter compounds as an adaptation to the stress of bitter-tasting toxins in plants.
- A developmental adjustment is a non-genetic response to stress that occurs during infancy or childhood, and that may persist into adulthood. This type of change may be irreversible. Developmental adjustment is possible because humans have a high degree of phenotypic plasticity. It may be the result of environmental stresses (such as inadequate food), which may stunt growth, or cultural practices (such as orthodontic treatments), which re-align the teeth and jaws.
- Acclimatization is the development of reversible changes to environmental stress that develop over a relatively short period of time. The changes revert to the normal baseline state after the stress is removed. Examples of acclimatization include tanning of the skin and physiological changes (such as increased sweating) that occur with heat acclimatization.
- More than any other species, humans respond to environmental stress with learned behaviors and technology, which are cultural responses. These responses allow us to change our environment to control stress, rather than changing our bodies genetically or physiologically to cope with stress. Examples include using shelter, fire, and clothing to cope with a cold climate.
6.4 Review Questions
- List four different types of responses that humans may make to cope with environmental stress.
- Define adaptation.
-
- Explain how natural selection may have resulted in most human populations having people who can and people who cannot taste PTC.
- What is a developmental adjustment?
- Define phenotypic plasticity.
- Explain why phenotypic plasticity may be particularly important in a species with a long generation time.
- Why may stunting of growth occur in children who have an inadequate diet? Why is stunting preferable to the alternative?
- What is acclimatization?
- How does acclimatization to heat come about, and what are two physiological changes that occur in heat acclimatization?
- Give an example of a cultural response to heat stress.
- Which is more likely to be reversible — a change due to acclimatization, or a change due to developmental adjustment? Explain your answer.
6.4 Explore More
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upp9-w6GPhU
Could we survive prolonged space travel? - Lisa Nip, TED-Ed, 2016.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hRnrIpUMyZQ&t=182s
How this disease changes the shape of your cells - Amber M. Yates, TED-Ed, 2019.
Attributions
Figure 6.4.1
Free_Awesome_Girl_With_Braces_Close_Up by D. Sharon Pruitt from Hill Air Force Base, Utah, USA on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/deed.en) license.
Figure 6.4.2
Tongue by Mahdiabbasinv on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en) license.
Figure 6.4.3
- White cauliflower on brown wooden chopping board by Louis Hansel @shotsoflouis on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
