18 3.6 The Influence of New Technology
Learning Objectives
- Determine the benefits and drawbacks of digital libraries.
- Define print-on-demand and self-publishing.
The book industry has changed enormously since its creation. From the invention of the papyrus scroll to the introduction of the e-book, new technologies continuously affect how people view and experience literature. With the advent of digital media, old-media industries, such as the book industry, must find ways to adapt. Some fear that this new technology will destroy the industry, while others maintain that it works to the industry’s advantage. However, one thing is clear—digital technology promises to reshape the publishing industry as we know it.
E-Books
The first e-book readers were related to the personal digital assistant (PDA) devices, pocket-sized electronics that could store and display large amounts of text, that became popular in the 1990s. However, early e-book readers lingered on the market, popular in certain techy niches but unable to gain traction with the wider population. Early e-readers had minimal battery life and text that was difficult to read. Through the 2000s, technological advances allowed for smaller and sleeker models, the Apple iPhone and the iPad helped make readers more comfortable with reading on a small screen. The second half of the decade saw the release of many e-readers. The technology got a boost when Oprah Winfrey praised the Kindle on her show in October 2008. By that holiday season, e-book reader sales were booming, and it wasn’t just the technologically savvy individuals who were interested anymore. Despite being criticized by some as providing an inferior reading experience to dedicated e-readers, the Apple iPad has been a powerful driving force behind e-book sales—more than 1.5 million books were downloaded on the Apple iPad during its first month of release in 2010 (Maneker, 2010).
E-books make up less than 5 percent of the current book market, but that number is growing. At the beginning of 2010, Amazon had about 400,000 titles available for the Kindle device. Some devices offer wireless accessibility, meaning that an e-reader doesn’t have to be connected to a computer to access titles; an open Wi-Fi connection is all it needs. With access to a dazzling array of books available with just a few clicks, it’s no wonder the contemporary consumer seems enamored with the e-book. An e-book reader has the space to store thousands of titles in an object smaller and lighter than the average hardcover novel. And though the devices themselves can be expensive, e-books are usually cheaper than their hardcopy equivalents; sometimes they’re even free. Thanks to efforts like the Gutenberg Project and Google Books (see the following section), more than a million public domain titles are available as free e-books.
Anything that gets people excited about books and reading should be good for the publishing industry, right? Unfortunately for U.S. publishers, it’s not that simple. Some publishers worry that e-book sales may actually end up hurting their bottom lines. During the Kindle’s first year, Amazon essentially set the standard price for bestselling or new release e-books at $9.99. Since Amazon was acting as a wholesaler and buying these books for half the publisher’s list price—generally around $25 for a new hardcover—the company was selling these titles at a loss. However, for Amazon, a short-term loss might have had long-term payoffs. At the start of 2010, the company controlled a 90 percent share of the e-book market. Faced with e-books that cost less than $10, traditional publishers worried that consumers would avoid purchasing a new hardcover priced at $25 (or even a $13 trade paperback).
Figure 3.13
Most e-readers are the size and shape of one hardcover book.
ndh – Kobo eReader – CC BY-NC 2.0.
In January 2010, the conflict between Amazon and the publishing establishment came to a head. Macmillan, one of the six major publishing companies in the United States, suggested a new business model to Amazon, one that resembled the deal that the Big Six publishers had worked out with Apple for e-book sales on the Apple iPad. Essentially, Amazon had been able to buy books from publishers at wholesale rates—half the hardcover list price—and then set whatever retail price it wanted. This allowed Amazon to choose to sell books at a loss in the hope of convincing more people to buy Kindles. Macmillan proposed a system in which Amazon would act more as a commission-earning agent than a wholesaler. In Macmillan’s proposed model, the publisher would set the retail price and take 70 percent of each sale, leaving 30 percent for the retailer. Macmillan couldn’t force Amazon to agree to this deal, but the publisher could strike a hard bargain: If Amazon refused Macmillan’s offer, it could still sell Macmillan titles under the wholesale model, but the publisher would delay e-book editions for 7 months after hardcover releases. What followed was a standoff. Amazon didn’t just reject Macmillan’s proposal; it removed the “buy” button from all Macmillan books listed on its website (including print books), essentially refusing to sell Macmillan titles. However, after a few days, Amazon capitulated and agreed to Macmillan’s terms, but not before issuing a strongly worded press release claiming that they agreed to sell Macmillan’s titles “at prices we believe are needlessly high for e-books,” because “Macmillan has a monopoly over their own titles (Rich & Stone, 2010).” Still, Macmillan and the other publishers seem to have won this battle: Amazon agreed that e-books for most new fiction and nonfiction books for adults will be priced at $12.99 to $14.99, though best sellers will still be $9.99 (Rich & Stone, 2010).
But the $10 book may be the least of the publishing industry’s worries. At the start of 2010, more than half of the bestselling titles on Kindle were free. Some of these were public domain novels such as Pride and Prejudice, but many others were books by living authors being promoted by publishers by giving away the book. The industry hasn’t yet come to a consensus about the utility of free e-books. Some publishers consider it a practice that devalues books in the eyes of customers. “At a time when we are resisting the $9.99 price of e-books,” David Young of the Hachette Book Group told The New York Times, “it is illogical to give books away for free (Rich, 2010).” Other publishers consider free e-books a promotional tool to build word-of-mouth and to introduce readers to new authors.
Other e-books emerge from outside the traditional publishing system. Four of the five bestselling novels in Japan in 2007 were cell phone novels, books that were both written and intended to be read on cell phones. Cell-phone novels are traditionally written by amateurs who post them on free websites. Readers can download copies at no cost, which means no one is making much of a profit from this new genre. Although the phenomenon has not caught on in the United States yet, the cell phone novel is feared by some publishers as a further sign of the devaluation of books in a world where browsers expect content to be free.
With e-book sales expected to triple by 2015, it’s hard to say what such a quickly growing industry will look like in the future (McQuivy, 2010). Some people have theorized that e-readers will lead to an increasing popularity of the short story, which can be bought and read in short increments. Others have claimed that they’ll destroy the book industry as we know it. Whatever the future of books looks like, everything—from the way books are produced to the way we read them—continues to change rapidly because of new technologies.
Digitizing Libraries
The idea of a digitized library has been around since the early years of the Internet. A digital library stores its materials in a digital format, accessible by computers. Some digital libraries can be accessed locally; others can be accessed remotely through a computer network. Michael Hart founded Project Gutenberg, the oldest digital library, in 1971, 3 years before the Internet went live. Hart’s initial goal was to make 10,000 of the most-consulted books publicly available and free by the end of the century. The forward-thinking Hart named his project after the inventor of the movable type printing press, perhaps realizing that book digitization had the potential to revolutionize the way humans produce and read books as much as Gutenberg’s invention had centuries earlier. At first, the process was slow for Hart and his fellow book-digitizing volunteers because they were forced to copy text manually until 1989. In the early 1990s, scanners and text-recognition software allowed them to somewhat automate the process.
