27 3.4 Classification of Igneous Rock — Physical Geology – 2nd Edition
3.4 Classification of Igneous Rock
As has already been described, igneous rocks are classified into four categories: felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic, based on either their chemistry or their mineral composition. The diagram in Figure 3.4.1 can be used to help classify igneous rocks by their mineral composition. An important feature to note on this diagram is the red line separating the non-ferromagnesian silicates in the lower left (K-feldspar, quartz, and plagioclase feldspar) from the ferromagnesian silicates in the upper right (biotite, amphibole, pyroxene, and olivine). In classifying intrusive igneous rocks, the first thing to consider is the percentage of ferromagnesian silicates. In most igneous rocks the ferromagnesian silicate minerals are clearly darker than the others, but it is still quite difficult to estimate the proportions of minerals in a rock.
Based on the position of the red line in Figure 3.4.1, it is evident that felsic rocks can have between 1% and 20% ferromagnesian silicates (the red line intersects the left side of the felsic zone 1% of the distance from the top of the diagram, and it intersects the right side of the felsic zone 20% of the distance from the top). Intermediate rocks have between 20% and 50% ferromagnesian silicates, and mafic rocks have 50% to 100% ferromagnesian silicates. To be more specific, felsic rocks typically have biotite and/or amphibole; intermediate rocks have amphibole and, in some cases, pyroxene; and mafic rocks have pyroxene and, in some cases, olivine.
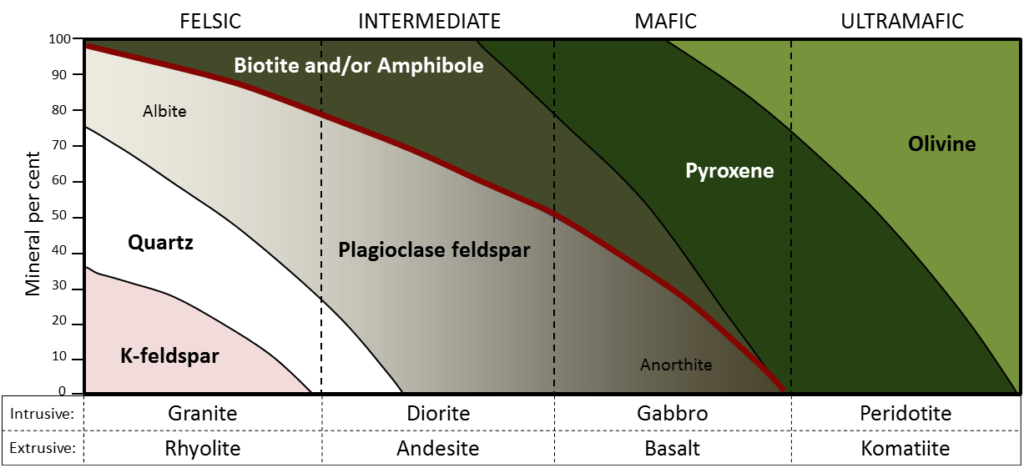
If we focus on the non-ferromagnesian silicates, it is evident that felsic rocks can have from 0% to 35% K-feldspar, from 25% to 35% quartz (the vertical thickness of the quartz field varies from 25% to 35%), and from 25% to 50% plagioclase (and that plagioclase will be sodium-rich, or albitic). Intermediate rocks can have up to 25% quartz and 50% to 75% plagioclase. Mafic rocks only have plagioclase (up to 50%), and that plagioclase will be calcium-rich, or anorthitic.
The dashed blue lines (labelled a, b, c, d) in Figure 3.4.2 represent four igneous rocks. Complete the table by estimating the mineral proportions (percent) of the four rocks (to the nearest 10%).
Hint: Rocks b and d are the easiest; start with those.
| Rock | Biotite/amphibole | Pyroxene | Olivine | Plagioclase | Quartz | K-feldspar |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | ||||||
| b | ||||||
| c | ||||||
| d |
See Appendix 3 for Exercise 3.5 answers.