- Broccoli on wooden chopping board by Louis Hansel @shotsoflouis on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
- Green cabbage close up by Craig Dimmick on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
- Cabbage hybrid/ brussel sprouts by Solstice Hannan on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
- Kale by Laura Johnston on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
- Tiny bok choy at the Asian market by Jodie Morgan on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License (https://unsplash.com/license).
Figure 6.4.4
Scoliosis_patient_in_cheneau_brace_correcting_from_56_to_27_deg by Weiss H.R. from Scoliosis Journal/BioMed Central Ltd. on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0) license.
Figure 6.4.5
- Tan Lines by k.steudel on Flickr is used under a CC BY 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/) license.
- Twin tan lines (all sizes) by Quinn Dombrowski on Flickr is used under a CC BY-SA 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/) license.
- Wedding ring tan line by Quinn Dombrowski on Flickr is used under a CC BY-SA 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/) license.
- Tan by Evil Erin on Flickr is used under a CC BY 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/) license.
Figure 6.4.6
Nepalese base camp by Mark Horrell on Flickr is used under a CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/) license.
References
TED-Ed. (2016, October 4). Could we survive prolonged space travel? - Lisa Nip. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upp9-w6GPhU&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2019, May 6). How this disease changes the shape of your cells - Amber M. Yates. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hRnrIpUMyZQ&feature=youtu.be
Weiss, H. (2007). Is there a body of evidence for the treatment of patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS)? [Figure 2 - digital photograph], Scoliosis, 2(19). https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-7161-2-19
Created by: CK-12/Adapted by Christine Miller
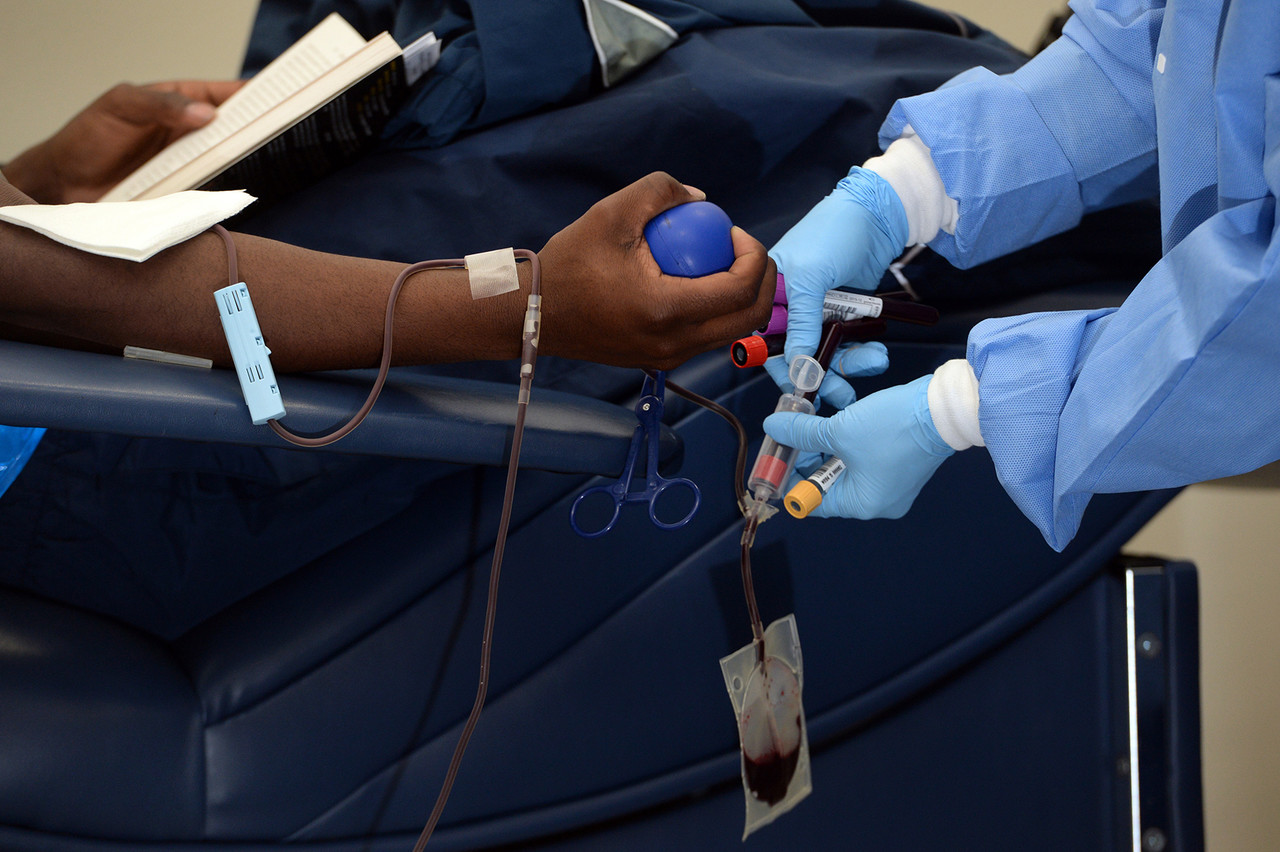
Giving the Gift of Life
Did you ever donate blood? If you did, then you probably know that your blood type is an important factor in blood transfusions. People vary in the type of blood they inherit, and this determines which type(s) of blood they can safely receive in a transfusion. Do you know your blood type?
What Are Blood Types?
Blood is composed of cells suspended in a liquid called plasma. There are three types of cells in blood: red blood cells, which carry oxygen; white blood cells, which fight infections and other threats; and platelets, which are cell fragments that help blood clot. Blood type (or blood group) is a genetic characteristic associated with the presence or absence of certain molecules, called antigens, on the surface of red blood cells. These molecules may help maintain the integrity of the cell membrane, act as receptors, or have other biological functions. A blood group system refers to all of the gene(s), alleles, and possible genotypes and phenotypes that exist for a particular set of blood type antigens. Human blood group systems include the well-known ABO and Rhesus (Rh) systems, as well as at least 33 others that are less well known.