Fast-forward to 2010. Project Gutenberg’s free online library boasts more than 30,000 public domain works available for free download. Stanford University uses a robotic page-turning scanner machine to digitize 1,000 book pages an hour. Stanford’s partner in digital library production is Google Books, which has scanned over 10 million books since it began Google Books in 2004. A Chinese company claims to have digitized more than half of all books that have been published in Chinese since 1949. In 2006, The New York Times estimated that humans have published at least 32 million books throughout history; the huge push for book digitization makes it seem entirely possible that nearly all known books could be digitized within 50 years (Kelly).
Some liken the prospect of these widely accessible, easily searchable, free libraries to the proliferation of free libraries in the 19th century, which led to a surge in literacy rates. One of Project Gutenberg’s stated goals is “to break down the bars of ignorance and illiteracy” through its library of digitized books (Hart & Newby, 2004). Digital libraries make a huge selection of texts available to people with Internet access, giving them the amazing potential to democratize knowledge. As Bill McCoy, the general manager of Adobe’s e-publishing business, told The New York Times in 2006, “Some of us have thousands of books at home, can walk to wonderful big-box bookstores and well-stocked libraries and can get Amazon.com to deliver next day. The most dramatic effect of digital libraries will be not on us, the well-booked, but on the billions of people worldwide who are underserved by ordinary paper books (Hart & Newby, 2004).” Digitized libraries can make fragile materials available to browsers without damaging originals; academic libraries are also able to share important texts without shipping books across the country.
Google Books, the largest online library, is not run by an academic institution, though it does claim several as partners. The bulk of free digital books available from Google Books or elsewhere come from the public domain, which constitutes approximately 15 percent of all books. Google Books has made over a million of these titles fully and freely searchable and downloadable. Other works in the Google Books digital library include in-print texts whose publishers have worked out a deal with Google. Some of these titles have their full text available online; others allow only a limited number of page previews. As part of its partnership with publishers, a Google Books search result will often provide links to the publisher’s website and to booksellers.
Google Books ran into trouble, however, when it began to digitize the millions of books with unclear legal status, such as out-of-print works that weren’t yet in the public domain. Many of these are considered orphan works, meaning that no one is exactly sure who owns their copyright. In 2004, the site announced plans to scan these texts and to make them searchable, but it would only show sentence-long snippets to searchers. Copyright holders could ask Google to remove these snippets at any time. Google claimed that this digitization plan would benefit authors, whose books would no longer linger in out-of-print limbo; it would also help researchers and readers, who would be able to locate (and perhaps purchase) previously unavailable works.
Publishers and authors did not agree with Google. Many objected to Google’s plan to scan first and look into copyright ownership later; others saw Google’s profiting from works still under copyright as a clear violation of intellectual property law. In 2005, the Authors Guild of America and the American Association of Publishers (AAP) sued Google for “massive copyright infringement.” Google argued that it was essentially creating a massive online card catalog; the Authors Guild and AAP alleged that Google was attempting to monopolize information and profit from it. In 2008, Google agreed to a $125 million settlement with the publishers and the Authors Guild. Some of that money would go directly to copyright holders; some would pay for legal fees; and some would go to found the Book Rights Registry, an independent nonprofit association that would ensure content users (like Google) are paying copyright owners. Copyright owners would get money from Google and from potential book sales; Google would get money from advertisers, book sales, and institutional subscriptions by libraries.
Still, not everyone agreed with the decision. The Open Book Alliance was formed by a diverse partnership of organizations, including Amazon, Internet Archive, and the National Writers Union, who fear that Google’s proprietary control of so much copyrighted material was an antitrust violation. As the group states on its website:
We will assert that any mass book digitization and publishing effort be open and competitive. The process of achieving this promise must be undertaken in the open, grounded in sound public policy and mindful of the need to promote long-term benefits for consumers rather than isolated commercial interests. The Open Book Alliance will counter Google, the Association of American Publishers and the Authors’ [sic] Guild’s scheme to monopolize the access, distribution and pricing of the largest digital database of books in the world.
Another concern, which was mentioned earlier, in the digital library world is digital decay. One librarian at Harvard University told The New York Times that “we don’t really have any methodology [to preserve digital material] as of yet…. We just store the disks in our climate-controlled stacks, and we’re hoping for some kind of universal Harvard guidelines (Cohen, 2010).”
Paper Books vs eBooks Statistics, Trends and Facts [2022]
From Toner Buzz. Posted by Rob Errera on 02/18/2022
-
Paper books vs eBooks statistics show print is here to stay!
Dead Tree Editions Just Won’t Die!
Like the monster in a horror movie, print books just won’t die. The most recent paper books vs eBooks statistics, research, and surveys back this up.
Print books are here to stay!
Let’s look at the most important eBook vs print book statistics, key differences between print and e-books, and where American publishers are taking the industry.
Popularity Contest: eBooks Versus Print Books
Are print books still popular? You’d better believe it!
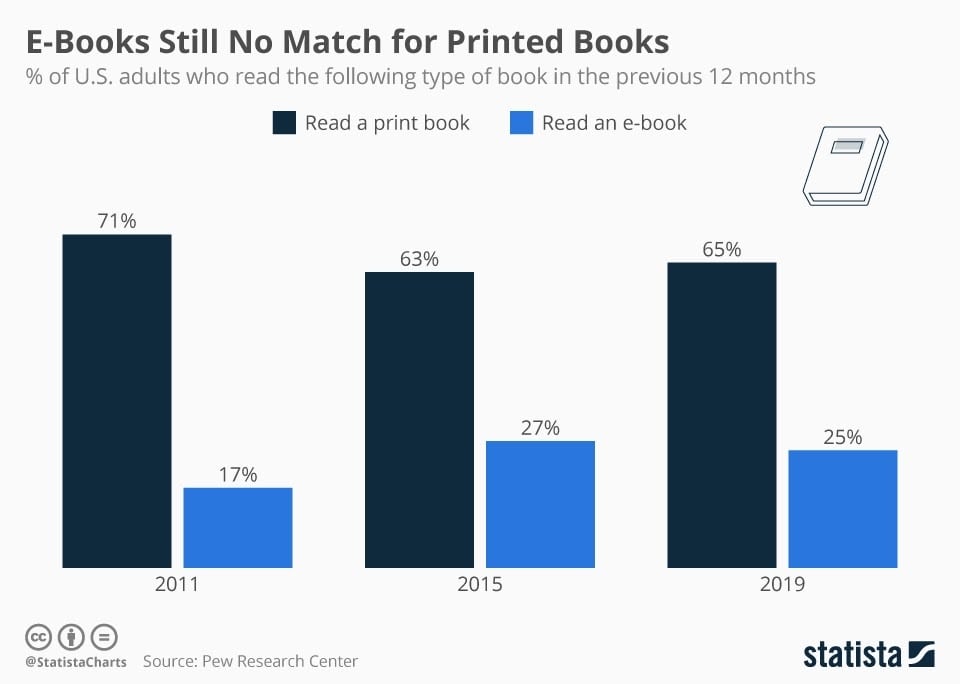
According to a survey conducted by the Pew Research Center on book consumption and book formats, traditional print is still the most popular reading format for both adults and children.