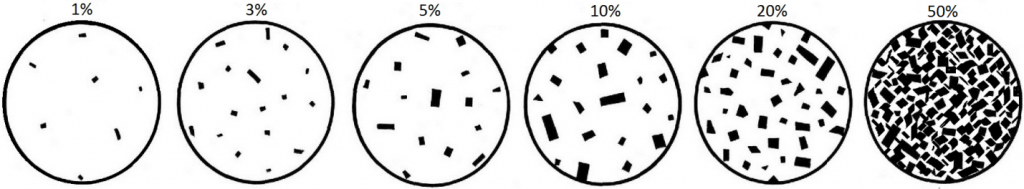
Figure 3.4.3 provides a diagrammatic representation of the proportions of dark minerals in light-colored rocks. You can use that when trying to estimate the ferromagnesian mineral content of actual rocks, and you can get some practice doing that by completing Exercise 3.6. Be warned! Geology students almost universally over-estimate the proportion of dark minerals.
The four igneous rocks shown below have differing proportions of ferromagnesian silicates. Estimate those proportions using the diagrams in Figure 3.4.3, and then use Figure 3.4.1 to determine the likely rock name for each one.
 |
 |
 |
 |
| ___% | ___% | ___% | ___% |
| __________ | __________ | __________ | __________ |
See Appendix 3 for Exercise 3.6 answers.
Igneous rocks are also classified according to their textures. The textures of volcanic rocks will be discussed in Chapter 4, so here we’ll only look at the different textures of intrusive igneous rocks. Almost all intrusive igneous rocks have crystals that are large enough to see with the naked eye, and we use the term phaneritic (from the Greek word phaneros meaning visible) to describe that. Typically that means they are larger than about 0.5 millimeters (mm) — the thickness of a strong line made with a ballpoint pen. (If the crystals are too small to distinguish, which is typical of most volcanic rocks, we use the term aphanitic (from the Greek word aphanos – unseen) The intrusive rocks shown in Figure 3.3.5 are all phaneritic, as are those shown in Exercise 3.6.
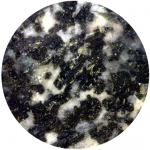
In general, the size of crystals is proportional to the rate of cooling. The longer it takes for a body of magma to cool, the larger the crystals can grow. It is not uncommon to see an intrusive igneous rock with crystals up to 1 centimeter (cm) long. In some situations, especially toward the end of the cooling stage, the magma can become water rich. The presence of liquid water (still liquid at high temperatures because it is under pressure) promotes the relatively easy movement of ions, and this allows crystals to grow large, sometimes to several centimeters (Figure 3.4.4). Finally, as already described, if an igneous rock goes through a two-stage cooling process, its texture will be porphyritic (Figure 3.3.7).
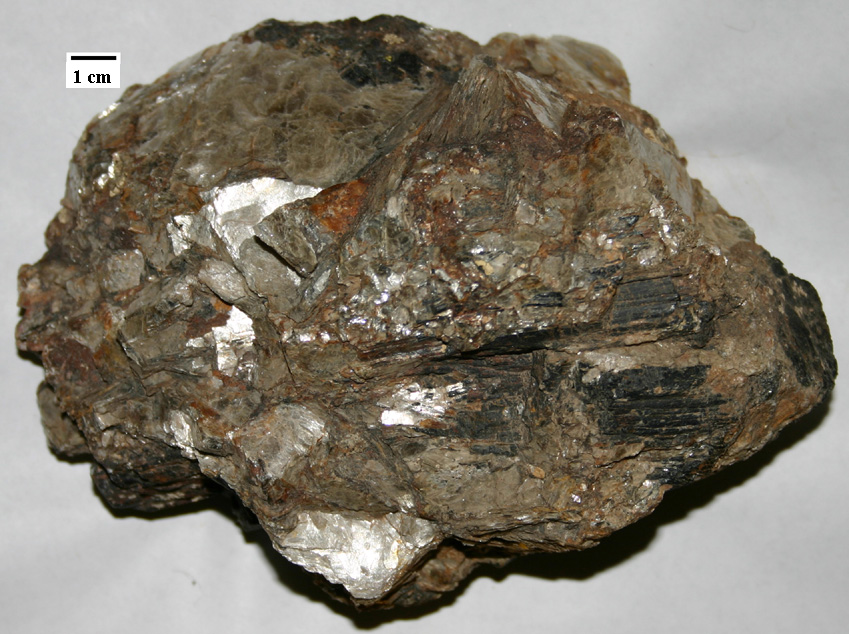

Image Descriptions
Attributions
- Figure 3.4.1, 3.4.2, 3.4.3: © Steven Earle. CC BY.
- Figure 3.4.4: Pegmatite. Public domain.