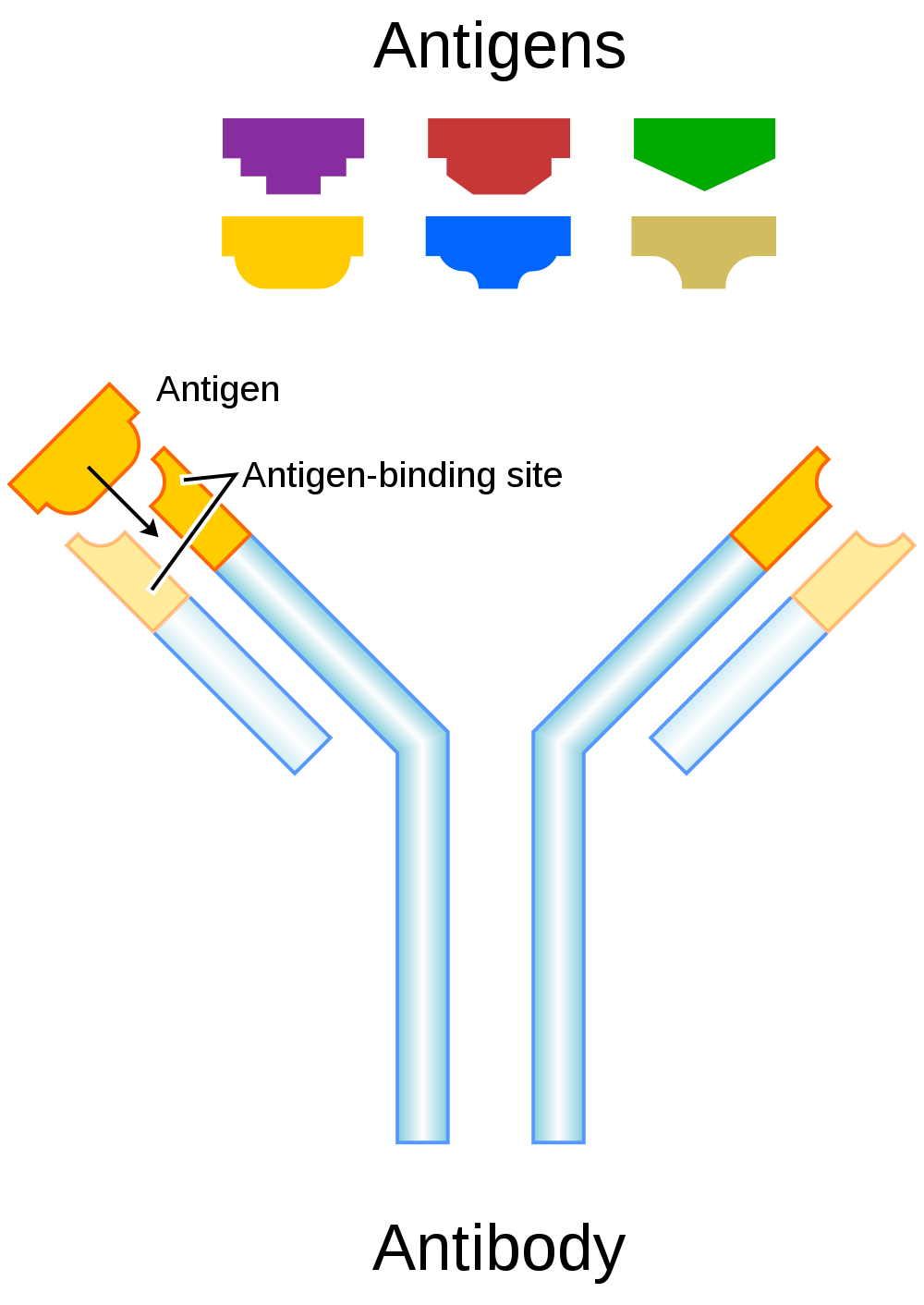
Antigens and Antibodies
Antigens — such as those on the red blood cells — are molecules that the immune system identifies as either self (produced by your own body) or non-self (not produced by your own body). Blood group antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins (proteins attached to chains of sugars), or glycolipids (lipids attached to chains of sugars), depending on the particular blood group system. If antigens are identified as non-self, the immune system responds by forming antibodies that are specific to the non-self antigens. Antibodies are large, Y-shaped proteins produced by the immune system that recognize and bind to non-self antigens. The analogy of a lock and key is often used to represent how an antibody and antigen fit together, as shown in the illustration below (Figure 6.5.2). When antibodies bind to antigens, it marks them for destruction by other immune system cells. Non-self antigens may enter your body on pathogens (such as bacteria or viruses), on foods, or on red blood cells in a blood transfusion from someone with a different blood type than your own. The last way is virtually impossible nowadays because of effective blood typing and screening protocols.
Genetics of Blood Type
An individual’s blood type depends on which alleles for a blood group system were inherited from their parents. Generally, blood type is controlled by alleles for a single gene, or for two or more very closely linked genes. Closely linked genes are almost always inherited together, because there is little or no recombination between them. Like other genetic traits, a person’s blood type is generally fixed for life, but there are rare instances in which blood type can change. This could happen, for example, if an individual receives a bone marrow transplant to treat a disease, such as leukemia. If the bone marrow comes from a donor who has a different blood type, the patient’s blood type may eventually convert to the donor’s blood type, because red blood cells are produced in bone marrow.
ABO Blood Group System
The ABO blood group system is the best known human blood group system. Antigens in this system are glycoproteins. These antigens are shown in the list below. There are four common blood types for the ABO system:
- Type A, in which only the A antigen is present.
- Type B, in which only the B antigen is present.
- Type AB, in which both the A and B antigens are present.
- Type O, in which neither the A nor the B antigen is present.
