The operating margin is a ratio that determines how much money a company is actually making in profit and equals operating income divided by revenue.
Learning Objectives
Calculate a company’s operating margin.
The operating margin is a ratio that determines how much money a company is actually making in profit and equals operating income divided by revenue.
Calculate a company’s operating margin.
The financial job of a company is to earn a profit, which is different than earning revenue. If a company doesn’t earn a profit, their revenues aren’t helping the company grow. It is not only important to see how much a company has sold, it is important to see how much a company is making.
The operating margin (also called the operating profit margin or return on sales ) is a ratio that shines a light on how much money a company is actually making in profit. It is found by dividing operating income by revenue, where operating income is revenue minus operating expenses.
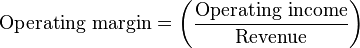
The higher the ratio is, the more profitable the company is from its operations. For example, an operating margin of 0.5 means that for every dollar the company takes in revenue, it earns $0.50 in profit. A company that is not making any money will have an operating margin of 0: it is selling its products or services, but isn’t earning any profit from those sales.
However, the operating margin is not a perfect measurement. It does not include things like capital investment, which is necessary for the future profitability of the company. Furthermore, the operating margin is simply revenue. That means that it does not include things like interest and income tax expenses. Since non-operating incomes and expenses can significantly affect the financial well-being of a company, the operating margin is not the only measurement that investors scrutinize. The operating margin is a useful tool for determining how profitable the operations of a company are, but not necessarily how profitable the company is as a whole.
Profit margin measures the amount of profit a company earns from its sales and is calculated by dividing profit (gross or net) by sales.
Calculate a company’s net and gross profit margin.
Profit margin is one of the most used profitability ratios. Profit margin refers to the amount of profit that a company earns through sales.
The profit margin ratio is broadly the ratio of profit to total sales times 100%. The higher the profit margin, the more profit a company earns on each sale.
Since there are two types of profit (gross and net), there are two types of profit margin calculations. Recall that gross profit is simply the revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS). Net profit is the gross profit minus all other expenses. The gross profit margin calculation uses gross profit and the net profit margin calculation uses net profit. The difference between the two is that the gross profit margin shows the relationship between revenue and COGS, while the net profit margin shows the percentage of the money spent by customers that is turned into profit.
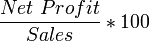
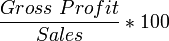
Companies need to have a positive profit margin in order to earn income, although having a negative profit margin may be advantageous in some instances (e.g. intentionally selling a new product below cost in order to gain market share).
The profit margin is mostly used for internal comparison. It is difficult to accurately compare the net profit ratio for different entities. Individual businesses’ operating and financing arrangements vary so much that different entities are bound to have different levels of expenditure. Comparing one business’ arrangements with another has little meaning. A low profit margin indicates a low margin of safety. There is a higher risk that a decline in sales will erase profits and result in a net loss or a negative margin.
The return on assets ratio (ROA) measures how effectively assets are being used for generating profit.
Calculate a company’s return on assets.
The return on assets ratio (ROA) is found by dividing net income by total assets. The higher the ratio, the better the company is at using their assets to generate income. ROA was developed by DuPont to show how effectively assets are being used. It is also a measure of how much the company relies on assets to generate profit.
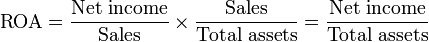
ROA can be broken down into multiple parts. The ROA is the product of two other common ratios – profit margin and asset turnover. When profit margin and asset turnover are multiplied together, the denominator of profit margin and the numerator of asset turnover cancel each other out, returning us to the original ratio of net income to total assets.
Profit margin is net income divided by sales, measuring the percent of each dollar in sales that is profit for the company. Asset turnover is sales divided by total assets. This ratio measures how much each dollar in asset generates in sales. A higher ratio means that each dollar in assets produces more for the company.
ROA does have some drawbacks. First, it gives no indication of how the assets were financed. A company could have a high ROA, but still be in financial straits because all the assets were paid for through leveraging. Second, the total assets are based on the carrying value of the assets, not the market value. If there is a large discrepancy between the carrying and market value of the assets, the ratio could provide misleading numbers. Finally, there is no metric to find a good or bad ROA. Companies that operate in capital intensive industries will tend to have lower ROAs than those who do not. The ROA is entirely contextual to the company, the industry and the economic environment.
The Basic Earning Power ratio (BEP) is Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) divided by Total Assets.
Calculate a company’s Basic Earning Power ratio.
Another profitability ratio is the Basic Earning Power ratio (BEP). The purpose of BEP is to determine how effectively a firm uses its assets to generate income.
The BEP ratio is simply EBIT divided by total assets. The higher the BEP ratio, the more effective a company is at generating income from its assets.

This may seem remarkably similar to the return on assets ratio (ROA), which is operating income divided by total assets. EBIT, or earnings before interest and taxes, is a measure of how much money a company makes, but is not necessarily the same as operating income:
EBIT = Revenue – Operating expenses + Non-operating income
Operating income = Revenue – Operating expenses
The distinction between EBIT and Operating Income is non-operating income. Since EBIT includes non-operating income (such as dividends paid on the stock a company holds of another), it is a more inclusive way to measure the actual income of a company. However, in most cases, EBIT is relatively close to Operating Income.
The advantage of using EBIT, and thus BEP, is that it allows for more accurate comparisons of companies. BEP disregards different tax situations and degrees of financial leverage while still providing an idea of how good a company is at using its assets to generate income.
BEP, like all profitability ratios, does not provide a complete picture of which company is better or more attractive to investors. Investors should favor a company with a higher BEP over a company with a lower BEP because that means it extracts more value from its assets, but they still need to consider how things like leverage and tax rates affect the company.
Return on equity (ROE) measures how effective a company is at using its equity to generate income and is calculated by dividing net profit by total equity.
Calculate the Return on Equity (ROE) for a business.
Return on equity (ROE) is a financial ratio that measures how good a company is at generating profit.
ROE is the ratio of net income to equity. From the fundamental equation of accounting, we know that equity equals net assets minus net liabilities. Equity is the amount of ownership interest in the company, and is commonly referred to as shareholders’ equity, shareholders’ funds, or shareholders’ capital.
In essence, ROE measures how efficient the company is at generating profits from the funds invested in it. A company with a high ROE does a good job of turning the capital invested in it into profit, and a company with a low ROE does a bad job. However, like many of the other ratios, there is no standard way to define a good ROE or a bad ROE. Higher ratios are better, but what counts as “good” varies by company, industry, and economic environment.
ROE can also be broken down into other components for easier use. ROE is the product of the net margin (profit margin), asset turnover, and financial leverage. Also note that the product of net margin and asset turnover is return on assets, so ROE is ROA times financial leverage.
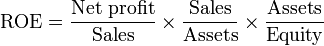
Breaking ROE into parts allows us to understand how and why it changes over time. For example, if the net margin increases, every sale brings in more money, resulting in a higher overall ROE. Similarly, if the asset turnover increases, the firm generates more sales for every unit of assets owned, again resulting in a higher overall ROE. Finally, increasing financial leverage means that the firm uses more debt financing relative to equity financing. Interest payments to creditors are tax deductible, but dividend payments to shareholders are not. Thus, a higher proportion of debt in the firm’s capital structure leads to higher ROE. Financial leverage benefits diminish as the risk of defaulting on interest payments increases. So if the firm takes on too much debt, the cost of debt rises as creditors demand a higher risk premium, and ROE decreases. Increased debt will make a positive contribution to a firm’s ROE only if the matching return on assets (ROA) of that debt exceeds the interest rate on the debt.