Survey says:
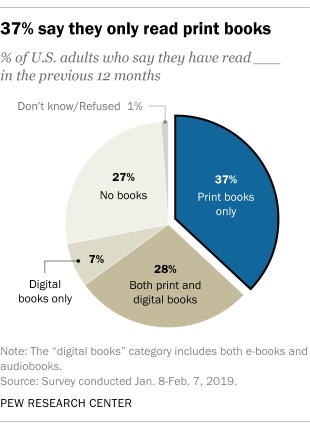
- 72% of adults in the United States read a book in some format over the last year
- 65% of respondents claimed they read a book in the last 12 months
- 37% of Americans claim they only read print books
- 28% say they read both print books and e-books
- 7% say they only read e-books
Other Interesting eBooks vs Printed Books Statistics
- Print books out-sell eBooks 4-to1
- 191 million e-books were sold in the United States in 2020
- Printed book sales amounted to 750.89 million units in 2020
- Print book sales have increased 13.2% between 2020 and 2021, and 21% between 2019 and 2021
- eBook sales grew by 22% in 2020
- eBook sales have decreased 8% in 2021 but are still 8% higher than they were in 2019
- In 2020, 19% of adult readers owned an e-reader, a decrease from 32% of adult readers who owned e-readers in 2014
Kindle vs Book Statistics
By far, the most popular e-reader on the market is Amazon’s Kindle.
The Kindle comes in a variety of formats — color, glare-free, etc. — but all use the AZW eBook format. Most other e-readers, like the Barnes & Noble Nook and Apple Books, use the more ubiquitous EPUB format for eBooks.
- 72% of the e-reader market belongs to Amazon Kindle
- 10% of the e-reader market belongs to Barnes & Noble Nook
- 18% of e-readers use an alternative app for digital reading
A more recent study from Pew Research suggests more people are reading on their smartphones and tablets, leading to a recent decrease in e-reader sales.
A 2012 report from NewZoo found 17.4 million active Kindle Fire users and 30.5 million iPad users in the United States. By 2018 Amazon reported selling close to 90 million e-readers. Statista projects the number of e-reader users to grow from 950.5 million in 2019 to 1.11 billion by 2023.
Check also ➜ How Many Books Are Published Each Year?
Demographics: Reader vs E-Reader
Book reading demographics vary according to education and income level.
College graduates make up 90% of book readers, while only 61% of high school graduates read books.
Those who dropped out of school have an even lower readership rate – a mere 32%.
Economics goes hand-in-hand with education. Individuals earning over $75,000 a year make up 86% of readers, while well those earning less than $30,000 annually make up only 62%.
Physical books are still the top moneymakers for publishers.
Publishing market research shows the economic juggernaut of traditional books. While publishers are experimenting with different media formats — especially audiobooks — they are still investing the bulk of their marketing efforts into physical book sales.
And they should…there’s still big money in old-fashioned publishing!
- Books sales revenue in 2019 totaled $26 billion
- Physical books generated 74.7% of the total revenue
- E-books accounted for only 7.48% of the revenue
- The remaining part of the revenue was generated by other formats like audiobooks
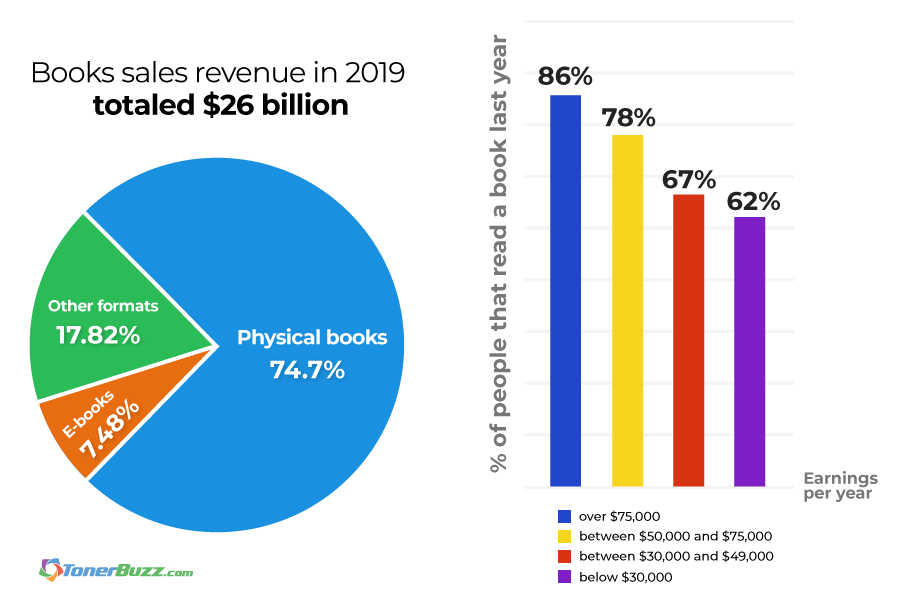
Source: The Association of American Publishers (AAP)
Canada Book Market Mirrors The US
Canadian booksellers see the same trends as the United States: people prefer print when it comes to long-form reading.
A 2020 survey from the Toronto Star supports these findings:
- 80% of Ontarians read a book in 2019
- 70% of those read print books
- 28% read e-books
- 56% of respondents said they only read print
- 14% prefer e-books
- 7% prefer audiobooks
And this trend is not just confined to North America. The same thing happens in a dozen different countries.
Reader vs. E-Reader Statistics: Educational Levels
College graduates:
- 90% read a book last year
- 81% read a print book
- 41% read an e-book
- 34% listened to an audiobook
High school graduates:
- 61% read a book last year
- 55% read a print book
- 15% read an e-book
- 12% listened to an audiobook

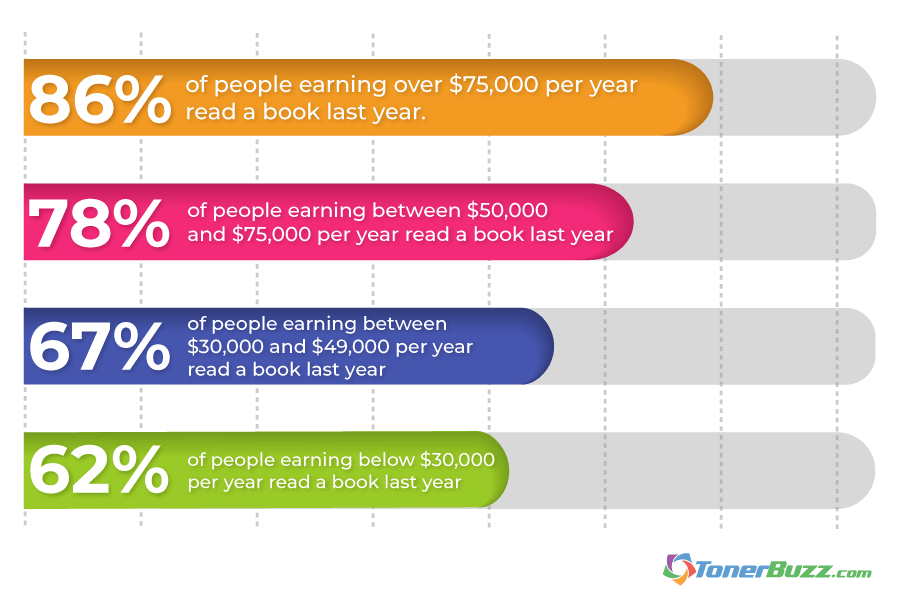
Reader vs. E-Reader Statistics: Income Levels
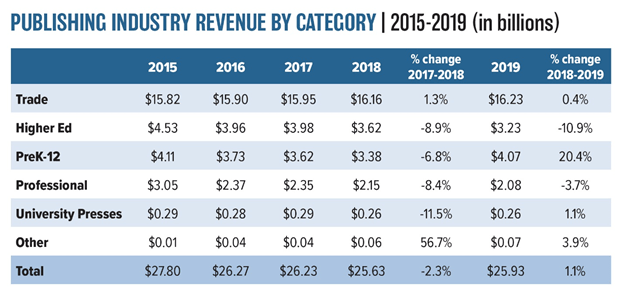
- 86% of people earning over $75,000 per year read a book last year.