Genetics of the ABO System
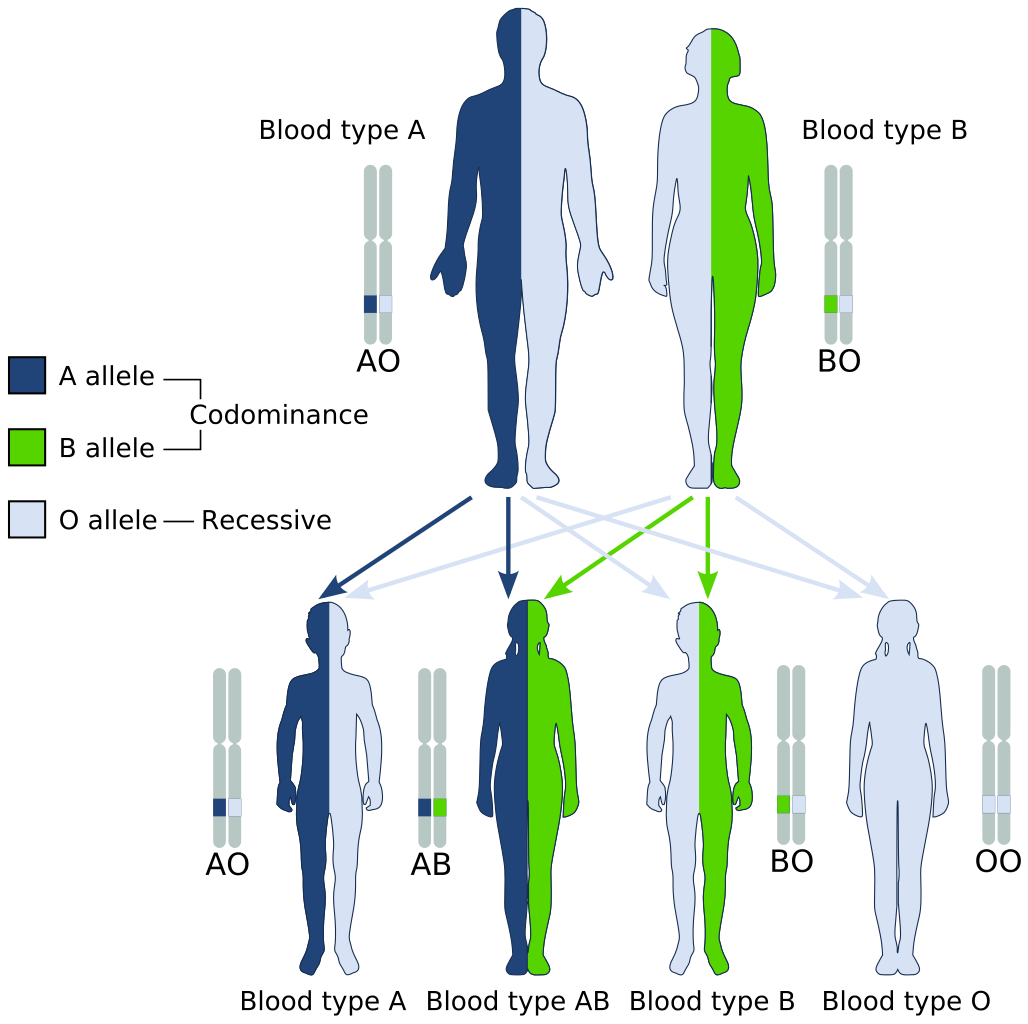
The ABO blood group system is controlled by a single gene on chromosome 9. There are three common alleles for the gene, often represented by the letters A , B , and O. With three alleles, there are six possible genotypes for ABO blood group. Alleles A and B, however, are both dominant to allele O and codominant to each other. This results in just four possible phenotypes (blood types) for the ABO system. These genotypes and phenotypes are shown in Table 6.5.1.
Table 6.5.1
ABO Blood Group System: Genotypes and Phenotypes
| ABO Blood Group System | |
| Genotype | Phenotype (Blood Type, or Group) |
| AA | A |
| AO | A |
| BB | B |
| BO | B |
| OO | O |
| AB | AB |
The diagram below (Figure 6.5.3) shows an example of how ABO blood type is inherited. In this particular example, the father has blood type A (genotype AO) and the mother has blood type B (genotype BO). This mating type can produce children with each of the four possible ABO phenotypes, although in any given family, not all phenotypes may be present in the children.
Medical Significance of ABO Blood Type
The ABO system is the most important blood group system in blood transfusions. If red blood cells containing a particular ABO antigen are transfused into a person who lacks that antigen, the person’s immune system will recognize the antigen on the red blood cells as non-self. Antibodies specific to that antigen will attack the red blood cells, causing them to agglutinate (or clump) and break apart. If a unit of incompatible blood were to be accidentally transfused into a patient, a severe reaction (called acute hemolytic transfusion reaction) is likely to occur, in which many red blood cells are destroyed. This may result in kidney failure, shock, and even death. Fortunately, such medical accidents virtually never occur today.
These antibodies are often spontaneously produced in the first years of life, after exposure to common microorganisms in the environment that have antigens similar to blood antigens. Specifically, a person with type A blood will produce anti-B antibodies, while a person with type B blood will produce anti-A antibodies. A person with type AB blood does not produce either antibody, while a person with type O blood produces both anti-A and anti-B antibodies. Once the antibodies have been produced, they circulate in the plasma. The relationship between ABO red blood cell antigens and plasma antibodies is shown in Figure 6.5.4.
