49 6.3 Depositional Environments and Sedimentary Basins — Physical Geology – 2nd Edition
6.3 Depositional Environments and Sedimentary Basins
Sediments accumulate in a wide variety of environments, both on the continents and in the oceans. Some of the more important of these environments are illustrated in Figure 6.3.1.
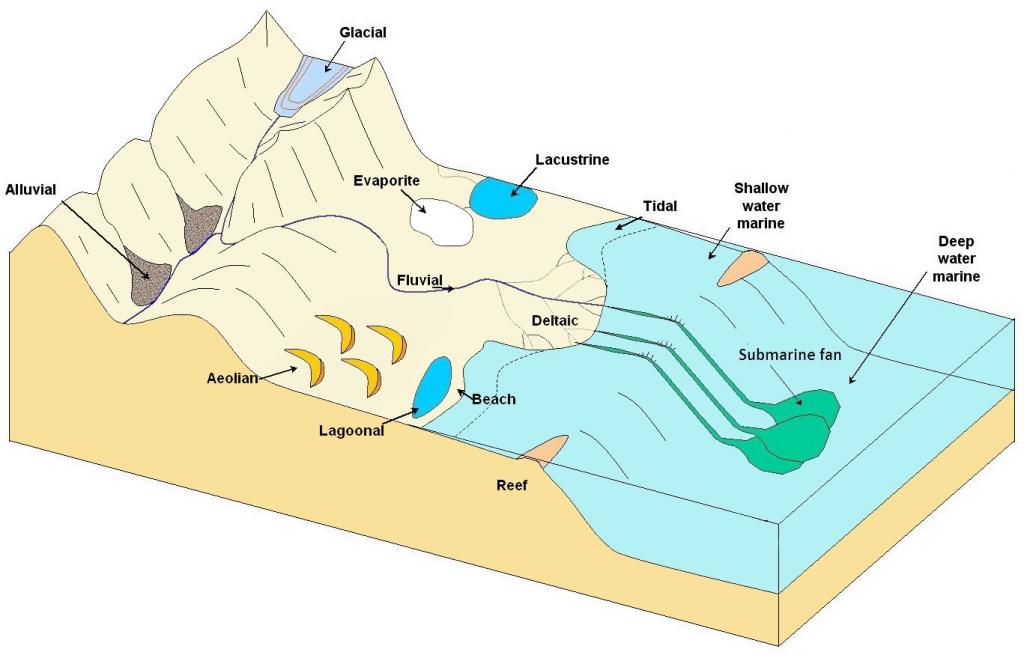
Table 6.4 provides a summary of the processes and sediment types that pertain to the various depositional environments illustrated in Figure 6.3.1. We’ll look more closely at the types of sediments that accumulate in these environments in the last section of this chapter. The characteristics of these various environments, and the processes that take place within them, are also discussed in later chapters on glaciation, mass wasting, streams, coasts, and the sea floor.
| Environment | Important transport processes | Depositional environments | Typical sediment types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glacial | gravity, moving ice, moving water | valleys, plains, streams, lakes | glacial till, gravel, sand, silt, and clay |
| Alluvial | gravity | steep-sided valleys | coarse angular fragments |
| Fluvial | moving water | streams | gravel, sand, silt, and organic matter (in swampy parts only) |
| Aeolian | wind | deserts and coastal regions | sand, silt |
| Lacustrine | moving water (flowing into a lake) | lakes | sand (near the edges only), silt, clay, and organic matter |
| Evaporite | moving water (flowing into a lake) | lakes in arid regions | salts, clay |
| Environment | Important Transport Processes | Depositional Environments | Typical Sediment Types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deltaic | moving water | deltas | sand, silt, clay, and organic matter (in swampy parts only) |
| Beach | waves, longshore currents | beaches, spits, sand bars | gravel, sand |
| Tidal | tidal currents | tidal flats | silt, clay |
| Reefs | waves and tidal currents | reefs and adjacent basins | carbonates |
| Shallow water marine | waves and tidal currents | shelves and slopes, lagoons | carbonates in tropical climates, sand/silt/clay elsewhere |
| Lagoonal | little transportation | lagoon bottom | carbonates in tropical climates |
| Submarine fan | underwater gravity flows | continental slopes and abyssal plains | gravel, sand, mud |
| Deep water marine | ocean currents | deep-ocean abyssal plains | clay, carbonate mud, silica mud |
Media Attributions
- Figure 6.3.1: Schematic diagram showing types of depositional environment © Mike Norton. Adapted by Steven Earle. CC BY-SA.
- Figure 6.3.2: © Steven Earle. CC BY.