- 78% of people earning between $50,000 and $75,000 per year read a book last year.
- 67% of people earning between $30,000 and $49,000 per year read a book last year.
- 62% of people earning below $30,000 per year read a book last year.
Print Book Youth Movement
One of the main reasons physical books are here to stay is because the next generation of readers has already embraced them.
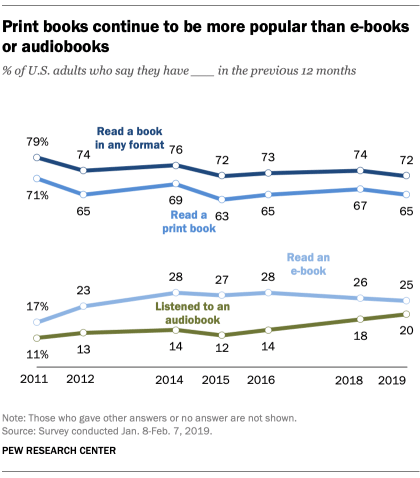
Studies by Pew Research Center show that the most avaricious readers are young adults, with 81% responding they read a book in some format in 2019.
Data gathered from surveys and studies helps shape market trends:
- 81% of people aged 18-29 read a book last year
- 72% of people aged 30-49 read a book last year
- 67% of people aged 50-64 read a book last year
- 68% of people aged 65 and older read a book last year
- 62% of 16 to 24-year-olds preferred print books to e-books
- 74% of 18 to 29-year-olds preferred physical books to e-books
- Only 4% of children’s fiction was published in digital formats in the past year
eBooks vs Print Books: Costs & Savings
In the early days of eBook publishing, the digital versions of books were priced much cheaper than the print versions.
This made sense.
There were no printing, paper, or shipping costs involved, so a digital book should naturally cost less. A decade ago, it was not uncommon to see a hardcover bestseller priced at $25 with a digital edition price around half that.
Today the prices of physical books are much closer, especially when it comes to new releases and popular authors.
The cost of the latest Susanne Collins or Stephen King book will be nearly the same in both hardcover and e-book editions.
The real savings of eBooks come with older works and backlist titles. The digital editions of books that have been available for a while drop significantly. You can get eBook editions of classic literature for very cheap (even free).
Independent authors also offer up a wide variety of eBooks that are priced less than books from traditional publishers.
There are bargain books in both the physical and digital realms. You can find plenty of one-dollar eBooks online, enough to max out your e-reader. You can also find a table filled with $5 hardcovers at the local warehouse store.
Overall, eBooks will save avid readers money, but not as much you’d expect.
Look at the current bestseller lists and you’ll actually find hardcover books less expensive than their Kindle counterparts.
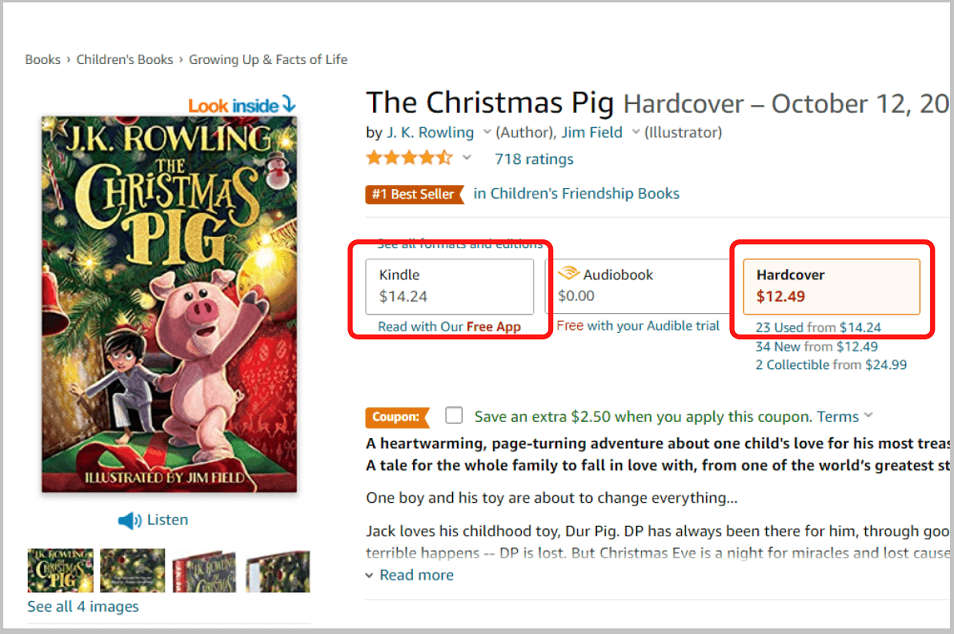
Books versus eBooks on Amazon
Amazing Bestseller list 10/12/21:
- JK Rowlings’s “The Christmas Pig” is $12.49 hardcover and $14.24 eBook – 1.75$ difference in favor of the the Hardcover
- Adam Schiff’s “Midnight in Washington” is $25.49 hardcover and 14.99 eBook – $10.50 difference
- Dave Grohl’s “The Storyteller” is $19.49 hardcover and $14.99 eBook – $4.50 difference
- Ron and Clint Howard’s “The Boys” is $20.49 hardcover and $14.99 eBook – $5.50 difference
- Nicholas Sparks “The Wish” is $15.99 hardcover and $14.99 eBook – $1.00 difference
- Anthony Doerr’s “Cloud Cuckoo Land” is $18.57 hardcover and $14.99 eBook – $3.58 difference
Based on the information above, new hardcover bestsellers sell for an average price of $19.30 while their eBook counterparts sell for around $15.
So, if you like to read hot-of-the-press bestsellers, choosing eBooks over physical books will save you about $4 per title … and a whole lot of shelf space!
It will be interesting to see how the coming year’s anticipated book shortage will affect eBook sales. Worldwide supply chain delays have already postponed many physical book shipments for Fall 2021 and delays are expected to well into 2022.
But eBook sales should experience none of these disruptions.
There is no paper, ink, printing, binding, and shipping to slow the process of getting book titles into the hands of consumers. This should benefit eBook sales in the months ahead.
Don’t Forget Your Local Library
You can’t get cheaper than free. Public libraries across the country allow you to borrow print and digital editions of books for a select period of time, usually a week or two.