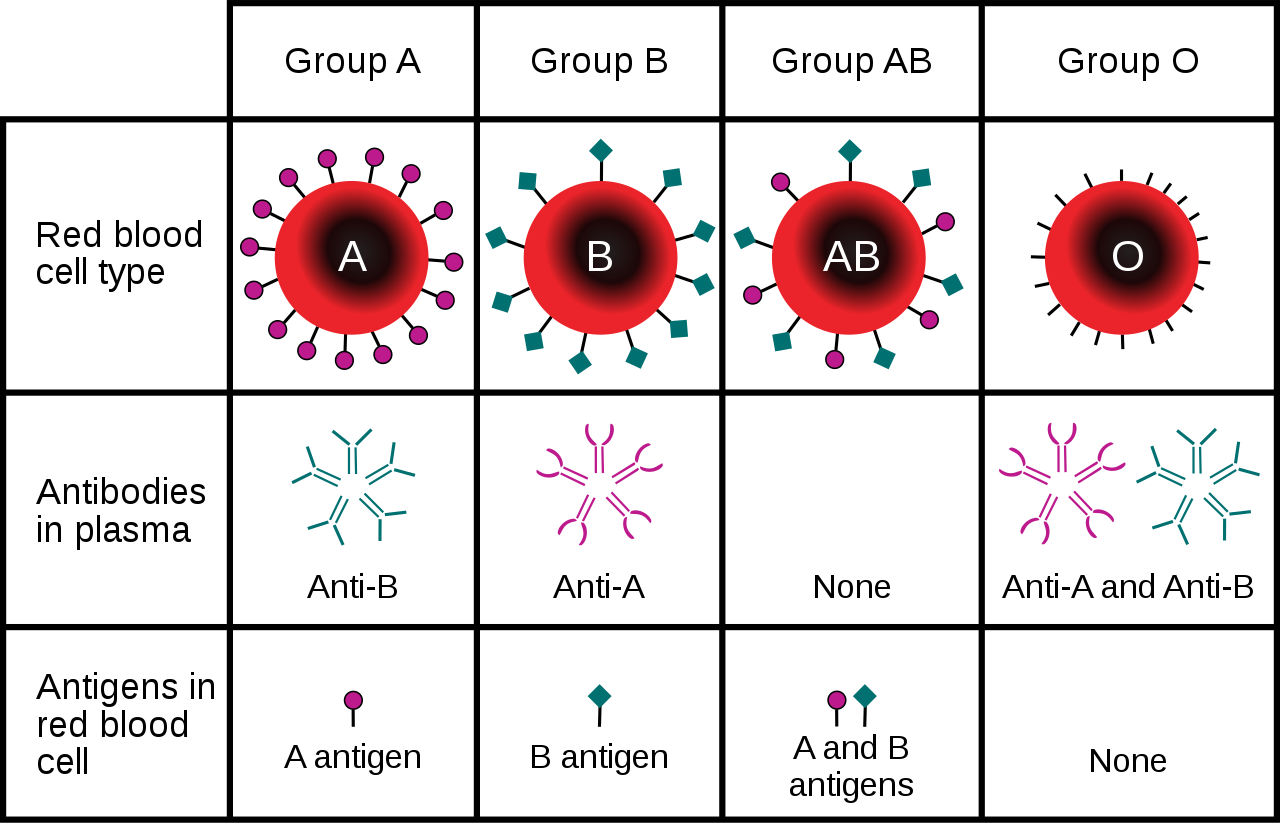
The antibodies that circulate in the plasma are for different antigens than those on red blood cells, which are recognized as self antigens.
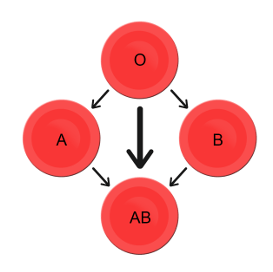
Which blood types are compatible and which are not? Type O blood contains both anti-A and anti-B antibodies, so people with type O blood can only receive type O blood. However, they can donate blood to people of any ABO blood type, which is why individuals with type O blood are called universal donors. Type AB blood contains neither anti-A nor anti-B antibodies, so people with type AB blood can receive blood from people of any ABO blood type. That’s why individuals with type AB blood are called universal recipients. They can donate blood, however, only to people who also have type AB blood. These and other relationships between blood types of donors and recipients are summarized in the simple diagram to the right.
Geographic Distribution of ABO Blood Groups
The frequencies of blood groups for the ABO system vary around the world. You can see how the A and B alleles and the blood group O are distributed geographically on the maps in Figure 6.5.6.
- Worldwide, B is the rarest ABO allele, so type B blood is the least common ABO blood type. Only about 16 per cent of all people have the B allele. Its highest frequency is in Asia. Its lowest frequency is among the indigenous people of Australia and the Americas.
- The A allele is somewhat more common around the world than the B allele, so type A blood is also more common than type B blood. The highest frequencies of the A allele are in Australian Aborigines, the Lapps (Sami) of Northern Scandinavia, and Blackfoot Native Americans in North America. The allele is nearly absent among Native Americans in Central and South America.
- The O allele is the most common ABO allele around the world, and type O blood is the most common ABO blood type. Almost two-thirds of people have at least one copy of the O allele. It is especially common in Native Americans in Central and South America, where it reaches frequencies close to 100 per cent. It also has relatively high frequencies in Australian Aborigines and Western Europeans. Its frequencies are lowest in Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
Figure 6.5.6 Maps of populations that have the A, B and O alleles.
Evolution of the ABO Blood Group System
The geographic distribution of ABO blood type alleles provides indirect evidence for the evolutionary history of these alleles. Evolutionary biologists hypothesize that the allele for blood type A evolved first, followed by the allele for blood type O, and then by the allele for blood type B. This chronology accounts for the percentages of people worldwide with each blood group, and is also consistent with known patterns of early population movements.
