Reading Economic Rent
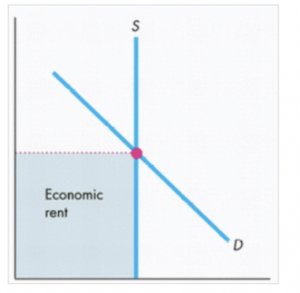
There are many different definitions of economic rent. It occurs primarily with resources that have a fixed supply. Economic rent is the revenue that can be earned from the land or other natural resource for which there is a fixed supply.
Price
 Quantity
Quantity
Notice the vertical supply curve, at a fixed level of output, price is solely defined by the demand curve. Land particularly has economic rent because of the fact that price has much to do with location. Economic rent refers to extra money that a person makes over the amount they expect. Thus, prime locations can have a great deal of economic rent.
Economic rent also occurs in the labor market. However, the level of economic rent is determined by how much that worker is able to earn at another job (called transfer earnings).
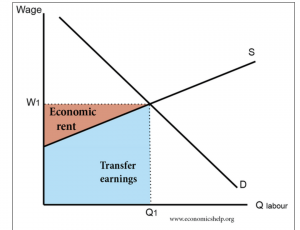
In terms of labor, transfer earnings are the minimum reward necessary to prevent a worker from transferring to their next best source of employment.

