52 6.3 Depositional Environments and Sedimentary Basins — Physical Geology – 2nd Edition
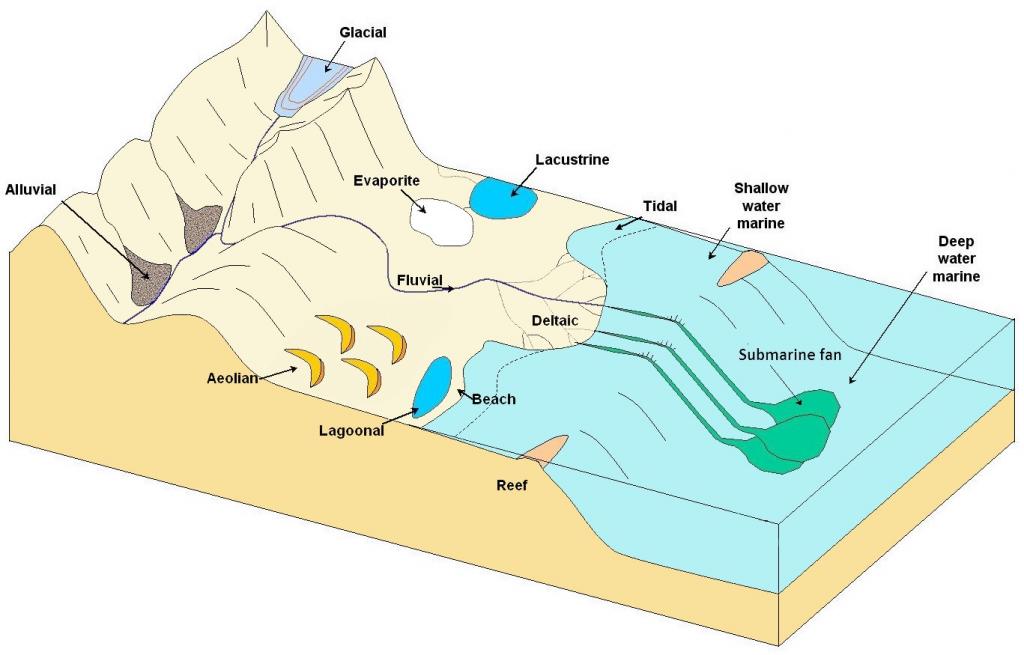
Table 6.4 provides a summary of the processes and sediment types that pertain to the various depositional environments illustrated in Figure 6.3.1. We’ll look more closely at the types of sediments that accumulate in these environments in the last section of this chapter. The characteristics of these various environments, and the processes that take place within them, are also discussed in later chapters on glaciation, mass wasting, streams, coasts, and the sea floor.
| Environment | Important transport processes | Depositional environments | Typical sediment types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glacial | gravity, moving ice, moving water | valleys, plains, streams, lakes | glacial till, gravel, sand, silt, and clay |
| Alluvial | gravity | steep-sided valleys | coarse angular fragments |
| Fluvial | moving water | streams | gravel, sand, silt, and organic matter (in swampy parts only) |
| Aeolian | wind | deserts and coastal regions | sand, silt |
| Lacustrine | moving water (flowing into a lake) | lakes | sand (near the edges only), silt, clay, and organic matter |
| Evaporite | moving water (flowing into a lake) | lakes in arid regions | salts, clay |
| Environment | Important Transport Processes | Depositional Environments | Typical Sediment Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deltaic | moving water | deltas | sand, silt, clay, and organic matter (in swampy parts only) |
| Beach | waves, longshore currents | beaches, spits, sand bars | gravel, sand |
| Tidal | tidal currents | tidal flats | silt, clay |
| Reefs | waves and tidal currents | reefs and adjacent basins | carbonates |
| Shallow water marine | waves and tidal currents | shelves and slopes, lagoons | carbonates in tropical climates, sand/silt/clay elsewhere |
| Lagoonal | little transportation | lagoon bottom | carbonates in tropical climates |
| Submarine fan | underwater gravity flows | continental slopes and abyssal plains | gravel, sand, mud |
| Deep water marine | ocean currents | deep-ocean abyssal plains | clay, carbonate mud, silica mud |
Trench basins form where a subducting oceanic plate dips beneath the overriding continental or oceanic crust. They can be several kilometres deep, and in many cases, host thick sequences of sediments from eroding coastal mountains. There is a well-developed trench basin off the west coast of Vancouver Island. A forearc basin lies between the subduction zone and the volcanic arc, and may be formed in part by friction between the subducting plate and the overriding plate, which pulls part of the overriding plate down. The Strait of Georgia is a forearc basin. A foreland basin is caused by the mass of the volcanic range depressing the crust on either side. Foreland basins are not only related to volcanic ranges, but can form adjacent to fold belt mountains like the Canadian Rockies. A rift basin forms where continental crust is being pulled apart, and the crust on both sides of the rift subsides. As rifting continues this eventually becomes a narrow sea, and then an ocean basin. The East African rift basin represents an early stage in this process.
Media Attributions
- Figure 6.3.1: Schematic diagram showing types of depositional environment © Mike Norton. Adapted by Steven Earle. CC BY-SA.
- Figure 6.3.2: © Steven Earle. CC BY.
<!– pb_fixme –>
<!– pb_fixme –>