The evolutionary forces of founder effect and genetic drift have no doubt played a significant role in the current distribution of ABO blood types worldwide. Geographic variation in ABO blood groups is also likely to be influenced by natural selection, because different blood types are thought to vary in their susceptibility to certain diseases. For example:
- People with type O blood may be more susceptible to cholera and plague. They are also more likely to develop gastrointestinal ulcers.
- People with type A blood may be more susceptible to smallpox and more likely to develop certain cancers.
- People with types A, B, and AB blood appear to be less likely to form blood clots that can cause strokes. However, early in our history, the ability of blood to form clots — which appears greater in people with type O blood — may have been a survival advantage.
- Perhaps the greatest natural selective force associated with ABO blood types is malaria. There is considerable evidence to suggest that people with type O blood are somewhat resistant to malaria, giving them a selective advantage where malaria is endemic.
Rhesus Blood Group System
Another well-known blood group system is the Rhesus (Rh) blood group system. The Rhesus system has dozens of different antigens, but only five main antigens (called D, C, c, E, and e). The major Rhesus antigen is the D antigen. People with the D antigen are called Rh positive (Rh+), and people who lack the D antigen are called Rh negative (Rh-). Rhesus antigens are thought to play a role in transporting ions across cell membranes by acting as channel proteins.
The Rhesus blood group system is controlled by two linked genes on chromosome 1. One gene, called RHD, produces a single antigen, antigen D. The other gene, called RHCE, produces the other four relatively common Rhesus antigens (C, c, E, and e), depending on which alleles for this gene are inherited.
Rhesus Blood Group and Transfusions
After the ABO system, the Rhesus system is the second most important blood group system in blood transfusions. The D antigen is the one most likely to provoke an immune response in people who lack the antigen. People who have the D antigen (Rh+) can be safely transfused with either Rh+ or Rh- blood, whereas people who lack the D antigen (Rh-) can be safely transfused only with Rh- blood.
Unlike anti-A and anti-B antibodies to ABO antigens, anti-D antibodies for the Rhesus system are not usually produced by sensitization to environmental substances. People who lack the D antigen (Rh-), however, may produce anti-D antibodies if exposed to Rh+ blood. This may happen accidentally in a blood transfusion, although this is extremely unlikely today. It may also happen during pregnancy with an Rh+ fetus if some of the fetal blood cells pass into the mother’s blood circulation.
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
If a woman who is Rh- is carrying an Rh+ fetus, the fetus may be at risk. This is especially likely if the mother has formed anti-D antibodies during a prior pregnancy because of a mixing of maternal and fetal blood during childbirth. Unlike antibodies against ABO antigens, antibodies against the Rhesus D antigen can cross the placenta and enter the blood of the fetus. This may cause hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), also called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness in which fetal red blood cells are destroyed by maternal antibodies, causing anemia. This illness may range from mild to severe. If it is severe, it may cause brain damage and is sometimes fatal for the fetus or newborn. Fortunately, HDN can be prevented by preventing the formation of anti-D antibodies in the Rh- mother. This is achieved by injecting the mother with a medication called Rho(D) immune globulin.
Geographic Distribution of Rhesus Blood Types
The majority of people worldwide are Rh+, but there is regional variation in this blood group system, as there is with the ABO system. The aboriginal inhabitants of the Americas and Australia originally had very close to 100 per cent Rh+ blood. The frequency of the Rh+ blood type is also very high in African populations, at about 97 to 99 per cent. In East Asia, the frequency of Rh+ is slightly lower, at about 93 to 99 per cent. Europeans have the lowest frequency of the Rh+ blood type at about 83 to 85 per cent.
What explains the population variation in Rhesus blood types? Prior to the advent of modern medicine, Rh+ positive children conceived by Rh- women were at risk of fetal or newborn death or impairment from HDN. This was an enigma, because presumably, natural selection would work to remove the rarer phenotype (Rh-) from populations. However, the frequency of this phenotype is relatively high in many populations.
Recent studies have found evidence that natural selection may actually favor heterozygotes for the Rhesus D antigen. The selective agent in this case is thought to be toxoplasmosis, a parasitic disease caused by the protozoan Toxoplasma gondii, which is very common worldwide. You can see a life cycle diagram of the parasite in Figure 6.5.7. Infection by this parasite often causes no symptoms at all, or it may cause flu-like symptoms for a few days or weeks. Exposure to the parasite has been linked, however, to increased risk of mental disorders (such as schizophrenia), neurological disorders (such as Alzheimer’s), and other neurological problems, including delayed reaction times. One study found that people who tested positive for antibodies to the parasite were more than twice as likely to be involved in traffic accidents.