As long as you return your borrowed books on time and in good condition, the local library offers a lifetime of free reading
Plus, libraries are one of the biggest buyers of books. Let them make the investment while your reap the reading rewards!
The Benefits of E-Books
A book isn’t paper and binding. It is the words and ideas contained between the covers.
An e-book contains all of the words and information of a print edition with a number of additional benefits:
- The key difference between e-books and printed books is this lack of a physical object.
- For starters, one difference is that an e-book is more portable than a print book.
- You can store an entire library of e-books on your phone or tablet and not take up an inch of physical shelf space. Kindle libraries can be vast and contain appropriate content for people of any age.
- E-books take up very little data. Even if your data is limited, a dozen full-length editions will occupy no more than a megabyte of disk space. It’s hard for print to compete in this area of books vs. e-books. Physical books take up a lot of physical space.
- E-books do not have a fixed font size. Make those letters big and easy to read before bed. Or change the color of the type or the background. The options are endless and the convenience outstanding.
- Adopting e-book technology can make you more well-read. Your Kindle will survey your e-book reading tastes and report suggestions based on titles with a related association.
- In addition, e-books have the benefit of a built-in dictionary. No more guessing at word meanings based on their context. You could look up word definitions on the fly. Even search the web to get deeper details about the eBook you’re reading.
- E-books also offer an excellent way to take notes regarding the text you were reading. Digital notes can be exported into any text editor and you’re halfway through your book report or online review!
- Like all digital files, eBooks are also very convenient for sharing. Reader-community apps, like Goodreads, allow you to share your reading progress with others almost like a built-in book club you can join or occasionally check in on.
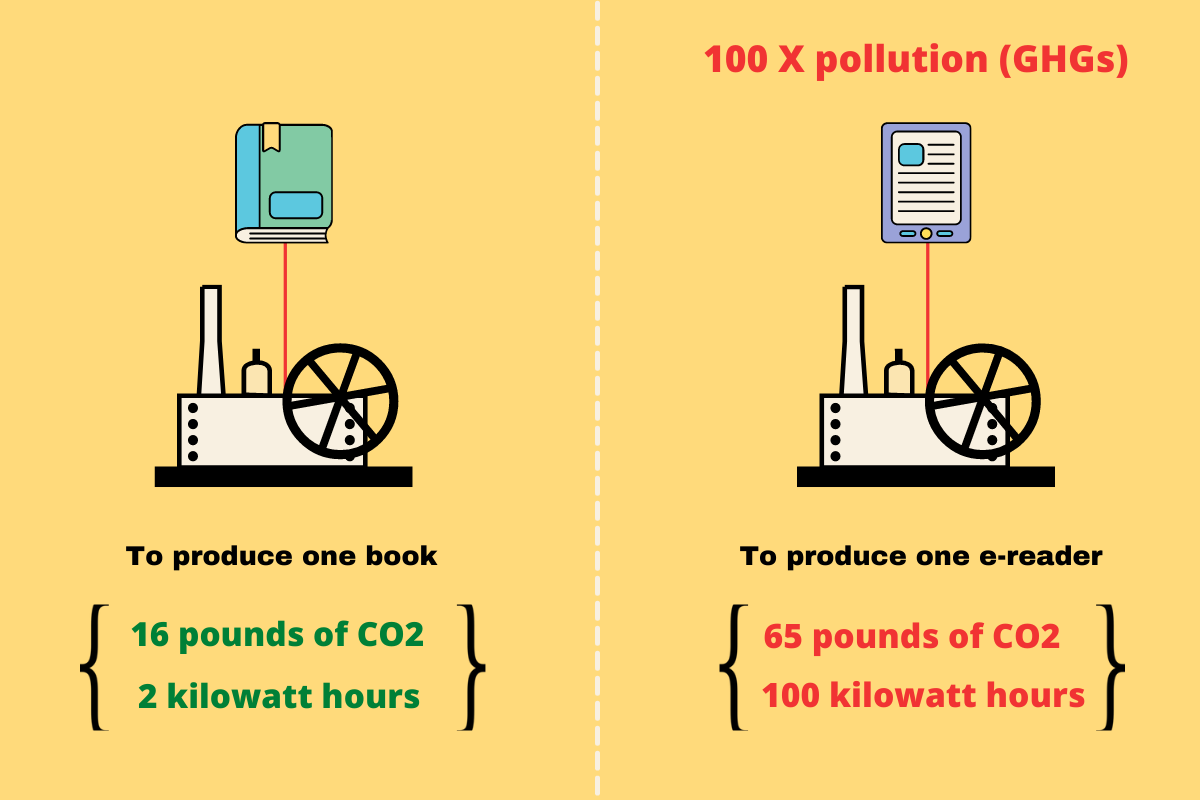
- E-books are also easier on the environment. Gone is the association with stinky paper mills and unnecessary tree slaughter. No glue, no expensive ink. Unlike paper books, eBooks leave little to no carbon footprint.
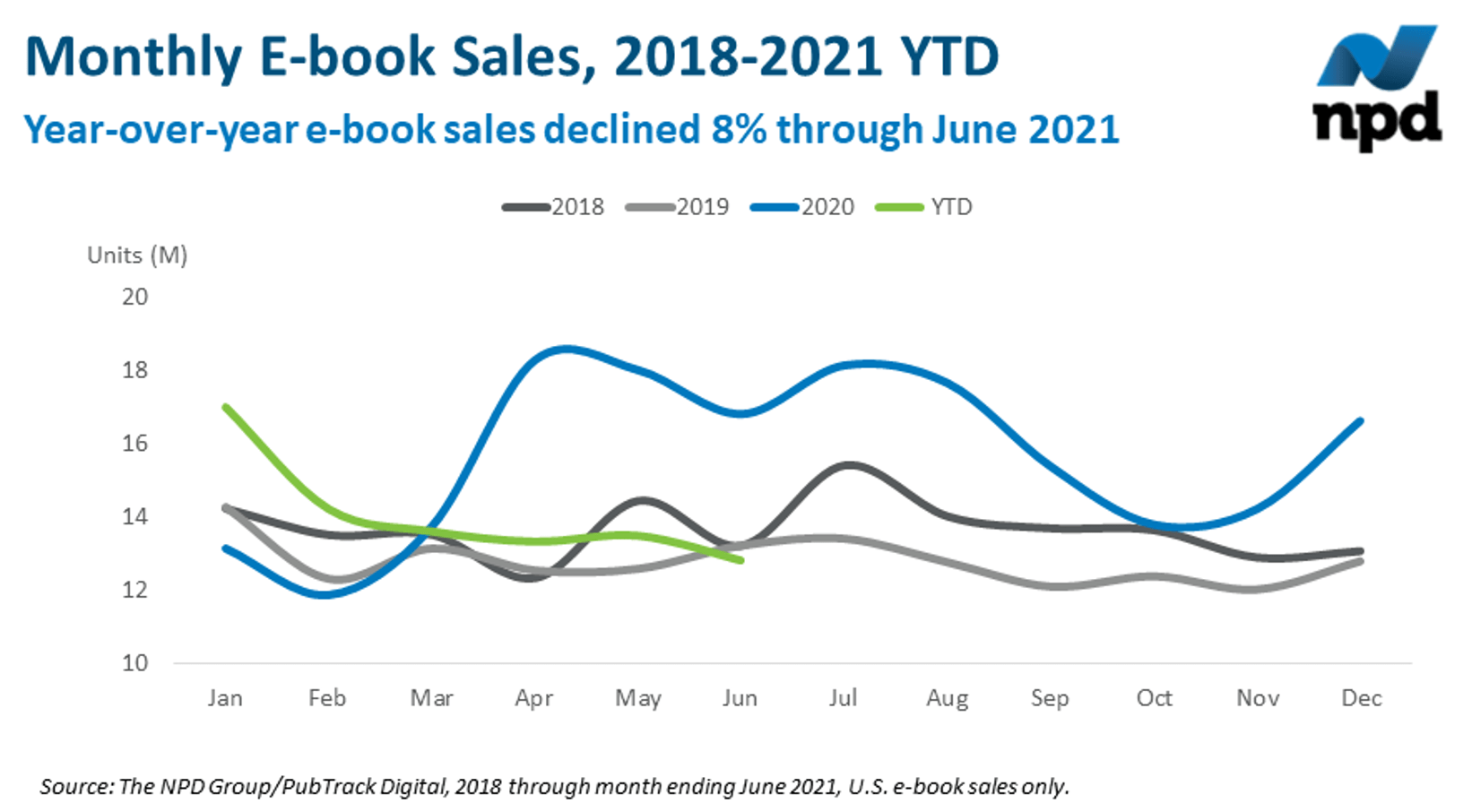
Latest eBook Sales Numbers
The Benefits of Print Books
A print book is a joy to behold!