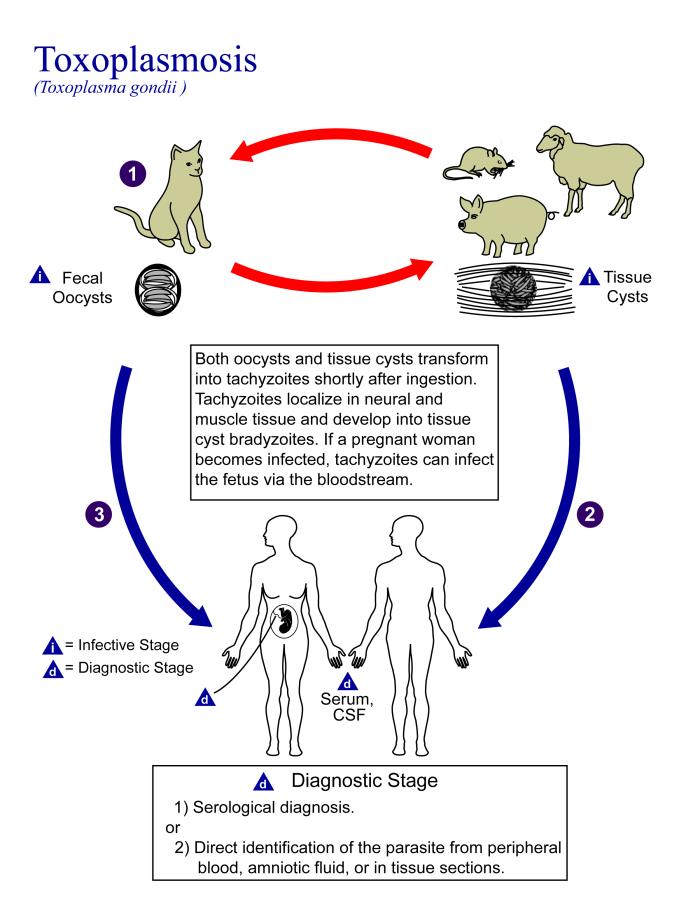
People who are heterozygous for the D antigen appear less likely to develop the negative neurological and mental effects of Toxoplasma gondii infection. This could help explain why both phenotypes (Rh+ and Rh-) are maintained in most populations. There are also striking geographic differences in the prevalence of toxoplasmosis worldwide, ranging from zero to 95 per cent in different regions. This could explain geographic variation in the D antigen worldwide, because its strength as a selective agent would vary with its prevalence.
Feature: Myth vs. Reality
Myth |
Reality |
| "Your nutritional needs can be determined by your ABO blood type. Knowing your blood type allows you to choose the appropriate foods that will help you lose weight, increase your energy, and live a longer, healthier life." | This idea was proposed in 1996 in a New York Times bestseller Eat Right for Your Type, by Peter D’Adamo, a naturopath. Naturopathy is a method of treating disorders that involves the use of herbs, sunlight, fresh air, and other natural substances. Some medical doctors consider naturopathy a pseudoscience. A major scientific review of the blood type diet could find no evidence to support it. In one study, adults eating the diet designed for blood type A showed improved health — but this occurred in everyone, regardless of their blood type. Because the blood type diet is based solely on blood type, it fails to account for other factors that might require dietary adjustments or restrictions. For example, people with diabetes — but different blood types — would follow different diets, and one or both of the diets might conflict with standard diabetes dietary recommendations and be dangerous. |
| "ABO blood type is associated with certain personality traits. People with blood type A, for example, are patient and responsible, but may also be stubborn and tense, whereas people with blood type B are energetic and creative, but may also be irresponsible and unforgiving. In selecting a spouse, both your own and your potential mate’s blood type should be taken into account to ensure compatibility of your personalities." | The belief that blood type is correlated with personality is widely held in Japan and other East Asian countries. The idea was originally introduced in the 1920s in a study commissioned by the Japanese government, but it was later shown to have no scientific support. The idea was revived in the 1970s by a Japanese broadcaster, who wrote popular books about it. There is no scientific basis for the idea, and it is generally dismissed as pseudoscience by the scientific community. Nonetheless, it remains popular in East Asian countries, just as astrology is popular in many other countries. |
6.5 Summary
- Blood type (or blood group) is a genetic characteristic associated with the presence or absence of antigens on the surface of red blood cells. A blood group system refers to all of the gene(s), alleles, and possible genotypes and phenotypes that exist for a particular set of blood type antigens.
- Antigens are molecules that the immune system identifies as either self or non-self. If antigens are identified as non-self, the immune system responds by forming antibodies that are specific to the non-self antigens, leading to the destruction of cells bearing the antigens.
- The ABO blood group system is a system of red blood cell antigens controlled by a single gene with three common alleles on chromosome 9. There are four possible ABO blood types: A, B, AB, and O. The ABO system is the most important blood group system in blood transfusions. People with type O blood are universal donors, and people with type AB blood are universal recipients.
- The frequencies of ABO blood type alleles and blood groups vary around the world. The allele for the B antigen is least common, and blood type O is the most common. The evolutionary forces of founder effect, genetic drift, and natural selection are responsible for the geographic distribution of ABO alleles and blood types. People with type O blood, for example, may be somewhat resistant to malaria, possibly giving them a selective advantage where malaria is endemic.
- The Rhesus blood group system is a system of red blood cell antigens controlled by two genes with many alleles on chromosome 1. There are five common Rhesus antigens, of which antigen D is most significant. Individuals who have antigen D are called Rh+, and individuals who lack antigen D are called Rh-. Rh- mothers of Rh+ fetuses may produce antibodies against the D antigen in the fetal blood, causing hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN).
- The majority of people worldwide are Rh+, but there is regional variation in this blood group system. This variation may be explained by natural selection that favors heterozygotes for the D antigen, because this genotype seems to be protected against some of the neurological consequences of the common parasitic infection toxoplasmosis.
6.5 Review Questions
- Define blood type and blood group system.
- Explain the relationship between antigens and antibodies.
- Identify the alleles, genotypes, and phenotypes in the ABO blood group system.
- Discuss the medical significance of the ABO blood group system.
- Compare the relative worldwide frequencies of the three ABO alleles.
- Give examples of how different ABO blood types vary in their susceptibility to diseases.
- Describe the Rhesus blood group system.
- Relate Rhesus blood groups to blood transfusions.
- What causes hemolytic disease of the newborn?
- Describe how toxoplasmosis may explain the persistence of the Rh- blood type in human populations.
- A woman is blood type O and Rh-, and her husband is blood type AB and Rh+. Answer the following questions about this couple and their offspring.
- What are the possible genotypes of their offspring in terms of ABO blood group?
- What are the possible phenotypes of their offspring in terms of ABO blood group?
- Can the woman donate blood to her husband? Explain your answer.
- Can the man donate blood to his wife? Explain your answer.
- Type O blood is characterized by the presence of O antigens — explain why this statement is false.
- Explain why newborn hemolytic disease may be more likely to occur in a second pregnancy than in a first.
6.5 Explore More
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xfZhb6lmxjk
Why do blood types matter? - Natalie S. Hodge, TED-Ed, 2015.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qcZKbjYyOfE
How do blood transfusions work? - Bill Schutt, TED-Ed, 2020.
Attributes
Figure 6.5.1
Following the Blood Donation Trail by EJ Hersom/ USA Department of Defense is in the public domain. [Disclaimer: The appearance of U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) visual information does not imply or constitute DoD endorsement.]
Figure 6.5.2
Antibody by Fvasconcellos on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 6.5.3
ABO system codominance.svg, adapted by YassineMrabet (original "Codominant" image from US National Library of Medicine) on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 6.5.4
ABO_blood_type.svg by InvictaHOG on Wikimedia Commons is released into the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Figure 6.5.5
Blood Donor and recipient ABO by CK-12 Foundation is used under a CC BY-NC 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) license.
Figure 6.5.6
- Map of Blood Group A by Muntuwandi at en.wikipedia on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/) license.
- Map of Blood Group B by Muntuwandi at en.wikipedia on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/) license.
- Map of Blood Group O by anthro palomar at en.wikipedia on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/) license.
Figure 6.5.7
Toxoplasma_gondii_Life_cycle_PHIL_3421_lores by Alexander J. da Silva, PhD/Melanie Moser, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Public Health Image Library (PHIL#3421) on Wikimedia Commons is in the public domain (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain).
Table 6.5.1
ABO Blood Group System: Genotypes and Phenotypes was created by Christine Miller.
References
Dean, L. (2005). Chapter 4 Hemolytic disease of the newborn. In Blood Groups and Red Cell Antigens [Internet]. National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2266/
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Toxoplasmosis [online article]. MayoClinic.org. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/toxoplasmosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20356249
MedlinePlus. (2019, January 29). Hemolytic transfusion reaction [online article]. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Chromosome_9&oldid=946440619
TED-Ed. (2015, June 29). Why do blood types matter? - Natalie S. Hodge. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xfZhb6lmxjk&feature=youtu.be
TED-Ed. (2020, February 18). How do blood transfusions work? - Bill Schutt. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qcZKbjYyOfE&feature=youtu.be
Wikipedia contributors. (2020, May 10). Chromosome 1. In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Chromosome_1&oldid=955942444
Wikipedia contributors. (2020, March 20). Chromosome 9. In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Chromosome_9&oldid=946440619
Genes causing a trait or disorder which are present on the X sex determining chromosome.
Genes causing a trait or disorder which are present on the X sex determining chromosome.
The body system which acts as a chemical messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In humans, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid gland and the adrenal glands.
A hormone is a signaling molecule produced by glands in multicellular organisms that target distant organs to regulate physiology and behavior.
The front lobe of the pituitary gland that synthesizes and secretes pituitary hormones.
The front lobe of the pituitary gland that synthesizes and secretes pituitary hormones.
A type of white blood cell and, specifically, a type of lymphocyte.
Many B cells mature into what are called plasma cells that produce antibodies (proteins) necessary to fight off infections while other B cells mature into memory B cells.
A type of white blood cell and, specifically, a type of lymphocyte.
Many B cells mature into what are called plasma cells that produce antibodies (proteins) necessary to fight off infections while other B cells mature into memory B cells.
Image shows a diagram of the gallbladder and it's connection to the cystic duct and then the common bile duct.
A membrane protein involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, or macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane.
An expression that gives the identities and quantities of the substances involved in a reaction. A chemical equation shows the starting compound(s)—the reactants—on the left and the final compound(s)—the products—on the right, separated by an arrow.
A sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA that codes for a molecule that has a function.