The smell of freshly printed pages, the smooth, silky feel of paper beneath your fingertips, the crinkle, and crackle of a story flowing by.
Print offers a unique reading experience.
Digital e-readers don’t engage the senses the way a physical book does. Reading a printed book is a tactile experience.
You feel it, you smell it, and you remember it.
This is one reason physical books are the more popular format for readers. Printed books touch readers on a more primal emotional level.
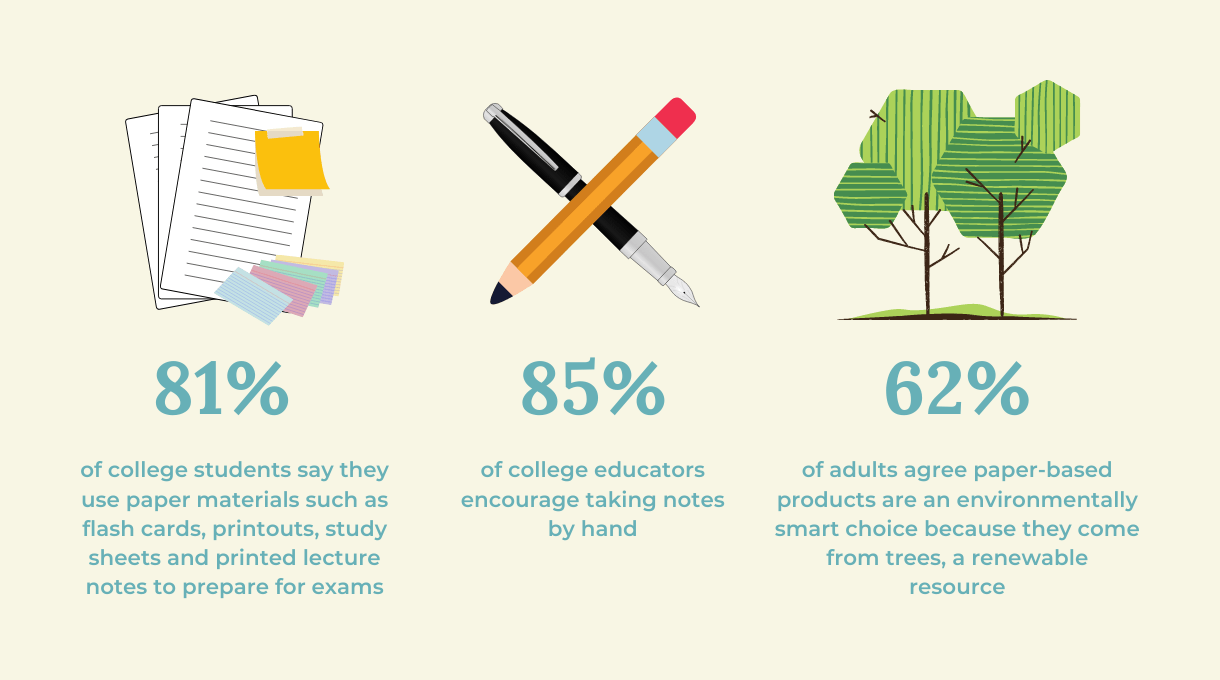
Physical Books vs eBooks Statistics Showing Why Traditional Books Are Better
- 66% of readers believe printed books offer a more unique and fulfilling reading experience than e-books.
- A majority of college students say they retain information longer when it is read in a printed format.
- Traditional books don’t cause the eye strain inherent to e-readers. Reading on an e-reader before bed disrupts sleep and impacts overall health
- Children learn better with paper books. Almost 90% of teachers and parents believe reading 15 pages on paper every day improves a child’s memory and language development.
- 64% of employees say they prefer paper agendas and memos to digital communication.
- E-readers take more carbon to produce than physical books.
- Discarded e-readers lead to toxic electronic waste. Old books can be recycled with other paper products.
Digital books bought online generally cost less. While a new hardcover can cost $30, the same book may only cost $15 on a Kindle e-reader. And that’s the top price for an eBook.
Most back titles are available for under five dollars. If you have limited income, e-readers and e-books are a better bargain when it comes to price.
In addition, reading a print book offers an uninterrupted “low tech” reading experience. E-readers and online reading in digital formats run the risk of pop-up ads, dying batteries, and power failures.
Despite its distribution limitations, print still reaches a broad demographic, especially among older readers.
For example, 41% of Americans over age 65 are not Internet users. The number of e-reader owners is even lower among this demographic.
The Future Of Printed Books
The statistics and surveys tell the story; despite the growing popularity of e-books, traditional publishing is here to stay.
The publishing industry uses market research to determine which book format a reader will prefer. U.S. libraries also contribute valuable data and figures on reader habits.
Another factor keeping traditional book publishing alive and well is the modern school system.
Textbook publishers have yet to embrace digital media. Heavy — and expensive — textbooks are still the norm for students. College students (and school boards) must buy the same textbooks year after year. Hey, the bulk of the information inside these textbooks hasn’t changed for centuries. Shouldn’t knowledge be free online somewhere?
Even though all the educational tools needed for academic success can be included on a lightweight laptop or tablet, print textbooks remain an essential part of classrooms.
This one of the main reasons readers prefer printed books over e-books — they were raised with print books all through school and they carry that love of physical books into adulthood.
The Future Of The eBook and E-Reader
A 2019 survey by Pew Research provides data and figures, which publishers use to determine which reading formats are most popular. While eBooks and e-readers were not the “print killers” some predicted they’d be, digital books continue to make slow gains in popularity.
The best-selling e-books are genre fiction — romance, crime, science-fiction, thrillers, and related genres.
The popularity of digital fiction in the United States is slated to grow over the next few years. As the popularity of e-books spreads, so too do the sales of e-book readers increase.
- Projected e-book sales in 2025 = $7.78 billion (up from $5.91 billion in 2019)
- Projected e-reader sales in 2025 = $98.95 million (up from $77.94 million in 2019)
What About Audiobooks?
We are in the midst of a “listening revolution” the likes of which the world hasn’t seen since the birth of radio.
The rise of podcasts and narrated stories means more people are listening to media than ever before.
However, these modern “books on tape” aren’t eating away at physical books or e-book sales as much as they’re bringing in new readers and giving seasoned readers a new way to enjoy the stories they love.
- One-in-five Americans listened to a book in 2019
- 100% of American publishers are creating audio
People Still Read Books… And Always Will
From a social media post to a blog article, people today read short-form writing on smartphones and tablets. But when they want to read in longer formats they turn to books, and, more often than not, they turn to “dead tree” editions printed with paper and ink.
Print books aren’t dying — they’re evolving, offering more accessible ways for people to enjoy them.
Technology has expanded our reading choices, allowing us to connect with books in different ways. In many ways — in terms of selection and availability — books are healthier than ever!
To get more insight into digital books vs. print books, we reached out to author Armand Rosamillia.
Rosamillia says his sales were pretty evenly split between print books, e-books, and audiobooks until the pandemic hit.
“Looking at my stats from the last 18 months, my sales are roughly 18% print, 27% audiobook, and 55% e-book,” Rosamillia reports. “Audio sales have nearly doubled since Covid, mostly affecting the print side.”
In addition to writing books, Rosamillia also runs The Little Free Library, a take-a-book / leave-a-book public bookshelf, which is a hit with younger readers.
Printed books are still preferred for nature journals, cookbooks, and children’s books. A recent Nielsen study found that parents and kids want to hold books and turn the pages together.
You can’t do that with an ebook.
The same goes for interactive books like coloring books, puzzles, and workbooks. You need traditional pages to get the most out of these books.
“Even though children are at ease with their tablets and technology (more so than I ever will be), they still gravitate toward the print books until they hit their teens, in my opinion,” Rosamillia says, “I have a Little Free Library on my property and the children go crazy whenever I put a new stack of picture books into it.”
And that’s good news for bibliophiles of any age!
Sources:
Statista
NDP
Paper and Packaging Board’s Fourth Annual Back-to-School Report: Paper and Productive Learning
The New York Times
Olympic College
hms.harvard.edu/news/e-readers-foil-good-nights-sleep
pewresearch.org/internet/2015/10/29/the-demographics-of-device-ownership/
pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/09/25/one-in-five-americans-now-listen-to-audiobooks/
pewresearch.org/internet/2014/04/03/older-adults-and-technology-use/
publishers.org/news/aap-statshot-annual-report-book-publishing-revenues-up-slightly-to-25-93-billion-in-2019/
thestar.com/business/opinion/2020/01/27/print-still-rules-when-it-comes-to-books-in-ontario.html
voxburner.com/blog-source/2015/5/18/16-24-prefer-books-as-physical-products
newzoo.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/PRESSRELEASE_2012_Kindle_Newzoo_15042012_V4.pdf
Print-on-Demand and Self-Publishing
Part of what made Gutenberg’s printing press so revolutionary was that it allowed books to be mass produced. In medieval times, readers often commissioned a scribe to copy a text by hand, a process that could take months or even years. But despite their many conveniences, printed books carry their own risks for authors and publishers. Producing books in bulk means that publishers are taking a gamble, attempting to publish enough books to satisfy demand, but not so many that unwanted copies linger in warehouses. When a book doesn’t sell as much as expected, the publisher may end up taking a loss if the costs of publishing the book exceed the revenue from its sale. Interestingly, modern technology has made it feasible for some authors and publishers to turn to an updated version of the medieval model of producing books on demand for specific customers, allowing them to avoid the risk of carrying a large inventory of books that may or may not sell. Print-on-demand, a system in which a book is printed only after an order is received, and the increasing trend of self-publishing may reshape the industry in the 21st century.
Self-publishing—a system that involves an author, not a third-party company, being in charge of producing and publishing a work—is not a new concept. Many authors self-published works in their lifetimes, including Virginia Woolf and Oscar Wilde. More recently, popular books like The Joy of Cooking and the Chicken Soup for the Soul series had their origins in self-publishing. Many authors also self-publish when they’re unable to get support from the traditional publishing world. Daniel Suarez’s techno-thriller Daemon was rejected by 48 agents before he opted for self-publishing. After creating interest on blogs, Suarez eventually got a two-book deal with Dutton, an imprint of Random House (McHugh, 2008). Additionally, self-publishing can be an attractive option for authors who want control over their own content. Instead of leaving decisions up to the publisher, authors can control their own editing, designing, and marketing.
One major challenge for authors who choose to strike out on their own is the stigma that’s sometimes attached to self-published books. Until recent years, most self-published authors went through the so-called vanity presses, which charge writers a premium for published copies of their books. As the name implies, these types of self-publishing ventures were often seen as preying on writers’ need to see their own work in print. To justify the cost of printing, a minimum order of a thousand copies was standard, and unless authors were able to find an audience, they had little hope of selling them all. Because there was no quality control and vanity presses would usually publish anyone with money, some readers were skeptical of self-published books. Major retailers and distributors generally refused to carry them, meaning that authors had to rely on their own marketing efforts to sell the books. Before the advent of the Internet, this usually meant either selling copies in person or relying on mail-order catalogs, neither of which is a very reliable way to sell enough copies to recoup costs.
However, beginning in the early 2000s, self-publishing has changed dramatically. Advances made in publishing technology have made it easier for self-published books to more closely resemble traditionally published ones. Free professional typesetting software has allowed writers to format their text for the page; Adobe Photoshop and similar programs have made image editing and graphic design feasible for amateurs and professionals. The Internet has revolutionized marketing and distribution, allowing authors of books about niche subjects to reach a worldwide audience. As a result, many new Internet-based self-publishing companies have sprung up, offering a variety of services. Some companies, such as Lulu Enterprises and CreateSpace, feature a low-cost service without many bells and whistles; others offer a package of services that may include professional editing, cover design, and marketing. The process has become streamlined as well. For example, to publish a book with Lulu, an author just has to upload a PDF of a properly formatted text file; decide what size, paper, and binding options to use; and make a cover using a premade template. Self-published books are generally quicker to produce and allow an author a higher share of the royalties, though it usually costs more on a per-book basis. As a result, self-published books often have a higher list price.
Whereas vanity publishers were stigmatized for charging authors sometimes thousands of dollars to publish their books, creating a book using the services of Lulu or CreateSpace doesn’t cost the author anything. That’s because users who upload their content aren’t creating an actual, physical copy of a book; instead, they’re essentially making a potential volume. With print-on-demand technology, books aren’t printed until an order is placed, which significantly lowers the financial risk for self-publishers. Print-on-demand is especially useful for books with a limited or niche audience. Print-on-demand isn’t only being used by self-publishers; both small presses and academic publishers are using the technology for older books without much of an audience. With print-on-demand, books that may only sell a few dozen copies a year can stay in print without the publisher having to worry about printing a full run of copies and being stuck with unsold inventory.
Although some self-published authors manage to find a huge audience, most don’t. Bob Young, the founder of Lulu, told the London Times that his goal is to publish 1 million books that each sell 100 copies, rather than 100 books that sell 1 million copies each (Whitworth, 2006). Lulu and other enterprising self-publishers disrupt the traditional notion of the publishing house, which acted as a sort of gatekeeper for the book industry—ushering a few talented, lucky writers in and keeping others out. In the world of self-publishing, there are no barriers—anyone with a book in a PDF file can whip up a nice-looking paperback in under 1 hour. This has democratized the industry, allowing writers who had been rejected by the traditional publishers to find their own audience. But it has also meant that a lot of writing with little literary merit has been published as well. Additionally, if a best seller in the Lulu world is a book that sells 500 copies, as Bob Young told the London Times, then few authors are going to be able to make a living through self-publishing. Indeed, most of the self-publishing success stories involve writers whose self-published efforts sold well enough to get them a book deal with one of the traditional publishing houses, a sign that for better or for worse, the traditional publishing model still has the social cachet and sales to dominate the industry.
Key Takeaways
- E-books have been increasing in popularity with customers since the 1990s. However, the publishing industry is worried that setting the price for e-books at $9.99, as Amazon initially did for most titles, would turn consumers away from buying more expensive physical books. Amazon lost money on every $9.99 e-book but hoped that the low prices would act as an incentive to buy its e-book reader, the Kindle device. In 2010, Macmillan and other publishers forced Amazon to change its pricing model to give publishers more control over e-book prices.
- Digital libraries began with Project Gutenberg in 1971. Digitized books allow anyone with an Internet connection access to millions of volumes, and some advocates hope that digital libraries will lead to a rise in global literacy rates. Millions of books in the public domain are available for free download. Google Books, the largest digital library, has run into trouble with its plan to digitize as many books as possible, even books under current copyright. The Open Book Alliance accuses Google of monopolizing copyrighted content to make a profit.
- Self-publishing used to carry a social stigma as well as a high cost. Thanks to print-on-demand services, self-publishing is an increasingly popular option for amateur and professional writers. It appeals to authors who may have a niche audience or who want more control over their work. Print-on-demand makes it possible for books to never go out of print.
Exercises
Go to the website of a company that specializes in print-on-demand or self-publishing services and examine some of the books featured there. Then, answer the following questions:
- How do these books look similar in form and content to books you’d expect to find in your local bookstore? How do they look different?
- How do prices differ from some of the major retail chains? Are the prices more similar to e-book, paperback, or hardcover prices?
- Would you be willing to purchase a book on one of these sites? Why or why not?
End-of-Chapter Assessment
Review Questions
-
Section 1
- What ancient book form did the codex replace, and why was the codex an improvement on that form?
- What is mechanical movable type, and how did it lead to the Gutenberg Revolution?
- What is copyright, and how has its legal interpretation changed over time?
- How has the publishing industry evolved since the invention of the printing press?
-
Section 2
- How was 18th-century literature affected by the changing role of women during this period?
- What are some of the ways that authors tried to create a distinctive American style in the 19th century?
- What changes in American society were reflected by 20th-century literature?
-
Section 3
- What are some of the advantages and disadvantages of hardcover books?
- What are the two kinds of paperback books, and how do they differ?
- What is an e-book, and how is it different from hardcopy books?
-
Section 4
- What is blockbuster syndrome, and how does it affect the publishing industry?
- What factors led to the rise and decline of book superstores?
- How do price wars affect the publishing industry?
-
Section 5
- What are some ways that e-books are changing the publishing industry?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of digital libraries?
- What is print-on-demand, and how does it influence the book industry?
Critical Thinking Questions
- One of the initial intentions of copyright law was to protect artists while also allowing a free market of ideas. Is copyright a good way to protect authors and their control over their work? Do you think copyright law means the same now as it did in the past? What are some concerns that are changing the meaning of copyright protection?
- If the Gutenberg Revolution was a time when advances in technology led to rapid changes in culture and society, will e-books and digital libraries lead to a similarly revolutionary change in the way we live our lives? Why or why not?
- The publishing industry is facing a time of rapid change. What are some factors threatening the traditional publishing mode, and what are some ways the industry could respond to these potential dangers?
- What impact do blockbuster books have on the book industry? And on readers?
- Some people argue that e-books will destroy the publishing industry, while others think that they’ll be its savior. How have e-books begun to transform the publishing industry, and what impact do you think they will have in the future?
Career Connection
Publishing a book is no longer a simple thing. Authors have to contend with questions about copyright, movie rights, e-books, and blog publicity. In confusing times, literary agents act as writers’ sidekicks. They discover new writers and then help those writers negotiate an increasingly complex market.
Read the article “A Book in You” from The New Yorker (http://www.newyorker.com/archive/2004/05/31/040531ta_talk_radosh), which discusses a literary agent who specializes in signing book deals with bloggers. Now, explore literary agent Betsy Lerner’s blog at http://betsylerner.wordpress.com. After exploring for a bit, read the “About Me” section (the link is at the top). These two sites will help you answer the following questions:
- Why does Kate Lee think that blogs are a good place to look for new authors to represent?
- What can you tell about Betsy Lerner’s attitude about the publishing industry from her blog? What about her attitude toward the writers she works with? What does she appear to find rewarding about her job?
- Based on Betsy Lerner’s blog, identify the daily work required to be an agent. What aspects of the job appear challenging and engaging? What seems to take up the most time?
References
Cohen, Patricia. “Fending Off Digital Decay, Bit by Bit,” New York Times, March 15, 2010, Arts section.
Hart, Michael S. and Gregory B. Newby, “Project Gutenberg Principle of Minimal Regulation,” Project Gutenberg, 2004, http://www.gutenberg.org/wiki/Gutenberg:Project_Gutenberg_Principle_of_Minimal_Regulation_
/_Administration_by_Michael_Hart_and_Greg_Newby.
Kelly, “Scan This Book!”
Maneker, Marion. “Parsing the iPad’s Book Sale Numbers,” The Big Money, May 4, 2010, http://www.thebigmoney.com/blogs/goodnight-gutenberg/2010/05/04/ibooks-vs-app-books-ipad.
McHugh, Josh. “How the Self-Published Debut Daemon Earned Serious Geek Cred,” Wired, April 21, 2008.
McQuivy, James L. “eBook Buying Is About to Spiral Upward,” Forrester Research: Making Leaders Successful Every Day, 2010, http://www.forrester.com/rb/Research/ebook_buying_is_about_to_spiral_upward/q/id/57664/t/2.
Rich, Mokoto. “With Kindle, the Best Sellers Don’t Need to Sell,” New York Times, January 23, 2010, Books section.
Rich, Mokoto. and Brad Stone, “Publisher Wins Fight With Amazon Over E-books,” New York Times, January 31, 2010, Technology section.
Whitworth, Damian. “Publish and Be Downloaded,” Times (London), March 8, 2006, Life and Style section.



Feedback/Errata